Abstract
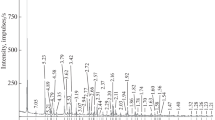
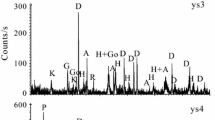
Thermal behavior of halloysite selected from Erdos, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in China, was investigated by thermogravimetry and differential thermal gravity (TG–DTG), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The XRD results indicated that the mineralogical composition of halloysite sample was determined as 7 Å halloysite with the d (001) value of 0.734 nm, a small amount of 10 Å halloysite with the d (001) value of 0.998 nm, quartz, calcite, anhydrite, siderite, and analcite. The crystal chemical formula of halloysite specimen is (Ca0.007Na0.039K0.048)(Al1.935Fe 3+0.032 Mn 2+0.003 Ti 4+0.002 Mg 2+0.015 Ca 2+0.021 )2 [(Si1.935Al 3+0.065 )2](OH)4·2H2O according to the oxygen atom method. The TG–DTG–DSC data showed that a small amount of water molecule layer in the interlayer and the dehydroxylation was observed at 493.6 °C. The XRD, FT-IR, and SEM data clearly show that the structure changes and dehydroxylation of the halloysite with the temperature increased from 200 to 1200 °C. The dehydration of the halloysite is followed by the loss of intensity and evolution of the OH vibration bands and the change in microstructure. Dehydroxylation is followed by the decrease in the intensity of the bands at 3696 and 3620 cm−1, which is completely disappeared at 700 °C. The thermal behavior of halloysite was influenced by the mineralogy composition and impurities.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berthier P. Analyse de l’halloysite. Ann Chim Phys. 1826;32:332–5.
Bates TF, Hildebrand FA, Swineford A. Morphology and structure of endellite and halloysite. Am Mineral. 1950;35:463–84.
Frost RL. Hydroxyl deformation in kaolins. Clay Clay Miner. 1998;46:280–9.
Singh B. Why does halloysite roll? A new model. Clay Clay Miner. 1996;44:191–6.
Joussein E, Petit S, Churchman J, Theng B, Righi D, Delvaux B. Halloysite clay minerals: a review. Clay Clay Miner. 2005;40:383–426.
Joussein E, Petit S, Delvaux B. Behavior of halloysite clay under formamide treatment. Appl Clay Sci. 2007;35:17–24.
Yuan P, Tan D, Annabi-Bergaya F. Properties and applications of halloysite nanotubes: recent research advances and future prospects. Appl Clay Sci. 2015;112–113:75–93.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Zhang J, Frost RL. Thermal analysis and infrared emission spectroscopic study of halloysite–potassium acetate intercalation compound. Thermochim Acta. 2010;511:124–8.
Nicolini KP, Fukamachi CR, Wypych F, Mangrich AS. Dehydrated halloysite intercalated mechanochemically with urea: thermal behavior and structural aspects. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2009;338:474–9.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yag J, Zhang J, Frost RL, Du X. Infrared spectroscopic study of halloysite–potassium acetate intercalation complex. J Mol Struct. 2011;990:21–5.
Liu M, Jia Z, Jia D, Zhou C. Recent advance in research on halloysite nanotubes–polymer nanocomposite. Prog Polym Sci. 2014;39:1498–525.
Singer A, Zarei M, Lange FM, Stahr K. Halloysite characteristics and formation in the northern Golan Heights. Geoderma. 2004;123:279–95.
Horváth E, Kristóf J, Frost RL, Réder Á, Vágvölgyi V, Cseh T. Hydrazine-hydrate intercalated halloysite under controlled-rate thermal analysis conditions. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2003;71:707–14.
Levis SR, Deasy PB. Characterisation of halloysite for use as a microtubular drug delivery system. Int J Pharm. 2002;243:125–34.
Lvov Y, Abdullayev E. Functional polymer–clay nanotube composites with sustained release of chemical agents. Prog Polym Sci. 2013;38:1690–719.
Yuan P, Tan D, Aannabi-Bergaya F, et al. Changes in structure, morphology, porosity, and surface activity of mesoporous halloysite nanotubes under heating. Clay Clay Miner. 2012;60:561–73.
Smith ME, Neal G, Trigg MB, Drerman J. Structural characterization of the thermal transformation of halloysite by solid state NMR. Appl Magn Reson. 1993;4:157–70.
Yuan P, Southon PD, Liu Z, Green MER. Functionalization of halloysite clay nanotubes by grafting with γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J Phys Chem C. 2008;112:15742–51.
Joussein E, Peit S, Finalips C-I. Differences in the dehydration rehydration behavior of halloysites: new evidence and interpretations. Clay Clay Miner. 2006;54:473–85.
Yuan P, Thill A, Bergaya F. Thermal-treatment-induced deformations and modifications of halloysite. Knoxville: Candice Janco; 2016.
Xiao-fan L, Jun-fang G, Fei-fei C, Fan Z, Ke Y. Characteristics of halloysite from Xishuangbanna Area, Yunnan Province, China. Acta Miner Sin. 2016;36:138–42.
Sun H, Peng T, Liu Y. Measurement and mechanism of layer charge of phyllosilicate with expansive layers. Acta Miner Sin. 2007;27:19–24.
Frost RL, Kristof J, Horvath E, Kloprogge JT. Rehydration and phase changes of potassium acetate-intercalated halloysite at 298 K. J Colloid Interf Sci. 2000;226:318–27.
Cheng H, Liu Q, Yang J, Frost RL. Thermogravimetric analysis of selected coal-bearing strata kaolinite. Thermochim Acta. 2010;507–508:84–90.
Sun J, Wu Z, Cheng H, Zhang Z, Frost RL. A Raman spectroscopic comparison of calcite and dolomite. Spectrochim Acta Part A. 2014;117:158–62.
Alberola JA, Mondragón R, Juliá JE, Hernández L, Cabedo L. Characterization of halloysite-water nanofluid for heat transfer applications. Appl Clay Sci. 2014;99:54–61.
Zhang Y, Liu Q, Wu Z, Zheng Q, Cheng H. Thermal behavior analysis of kaolinite–dimethylsulfoxide intercalation complex. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;110:1167–72.
Szczepanik B, Słomkiewicz P, Garnuszek M, et al. The effect of chemical modification on the physico-chemical characteristics of halloysite: FTIR, XRF, and XRD studies. J Mol Struct. 2015;1084:16–22.
Horváth E, Kristóf J, Kurdi R, Makó É, Khunová V. Study of urea intercalation into halloysite by thermoanalytical and spectroscopic techniques. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2011;105:53–9.
Ledoux RL, White JL. Infrared study of the OH groups in expanded kaolinite. Science. 1964;143:244–6.
Suárez M, García-Romero E. FTIR spectroscopic study of palygorskite: influence of the composition of the octahedral sheet. Appl Clay Sci. 2006;31:154–63.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (51604158) and College student innovative projects of Inner Mongolia University of Technology (Grant No. 2016046).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Thermal behavior analysis of halloysite selected from Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in China. J Therm Anal Calorim 129, 1333–1339 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6324-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6324-2