Abstract
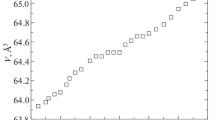
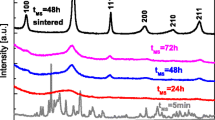
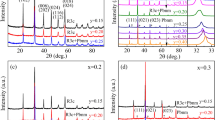
The 0.6BiFeO3–0.4(Bi0.5Na0.5)(1−x)Ba x TiO3 (short for BF-BN(1−x)Ba x T) (x = 0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5) solid-solution ceramics were fabricated by a sol–gel method. The presence of constituent phases in ceramics was investigated by X-ray diffraction. It indicates that all of the samples are single phase. Not only that, it also proves the rhombohedral structure of the samples. Multiferroic properties dependent on the doping content of Ba ions were studied systematically. The ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism were tested, displaying the maximum values of remnant polarization and remnant magnetization at x = 0.4 simultaneously. With the increasing in x, the peak of dielectric constant depending on temperature shifts toward to the lower temperature range. In addition, the dielectric diffuse degree also increases monotonically as x increases to 0.5.
Graphical Abstract
(a–e) Magnetization hysteresis loops of BF-BN(1−x)Ba x T (x = 0, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5) solid solutions at room temperature and (f) the evolutions of M r and H c with x.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spaldin NA, Fiebig M (2005) The renaissance of magnetoelectric multiferroics. Science 309:391–392
Nan CW, Bichurin MI, Dong SX, Viehland D, Srinivasan G (2008) Multiferroic magnetoelectric composites: historical perspective, status, and future directions. J Appl Phys 103:031101
Eerenstein W, Mathur ND, Scott JF (2006) Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature 442:759–765
Chaudhuri AR, Krupanidhi SB (2010) Investigation of true remnant polarization response in heterostructured artificial biferroics. Solid State Commun 150:660–662
Hill NA (2000) Why are there so few magnetic ferroelectric. J Phys Chem B 104:6694–6709
Kumar N, Panwar N, Gahtori B, Singh N, Kishan H, Awana VPS (2010) Structural, dielectric and magnetic properties of Pr substituted Bi1−x Pr x FeO3. J Alloy Compd 501:29–32
Feridoon A, Robert F, Michael T, Robert C, Floriana T, David C (2010) Microstructure and properties of Co-, Ni-, Zn-, Nb- and W-modified multiferroic BiFeO3 ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc 30:727–736
Kumar MM, Palkar VR, Srinivas K, Suryanarayana SV (2000) Ferroelectricity in a pure BiFeO3 ceramic. Appl Phys Lett 76:2764
Ghosh AK, Dwivedi GD, Chatterjee B, Rana B, Barman A, Chatterjee S, Yang HD (2013) Role of codoping on multiferroic properties at room temperature in BiFeO3 ceramic. Solid State Commun 166:22–26
Sakata K, Takenaka T, Naitou Y (1992) Phase relations, dielectric and piezoelectric properties of ceramics in the system (Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3–PbTiO3. Ferroelectrics 131:219–226
Huo SX, Yuan SL, Qiu Y, Ma ZZ, Wang CH (2012) Crystal structure and multiferroic properties of BiFeO3–Na0.5K0.5NbO3 solid solution ceramics prepared by Pechini method. Mater Lett 68:8–10
Ma ZZ, Tian ZM, Li JQ, Wang CH, Huo SX, Duan HN, Yuan SL (2011) Enhanced polarization and magnetization in multiferroic (1 − x)BiFeO3–xSrTiO3 solid solution. Solid State Sci 13:2196–2200
Dorcet V, Trolliard G, Boullay P (2008) Reinvestigation of phase transitions in Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 by TEM. Part 1: first order rhombohedral to orthorhombic phase transition. Chem Mater 20:5061–5073
Wu JG, Kang GQ, Liu HJ, Wang J (2009) Ferromagnetic, ferroelectric and fatigue behavior of (111)-oriented BiFeO3/(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3 lead free bilayered thin films. Appl Phys Lett 94:172906
Singh A, Pandey V, Kotnala RK, Pandey D (2008) Direct evidence for multiferroic magnetoelectric coupling in 0.9BiFeO3–0.1BaTiO3. Phys Rev Lett 101:247602
Tian ZM, Zhang YS, Yuan SL, Wu MS, Wang CH, Ma ZZ, Huo SX, Duan HN (2012) Enhanced multiferroic properties and tunable magnetic behavior in multiferroic BiFeO3–Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 solid solutions. Mater Sci Eng, B 177:74–78
Lei ZW, Huang Y, Liu M, Ge W, Ling YH, Peng R, Mab XY, Chen XB, Lu YL (2014) Ferroelectric and ferromagnetic properties of Bi7−x La x Fe1.5Co1.5Ti3O21 ceramics prepared by the hot-press method. J Alloy Compd 600:168–171
Kumar M, Shankar S, Kotnala RK, Parkash O (2013) Evidences of magneto-electric coupling in BFO-BT solid solutions. J Alloy Compd 577:222–227
Qin HB, Zhang HL, Zhang BP, Xu LH (2011) Hydrothermal synthesis of perovskite BiFeO3–BaTiO3 crystallites. J Am Ceram Soc 94:3671–3674
Kim JW, Do D, Kim SS (2012) Enhanced electrical properties of rare-earth-substituted (Bi0.9RE0.1)(Fe0.975Cr0.025)O3 (RE = Nd, Gd, Eu) thin films. J Korean Phys Soc 61:1404–1408
Leontsev SO, Eitel RE (2009) Dielectric and piezoelectric properties in Mn-modified (1 − x)BiFeO3–xBaTiO3 ceramics. J Am Ceram Soc 92:2957–2961
Wu MS, Huang ZB, Han CX, Yuan SL, Lu CL, Xia SC (2012) Enhanced multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 ceramics by Ba and high-valence Nb co-doping. Solid State Commun 152:2142–2146
Katlakunta S, Raju P, Meena SS, Srinath S, Sandhya R, Kuruva P, Murthy SR (2014) Multiferroic properties of microwave sintered BaTiO3–SrFe12O19 composites. Phys B 448:323–326
Merz WJ (1949) The electric and optical behavior of BaTiO3 single-domain crystals. Phys Rev 76:1221–1225
Smolensky GA, Isupov VA, Agranovskaya AI, Krainik NN (1961) New ferroelectrics of complex composition. Sov Phys Solid State 2:2651–2654
Palkar VR, Kundaliya DC, Malik SK, Bhattacharya S (2004) Magnetoelectricity at room temperature in the Bi0.9−x Tb x La0.1FeO3. Phys Rev B 69:212102
Meera R, Yadav KL (2013) Structural, dielectric and ferroelectric properties of Ba1−x (Bi0.5Na0.5) x TiO3. Ceram Int 39:3627–3633
Uchino K, Nomura S (1982) Critical exponents of the dielectric constants in diffused-phase-transition crystals. Ferroelectrics 44:55–61
Tian ZM, Yuan SL, Wang XL, Zheng XF, Yin SY, Wang CH, Liu L (2009) Size effect on magnetic and ferroelectric properties in Bi2Fe4O9 multiferroic ceramics. J Appl Phys 106:103912
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 11174092 and 11474111). We would like to thank the staff of Analysis Center of HUST for their assistance in various measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, C.M., Wang, L.G., Yuan, S.L. et al. Room-temperature multiferroic properties of 0.6BiFeO3–0.4(Bi0.5Na0.5)(1−x)Ba x TiO3 solid-solution ceramics. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 76, 289–297 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3776-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-015-3776-3