Abstract
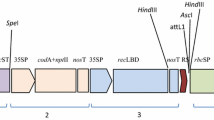
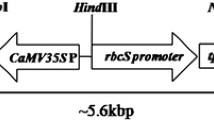
Stemborers and leaffolders are two groups of lepidopteran pests that cause severe damage to rice in many areas of the world. In this study, a cry1C* gene encoding Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) δ-endotoxin was synthesized by codon optimization as the first step towards gene stacking in our resistance management strategy of transgenic rice. Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of this gene into Minghui 63 (Oryza sativa L.), an elite indica CMS restorer line, produced 120 independently transformed plants, 19 of which had a single-copy transgene. Preliminary screening of T1 families of these 19 transformants in the field identified five lines showing a high level of resistance to leaffolders (Cnaphalocrocis medinalis) and stemborers. Hybrids were produced by crossing these five lines with Zhenshan 97A, the male-sterile line for Shanyou 63, the most widely cultivated hybrid in China. These five lines and their hybrids were highly resistant to yellow stemborer (Tryporyza incertulas) as revealed by an insect bioassay. The content of Cry1C* protein varied considerably among the five lines as well as among the corresponding hybrids. T1c-19, a line showing the highest content of Cry1C* protein, and its hybrid were tested in the field for insect resistance and agronomic performance and found to be highly resistant to stemborers and leaffolders throughout the growth period, resulting in a significantly increased grain yield compared with the respective controls. These results indicate that T1c-19 can be used for production of insect-resistant hybrid rice and as a germplasm for gene stacking to produce rice plants with two toxins.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Bt :
-
Bacillus thuringiensis
- CaMV:
-
Cauliflower Mosaic Virus
- CMS:
-
Cytoplasm male sterile
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
References
Alam M, Datta K, Abrigo E, Oliva N, Tu J, Virmani SS, Datta SK (1999) Transgenic insect-resistant maintainer line (IR68899B) for improvement of hybrid rice. Plant Cell Rep 18:7–8
Alcantara EP, Aguda RM, Curtiss A, Dean DH, Cohen MB (2004) Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin binding to brush border membrane vesicles of rice stem borers. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 55:169–177
Ballester V, Granero F, Tabashnik BE, Malvar T, Ferré J (1999) Integrative model for binding of Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in susceptible and resistant larvae of the diamondback moth (Plutella xylostella). Appl Environ Microbiol 65:1413–1419
Barton KA, Whiteley HR, Yang NS (1987) Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin expressed in transgenic Nicotiana tabacum provides resistance to lepidopteran insects. Plant Physiol 85:1103–1109
Bashir K, Husnain T, Fatima T, Latif Z, Mehdi SA, Riazuddin S (2004) Field evaluation and risk assessment of transgenic indica basmati rice. Mol Breed 13:301–312
Bates SL, Zhao JZ, Roush RT, Shelton AM (2005) Insect resistance management in GM crops: past, present and future. Nat Biotechnol 23:57–62
Block MD, Botterman J, Vandewiele M, Dockx JT, Gosselé V, Movva NR, Thompson C, Montagu MV, Leemans J (1987) Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme. EMBO J 6:2513–2518
Cao J, Tang JD, Strizhov N, Shelton AM, Earle ED (1999) Transgenic broccoli with high levels of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1C protein control diamondback moth larvae resistant to Cry1A or Cry1C. Mol Breed 5:131–141
Cao J, Zhao JZ, Tang JD, Shelton AM, Earle ED (2002) Broccoli plants with pyramided cry1Ac and cry1C Bt genes control diamondback moths resistant to Cry1A and Cry1C proteins. Theor Appl Genet 105:258–264
Chen H, Tang W, Xu CG, Li XH, Lin YJ, Zhang Q (2005) Transgenic indica rice plants harboring a synthetic cry2A* gene of Bacillus thuringiensis exhibit enhanced resistance against rice lepidopteran pests. Theor Appl Genet 111:1330–1337
Cheng X, Sardana R, Kaplan H, Altosaar I (1998) Agrobacterium-transformed rice plants expressing synthetic cry1Ab and cry1Ac genes are highly toxic to striped stem borer and yellow stem borer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2767–2772
