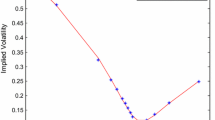
Abstract
In this article we consider the problem of pricing and hedging high-dimensional Asian basket options by Quasi-Monte Carlo simulations. We assume a Black–Scholes market with time-dependent volatilities, and we compute the deltas by means of the Malliavin Calculus as an extension of the procedures employed by Kohatsu-Higa and Montero (Physica A 320:548–570, 2003). Efficient path-generation algorithms, such as Linear Transformation and Principal Component Analysis, exhibit a high computational cost in a market with time-dependent volatilities. To face this challenge we then introduce a new and faster Cholesky algorithm for block matrices that makes the Linear Transformation more convenient. We also propose a new-path generation technique based on a Kronecker Product Approximation. Our procedure shows the same accuracy as the Linear Transformation used for the computation of deltas and prices in the case of correlated asset returns, while requiring a shorter computational time. All these techniques can be easily employed for stochastic volatility models based on the mixture of multi-dimensional dynamics introduced by Brigo et al. (2004a, Risk 17(5):97–101, b).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acworth P, Broadie M, Glasserman P (1998) A comparison of some Monte Carlo and quasi-Monte Carlo techniques for option pricing. In: Hellekalek P, Larcher G, Niederreiter H, Zinterhof P (eds) Monte Carlo and quasi-Monte Carlo methods 1996. Lecture notes in statistics, vol 127. Springer, New York, pp 1–18
Alfonsi A (2005) On the discretization schemes for the CIR (and Bessel squared) processes. Monte Carlo Methods Appl 11(4):355–384
Brigo D, Mercurio F, Rapisarda F (2004a) Connecting univariate smiles and basket dynamics: a new multidimensional dynamics for basket options. Available at http://www.ima.umn.edu/talks/workshops/4-12-16.2004/rapisarda/MultivariateSmile.pdf
Brigo D, Mercurio F, Rapisarda F (2004b) Smile at the uncertainty. Risk 17(5):97–101
Caflisch R, Morokoff W, Owen A (1997) Valuation of Mortgage-backed securities using Brownian bridges to reduce effective dimension. J Comput Financ 1(1):27–46
Dahl LO, Benth FE (2002) Fast evaluation of the Asian option by singular value decomposition. In: Fang KT, Hickernell FJ, Niederreiter H (eds) Monte Carlo and Quasi-Monte Carlo methods 2000. Springer, Berlin, pp 201–214
Fournié E, Lasry J-M, Lebuchoux J, Lions P-L, Touzi N (1999) Applications of Malliavin calculus to Monte-Carlo methods in finance. Finance Stoch 3:391–412
Glasserman P (2004) Monte Carlo methods in financial engineering. Springer, New York
Imai J, Tan KS (2006) A general dimension reduction technique for derivative pricing. J Comput Financ 10(2):129–155
Kohatsu-Higa A, Montero M (2003) Malliavin calculus applied to finance. Physica A 320:548–570
Lamberton D, Lapeyre B (1996) Introduction to stochastic calculus applied to finance. Chapman & Hall
Matoušek J (1998) On the L 2-discrepancy for anchored boxes. J Complex 14:527–556
Nualart D (2006) Malliavin calculus and related topics. Springer, Berlin
Owen A (1998) Latin supercube sampling for very high-dimensional simulations. ACM Trans Model Comput Simul 8:71–102
Papageorgiou A (2002) The Brownian bridge does not offer a consistent avantage in quasi-Monte Carlo integration. J Complex 18:171–186
Paskov S, Traub J (1995) Faster valuation of financial derivatives. J Portf Manage 22(1):113–120
Pitsianis N, Van Loan CF (1993) Approximation with Kronecker products. In: Linear algebra for large scale and real time application, pp 293–314
Sabino P (2009) Monte Carlo and quasi-Monte Carlo methods in option pricing and hedging. PhD thesis. Available at http://www.dm.uniba.it/dottorato/cicli/21c/dottorato/tesi
Sabino P (2011) Implementing quasi-Monte Carlo simulations with linear transformations. Comput Manage Sci 8:51–74
Sobol IM (1976) Uniformly distributed sequences with an additional uniform property. USSR J Comput Math Math Phys 16:1332–1337 (english translation)
Stein M (1987) Large sample properties of simulations using latin hypercube sampling. Technometrics 29(2):143–151
Wang X (2009) Dimension reduction techniques in Quasi-Monte Carlo methods in option pricing. INFORMS J Comput 21(3):488–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cufaro Petroni, N., Sabino, P. Pricing and Hedging Asian Basket Options with Quasi-Monte Carlo Simulations. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 15, 147–163 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-011-9228-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-011-9228-9
Keywords
- Computational finance
- Quasi-Monte Carlo algorithms
- Malliavin Calculus
- Pricing and hedging options
- Asian basket options