Summary
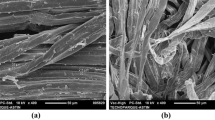
New regenerated cellulose fibers were developed during the last decades as environmentally friendly systems. In this work, three fibers: lyocell, modal and viscose were subjected to an enzymatic treatment. Likewise, different lyocell fibers were washed in a Na2CO3 solution under severe conditions. Analysis was performed by means of differential scanning calorimetry, thermogravimetry and scanning electron microscopy. In all samples, at low temperature, water desorption was detected. Furthermore, thermal analysis shows wide exothermic processes that began between 250 and 300°C corresponding to the main thermal degradation and it is associated to a depolymerization and decomposition of the regenerated cellulose. It is accompanied with mass more than 60% mass loss. Kinetic analysis was performed and activation energy values 152-202 kJ mol-1 of the main degradation process are in agreement with literature values of cellulose samples.
Similar content being viewed by others

Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suñol, J., Miralpeix, D., Saurina, J. et al. Thermal behavior of cellulose fibers with enzymatic or Na2CO3 treatment. J Therm Anal Calorim 80, 117–121 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-0622-9
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-005-0622-9