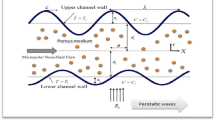
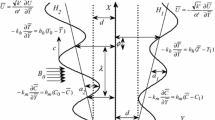
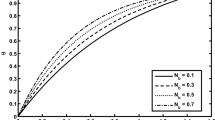
Abstract
An innovative approach to escalate the heat generation in peristalsis flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel is proposed. Three different shapes of nanoparticles, namely (1) spherical, (2) disc and (3) cylindrical are utilized. Results for temperature, velocity and concentrations have been obtained analytically. The physical features for heat generation, concentration, pressure gradient, pressure rise and magnetic parameter have been elaborated graphically, whereas effects of Nusselt number and skin friction have been numerically computed by using the MATLAB software. For bolus features, trapping phenomena are also inspected by dint of stream lines. It is found that cylindrical shapes of nanoparticles have very low thermal conductivity as compared to spherical and disc shapes. Moreover, it is seen that the heat generation parameter always increases the temperature of nanofluid, and consequently, the trapping phenomena produce more boluses for larger values of heat source parameter.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Latham TW. Fluid motion in a peristaltic pump. MS. Thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, (1966).
Shapiro AH, Jaffrin MY, Wienberg SL. Peristaltic pumping with long wavelengths at low Reynolds number. J Fluid Mech. 1969;37:799–825.
Pandey SK, Chaube MK. Peristaltic flow of a micropolar fluid through a porous medium in the presence of an external magnetic field. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul. 2011;16(9):3591–601.
Ebaid A. A new numerical solution for the MHD peristaltic flow of a bio-fluid with variable viscosity in a circular cylindrical tube via Adomian decomposition method. Phys Lett A. 2008;372:5321–8.
Ebaid A. Effects of magnetic field and wall slip conditions on the peristaltic transport of a Newtonian fluid in an asymmetric channel. Phys Lett A. 2008;372:4493–9.
Bhatti MM, Abbas MA, Rashidi MM. Combine effects of magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) and partial slip on peristaltic blood flow of Ree-Eyring fluid with wall properties. Eng Sci Technol Int J. 2016;19(3):1497–502.
Mekheimer KS. Effect of the induced magnetic field on peristaltic flow of a couple stress fluid. Phys Lett A. 2008;372:4271–8.
Souidi F, Ayachi K, Benyahia N. Entropy generation rate for a peristaltic pump. J Non Equilib Thermodyn. 2009;34:171–94.
Ranjit NK, Shit GC. Entropy generation on electro-osmotic flow pumping by a uniform peristaltic wave under magnetic environment. Energy. 2017;128:649–60.
Zeeshan A, Ijaz N, Abbas T, Ellahi R. The sustainable characteristic of Bio-bi-phase flow of peristaltic transport of MHD Jeffery fluid in human body. Sustainability. 2018;10(8):2671.
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Asadollahi A. Peristaltic blood flow of couple stress fluid suspended with nanoparticles under the influence of chemical reaction and activation energy. Symmetry. 2019;11(2):276.
Choi SUS. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticle. In: Siginer DA, Wang HP, editors. Developments and applications of non-Newtonian flows, vol. 66. ASME FED; 1995. p. 99–105.
Ouenzerfi S, Harmand S. Experimental droplet study of inverted Marangoni effect of a binary liquid mixture on a nonuniform heated substrate. Langmuir. 2016;32(10):2378–88.
Alamri SZ, Khan AA, Azeez M, Ellahi R. Effects of mass transfer on MHD second grade fluid towards stretching cylinder: a novel perspective of Cattaneo-Christov heat flux model. Phys Lett A. 2019;383:276–81.
Huang D, Wu Z, Sunden B, Li W. A brief review on convection heat transfer of fluids at supercritical pressures in tubes and the recent progress. Appl Energy. 2016;162:494–505.
Mishra SR, Bhatti MM. Simultaneous effects of chemical reaction and Ohmic heating with heat and mass transfer over a stretching surface: a numerical study. Chin J Chem Eng. 2017;25(9):1137–42.
Mishra SR, Pattnaik PK, Bhatti MM, Abbas T. Analysis of heat and mass transfer with MHD and chemical reaction effects on viscoelastic fluid over a stretching sheet. Indian J Phys. 2017;91(10):1219–27.
