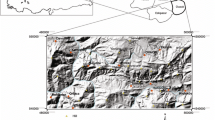
The purpose of this study was to develop techniques for landslide susceptibility using artificial neural networks and then to apply these to the selected study area at Janghung in Korea. Landslide locations were identified from interpretation of satellite images and field survey data, and a spatial database of the topography, soil, forest, and land use. Thirteen landslide-related factors were extracted from the spatial database. These factors were then used with an artificial neural network to analyze landslide susceptibility. Each factor's weight was determined by the back-propagation training method. Five different training sets were applied to analyze and verify the effect of training. Then the landslide susceptibility indices were calculated using the back-propagation weights, and susceptibility maps were constructed from Geographic Information System (GIS) data for the five cases. Landslide locations were used to verify results of the landslide susceptibility maps and to compare them. The artificial neural network proved to be an effective tool for analyzing landslide susceptibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Atkinson, P. M., and Tatnall, A. R. L., 1997, Introduction to neural networks in remote sensing: Int. J. Remote Sensing, v. 18, no. 4, p. 699–709.
Benediktsson, J. A., Swain, P. H., and Ersoy, O. K., 1990, Multisource data classification and feature extraction with neural networks: IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing, v. 28, p. 540–552.
Chung, C. F., and Fabbri, A. G., 1999, Probabilistic prediction models for landslide hazard mapping: Photogrammetr. Eng. Remote Sensing, v. 65, no.12, p. 1389–1399.
Clerici, A., Perego, S., Tellini, C., and Vescovi, P., 2002, A procedure for landslide susceptibility zonation by the conditional analysis method: Geomorphology, v. 48 p. 349–364.
Dai, F. C., and Lee, C. F., 2002, Landslide characteristics and slope instability modeling using GIS, Lantau Island, Hong Kong: Geomorphology, v. 42 p. 213–228.
Donati, L., and Turrini, M. C., 2002, An objective method to rank the importance of the factors predisposing to landslides with the GIS methodology: Application to an area of the Apennines (Valnerina; Perugia, Italy): Eng. Geol., v. 63 p. 277–289.
Fernández, C. I., Castillo, T. F., Hamdouni, R. E., and Montero, J. C., 1999, Verification of landslide susceptibility mapping: A case study: Earth Surf. Process. Landforms, v. 24, p. 537–544.
Garrett, J., 1994. Where and why artificial neural networks are applicable in civil engineering: J. Comp. Civil Eng., v. 8, no. 2, p. 129–130.
Guzzetti, F., Carrarra, A., Cardinali, M., and Reichenbach, P., 1999, Landslide hazard evaluation: A review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study. Central Italy: Geomorphology, v. 31, p. 181–216.
Hines, J. W., 1997, Fuzzy and neural approaches in engineering. Wiley, New York, p. 210.
Lee, D. 1988. Geology of Korea. Kyohak-Sa Inc, Seoul, 514.
Lee, D., Xu, L. J., 2001, Assessment of landslide susceptibility on the natural terrain of Lantau Island, Hong Kong: Environ. Geol., v. 40, p. 381—391.
Lee, S., Choi, J., and Min, K., 2002a, Landslide susceptibility analysis and verification using the Bayesian probability model: Environ. Geol., v. 43, p. 121–130.
Lee, S., Chwae, U., and Min, K., 2002b, Landslide susceptibility mapping by correlation between topography and geological structure: the Janghung area, Korea: Geomorphology, v. 46, p. 149–162.
Lee, S., and Min, K., 2001, Statistical analysis of landslide susceptibility at Yongin, Korea: Environ. Geol., v. 40, p. 1095–1113.
Luzi, L., Pergalani, F., and Terlien, M. T. J., 2000, Slope vulnerability to earthquakes at subregional scale, using probabilistic techniques and geographic information systems: Eng. Geol., v. 58, p. 313–336.
Mandy, L. G., Andrew, M. W., Richard, A., and Stephan, G. C., 2001, Assessing landslide potential using GIS, soil wetness modeling and topographic attributes, Payette River, Idaho: Geomorphology, v. 37, p. 149–165.
Paola, J. D., and Schowengerdt, R. A., 1995, A review and analysis of backpropagation neural networks for classification of remotely sensed multi-spectral imagery: Int. J. Remote Sensing, v. 16, no. 16, p. 3033–3058.
Randall, W. J., Edwin, L. H., and John, A. M., 2000, A method for producing digital probabilistic seismic landslide hazard maps: Eng. Geol., v. 58, p. 271–289.
Schaale, M., and Furrer, R., 1995, Land surface classification by neural networks: Int. J. Remote Sensing, v. 16, no. 16, p. 3003–3031.
Serpico, S. B., and Roli, F., 1995, Classification of multisensor remote-sensing images by structured neural network: IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing, v. 33, p. 562–578.
Temesgen, B., Mohammed, M. U., and Korme, T., 2001, Natural hazard assessment using GIS and remote sensing methods, with particular reference to the landslides in the Wondogenet Area, Ethiopia: Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Part C: Solar, Terrestrial Planet. Sci., v. 26, p. 665–675.
Turrini, M. C., and Visintainer, P., 1998, Proposal of a method to define areas of landslide hazard and application to an area of the Dolomites, Italy: Eng. Geol., v. 50, p. 255–265.
Zhou, W., 1999, Verification of the nonparametric characteristics of backpropagation neural networks for image classification: IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sensing, v. 37, p. 771–779.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Ryu, JH., Lee, MJ. et al. The Application of Artificial Neural Networks to Landslide Susceptibility Mapping at Janghung, Korea. Math Geol 38, 199–220 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-005-9012-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11004-005-9012-x