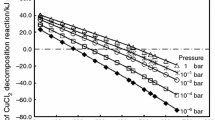
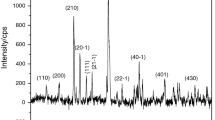
Abstract
The kinetics and mechanisms involved in evaporation and decomposition of CuCl2(s) from the eutectics of CuCl2(s)–NaCl(s) were investigated in this work. Based on DTA/TG, it was found that anhydrous CuCl2(s) was decomposed into CuCl(s) at 455.5 °C; then, the CuCl(s) thus obtained melt at the same temperature. After that small part of the CuCl(l) evaporated at 488.5 °C and most of CuCl(l) aggregated to form Cu3Cl3(l) in the temperature range of 488.5–667.3 °C. The boiling point of Cu3Cl3(l) was 667.3 °C. CuCl2(s) was completely decomposed into CuCl(s) in 20–40 min at 500–650 °C in Ar atmosphere. The evaporation rate constants (k) of CuCl2(s) in the time range of 20–120 min were 0.0018, 0.0072 and 0.0158 mg min−1 at the temperatures of 500, 600 and 650 °C, respectively, which were very close to the corresponding values of CuCl(s). Anhydrous CuCl2(s) reacted with NaCl to form some eutectics with a eutectic point of 374 °C. The k values of the eutectics were about one-tenth and half of those of pure CuCl2 at 600 and 500 °C, respectively. The evaporation of eutectic was inhibited more at a higher temperature of 600 °C. The addition of NaCl significantly inhibited both evaporation and decomposition of CuCl2(s) from the eutectics.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kekesi T, Mimura K, Isshiki M. Copper extraction from chloride solutions by evaporation and reduction with hydrogen. Mater Trans JIM. 1995;36:649–58.
Kekesi T, Isshiki M. Ultra high purification of copper chloride solutions by anion exchange. Hydrometallurgy. 1997;45:345–61.
Sakaue T, Yoshimaru K. Copper powder for termination electrode in MLCC. J Jpn Soc Powder Powder Metall. 2013;50:908–11.
Guo J, Shen S, Zhao Y, Wang F. Growth of single-crystalline particles of metallic copper. J Cryst Growth. 2016;451:132–8.
Xu L, Sithambaram S, Zhang Y, Chen C, Jin L, Joesten R, Suib SL. Novel urchin-like CuO synthesized by a facile reflux method with efficient olefin epoxidation catalytic performance. Chem Mater. 2009;21:1253–9.
Wang Z, Marin G, Naterer GF, Gabriel KS. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the thermal decomposition of cupric chloride in its hydrolysis reaction. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:815–23.
Serban M, Lewis MA, Basco JK. Kinetic study of the hydrogen and oxygen production reactions in the copper-chloride thermochemical cycle. In: AIChE 2004 Spring National Meeting, New Orleans, LA, April 2004. p. 25–9.
Hilden DL, Gregory NW. Vapor-phase absorbance and thermodynamic properties of cuprous chloride and cuprous bromide. J Phys Chem. 1979;70:1632–7.
Schäfer H. Gaseous chloride complexes with halogen bridges-homo-complexes and hetero-complexes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1976;15:713–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Shen, S., Zhao, D. et al. Evaporation and decomposition of eutectics of cupric chloride and sodium chloride. J Therm Anal Calorim 129, 1445–1452 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6360-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6360-y