Ellahi R, Alamri SZ, Basit A, Majeed A. Effects of MHD and slip on heat transfer boundary layer flow over a moving plate based on specific entropy generation. J Taibah Univ Sci. 2018;12(4):476–82.
Maskaniyan M, Nazari M, Rashidi S, Mahian O. Natural convection and entropy generation analysis inside a channel with a porous plate mounted as a cooling system. Therm Sci Eng Prog. 2018;6:186–93.
Hajar Yousaf MA, Ismael F, Abbas T, Ellahi R. Numerical study of momentum and heat transfer of MHD Carreau nanofluid over exponentially stretched plate with internal heat source/sink and radiation. Heat Transf Res. 2019;50(7):649–58.
Sohail A, Fatima M, Ellahi R, Akram KB. A videographic assessment of Ferrofluid during magnetic drug targeting: an application of artificial intelligence in nanomedicine. J Mol Liq. 2019;285:47–57.
Alamri SZ, Ellahi R, Shehzad N, Zeeshan A. Convective radiative plane Poiseuille flow of nanofluid through porous medium with slip: an application of Stefan blowing. J Mol Liq. 2019;273:292–304.
Duursma D, Sefiane K, Dehaene A, Harmand S, Wang Y. Flow and heat transfer of single-and two-phase boiling of nanofluids in microchannels. Heat Transf Eng. 2015;36:1252–65.
Ellahi R, Zeeshan A, Hussain F, Abbas T. Study of shiny film coating on multi-fluid flows of a rotating disk suspended with nano-sized silver and gold particles: a comparative analysis. Coatings. 2018;8(12):422.
Rashidi S, Akbarzadeh M, Karimi N, Masoodi R. Combined effects of nanofluid and transverse twisted-baffles on the flow structures heat transfer and irreversibilities inside a square duct—a numerical study. Appl Therm Eng. 2018;130:135–48.
Mahian O, Kolsi L, Amani M, Estellé P, Ahmadi G, Kleinstreuer C, Marshall JS, Taylor RA, AbuNada E, Rashidi S, Niazmand H, Wongwises S, Hayat T, Kasaeian AB, Pop I. Recent advances in modeling and simulation of nanofluid flows—Part II: applications. Phys Rep. 2019;791:1–59.
Nasiri H, Jamalabadi MYA, Sadeghi R, Safaei M R, Nguyen TK, Shadloo MS. A smoothed particle hydrodynamics approach for numerical simulation of nanofluid flows. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018, 1–9.
Raei B, Shahraki F, Jamialahmadi M, Peyghambarzadeh SM. Experimental study on the heat transfer and flow properties of γ-Al2O3/water nanofluid in a double-tube heat exchanger. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2017;127(3):2561–75.
Majka TM, Raftopoulos KN, Pielichowski K. The influence of POSS nanoparticles on selected thermal properties of polyurethane-based hybrids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2018;133(1):289–301.
Khan I, Khan WA. Effect of viscous dissipation on MHD water-Cu and EG-Cu nanofluids flowing through a porous medium. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(1):645–56.
Saqib M, Ali F, Khan I, Sheikh NA, Shafie SB. Convection in ethylene glycol-based molybdenum disulfide nanofluid. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2019;135(1):523–32.
Khan I. New idea of Atangana and Baleanu fractional derivatives to human blood flow in nanofluids. Chaos. 2019;29(1):013121.
Saqib M, Khan I, Shafie S. Application of fractional differential equations to heat transfer in hybrid nanofluid: modeling and solution via integral transforms. Adv Differ Equ. 2019;2019:52.
Akbar NS, Raza M, Ellahi R. Peristaltic flow with thermal conductivity of H2O + Cu nanofluid and entropy generation. Results Phys. 2015;5:115–24.
Yu W, Choi SUS. The role of interfacial layers in the enhanced thermal conductivity of nanofluids: a renovated Hamilton Crosser model. J Nanoparticle Res. 2004;6:355–61.
Halelfadl S, Mare T, Estelle P. Efficiency of carbon nanotubes water based nanofluids as coolants. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 2014;53:104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, L.A., Raza, M., Mir, N.A. et al. Effects of different shapes of nanoparticles on peristaltic flow of MHD nanofluids filled in an asymmetric channel. J Therm Anal Calorim 140, 879–890 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08348-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-019-08348-9