Abstract
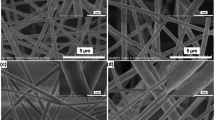
Iron doped boehmite nanofibres with varying iron content have been prepared at low temperatures using a hydrothermal treatment in the presence of poly(ethylene oxide) surfactant. The resultant nanofibres were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). TEM images showed the resulting nanostructures are predominantly nanofibres when Fe doping is no more than 5%; in contrast nanosheets were formed if Fe doping was above 5%. For the 10% Fe doped boehmite, a mixed morphology of nanofibres and nanosheets were obtained. Nanotubes instead of nanofibres were observed in samples with 20% added iron. The Fe doped boehmite and the subsequent nanofibres/nanotubes were analysed by thermogravimetric and differential thermogravimetric methods. Boehmite nanofibres decompose at higher temperatures than non-hydrothermally treated boehmite and nano-sheets decompose at lower temperatures than the nanofibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. H. Fendler and F. C. Meldrum, Adv. Mater. (Weinheim, Germany), 7 (1995) 607.
B. B. Lakshmi, C. J. Patrissi and C. R. Martin, Chem. Mater., 9 (1997) 2544.
Y. Sun and Y. Xia, Nature, 298 (2002) 2176.
M. S. Gudiksen, L. J. Lauhon, J. Wang, D. C. Smith and C. M. Lieber, Nature, 415 (2002) 617.
J.-L. Le Loarer, H. Nussbaum and D. Bortzmeyer, (Rhodia Chimie, Fr.). Application: WO, 1998, p. 44.
V. S. Burkat, V. S. Dudorova, V. S. Smola and T. S. Chagina, Light Metals (Warrendale, PA, United States), (1985) 1443.
C. Nedez, J.-P. Boitiaux, C. J. Cameron and B. Didillon, Langmuir, 12 (1996) 3927.
Y. Chen, L. Jin and Y. Xie, J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 13 (1998) 735.
D. S. Xue, Y. L. Huang, Y. Ma, P. H. Zhou, Z. P. Niu, F. S. Li, R. Job and W. R. Fahrner, J. Mater. Sci. Lett., 22 (2003) 1817.
A. P. Philipse, A.-M. Nechifor and C. Patmamanoharan, Langmuir, 10 (1994) 4451.
K. Okada, A. Tanaka, S. Hayashi, K. Daimon and N. Otsuka, J. Mater. Res., 9 (1994) 1709.
S. Ananthakumar, V. Raja and K. G. K. Warrier, Mater. Lett., 43 (2000) 174.
C. Kaya, J. Y. He, X. Gu and E. G. Butler, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 54 (2002) 37.
J. Bugosh, J. Phys. Chem., 65 (1961) 1789.
M. P. B. Van Bruggen, Langmuir, 14 (1998) 2245.
D. Kuang, Y. Fang, H. Liu, C. Frommen and D. Fenske, J. Mater. Chem., 13 (2003) 660.
H. Y. Zhu, D. Y. Song, Y. Q. Bai, S. P. Ringer, Z. Gao, Y. X. Xi, W. Martens, J. D. Riches and R. L. Frost, J. Phys. Chem. B, 108 (2004) 4245.
H. Y. Zhu, J. D. Riches and J. C. Barry, Chem. Mater., 14 (2002) 2086.
L. Wood and J. Lindley, (Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd., UK), Application: EP EP, 1980, p. 21.
W. Teunissen, A. A. Bol and J. W. Geus, Catal. Today, 48 (1999) 329.
J. M. Bouzaid, R. L. Frost, A. W. Musumeci and W. N. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 745.
R. L. Frost, J. M. Bouzaid, A. W. Musumeci, J. T. Kloprogge and W. N. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 437.
R. L. Frost, J. Kristof, W. N. Martens, M. L. Weier and E. Horvath, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 83 (2006) 675.
R. L. Frost, A. W. Musumeci, J. T. Kloprogge, M. L. Weier, M. O. Adebajo and W. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 86 (2006) 205.
R. L. Frost, R.-A. Wills, J. T. Kloprogge and W. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 84 (2006) 489.
R. L. Frost, R.-A. Wills, J. T. Kloprogge and W. N. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 83 (2006) 213.
R. L. Frost, J. Kristof, M. L. Weier, W. N. Martens and E. Horvath, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 79 (2005) 721.
R. L. Frost, M. L. Weier and W. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 82 (2005) 115.
R. L. Frost, M. L. Weier and W. Martens, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 82 (2005) 373.
Y.-H. Lin, M. O. Adebajo, R. L. Frost and J. T. Kloprogge, J. Therm. Anal. Cal., 81 (2005) 83.
H. Y. Zhu, X. P. Gao, D. Y. Song, S. P. Ringer, Y. X. Xi and R. L. Frost, Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 85 (2005) 226.
H. D. Ruan, R. L. Frost and J. T. Kloprogge, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 57A (2001) 2575.
H. D. Ruan, R. L. Frost, J. T. Kloprogge and L. Duong, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 58A (2002) 479.
H. D. Ruan, R. L. Frost, J. T. Kloprogge and L. Duong, Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 58A (2002) 479.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Frost, R.L., Martens, W.N. et al. XRD, TEM and thermal analysis of Fe doped boehmite nanofibres and nanosheets. J Therm Anal Calorim 90, 755–760 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8248-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-006-8248-0