Datta K, Vasquez A, Tu J, Torrizo L, Alam MF, Oliva N, Abrigo E, Khush GS, Datta SK (1998) Constitutive and tissue specific differential expression of the gene in transgenic rice plants conferring resistance to rice insect pest. Theor Appl Genet 97:20–30
Escriche B, Ferré J, Silva FJ (1997) Occurrence of a common binding site in Mamestra brassicae, Phthorimaea operculella and Spodoptera exigua for insecticidal crystal proteins Cry1A from Bacillus thuringiensis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 27:651–656
Ferré J, Van Rie J (2002) Biochemistry and genetics of insect resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis. Annu Rev Entomol 47:501–533
Ferré J, Real MD, Van Rie J, Jansens S, Peferoen M (1991) Resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis bioinsecticide in a field population of Plutella xylostella is due to a change in a midgut membrane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5119–5123
Fischhoff DA, Bowdish KS, Perlak FJ, Marrone PG, McCoormick SM, Niedermeyer JG, Dean DA, Kusano KK, Mayer EJ, Rochester DE, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1987) Insect tolerant transgenic tomato plants. Biotechnology 5:807–813
Frutos R, Rang C, Royer M (1999) Managing insect resistance to plants producing Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. Crit Rev Biotechnol 19:227–276
Fujimoto H, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Kyozuka J, Shimamoto K (1993) Insect resistant rice generated by introduction of a modified δ-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis. Biotechnology 11:1151–1155
Ghareyazie B, Alinia F, Menguito CA, Rubia LG, Palma JM, Liwanag EA, Cohen MB, Khush GS, Bennett J (1997) Enhanced resistance to two stem borers in an aromatic rice containing a synthetic cry1A(b) gene. Mol Breed 3:401–414
Gould F, Anderson A, Reynolds A, Bumgarner L, Moar W (1995) Selection and genetic analysis of a Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) strain with high levels of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxins. J Econ Entomol 88:1545–1559
Gould F (1998) Sustainability of transgenic insecticidal cultivars: integrating pest genetics and ecology. Annu Rev Entomol 43:701–726
Greenplate JT, Penn SR, Shappley Z, Oppenhizen M, Mann J, Reich B, Osborn J (2000) Bollgard II efficacy: quantification of total lepidopteran activity in a two-gene product. Proc Beltwide Cotton Conf 2:1041–1043
Hama H, Suzuki K, Tanaka H (1992) Inheritance and stability of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis formulations of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Linnaeus) (Lepidoptera: Yponomeutidae). Appl Entomol Zool 27:355–362
Hua X, Ma W, Fan YL (1993) Transgenic tobacco by cotransformation of proteinase inhibitor II and δ-endotoxin. Chinese Sci Bull 38:747–751
James C (2005) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2004. ISAAA, Ithaca, N.Y.
Kain WC, Zhao JZ, Janmaat AF, Myers J, Shelton AM, Wang P (2004) Inheritance of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin in a greenhouse-derived strain of cabbage looper (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 97:2073–2078
Karim S, Dean DH (2000) Toxicity and receptor binding properties of Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxins to the midgut brush border membrane vesicles of the rice leaf folders, Cnaphalocrocis medinalis and Marasmia patnalis. Curr Microbiol 41:276–283
Lin YJ, Zhang Q (2005) Optimizing the tissue culture conditions for high efficiency transformation of indica rice. Plant Cell Rep 23:540–547
Liu KD, Wang J, Li HB, Xu CG, Zhang QF (1997) A genome-wide analysis of wide-compatibility in rice and the precise location of the S5 locus in the molecular map. Theor Appl Genet 95:809–814
Maqbool SB, Husnain T, Raizuddin S, Christou P (1998) Effective control of yellow rice stem borer and rice leaf folder in transgenic rice indica varieties Basmati 370 and M 7 using novel δ-endotoxin cry2A Bacillus thuringiensis gene. Mol Breed 4:501–507
Maqbool SB, Raizuddin S, Loc TN, Gatehouse AMR, Gatehouse JA, Christou P (2001) Expression of multiple insecticidal genes confers broad resistance against a range of different rice pests. Mol Breed 7:85–93
McGaughey WH (1985) Insect resistance to the biological insecticide Bacillus thuringiensis. Science 229:193–195
Nayak P, Basu D, Das S, Basu A, Ghosh D, Ramakrishnan NA, Ghosh M, Sen SK (1996) Transgenic elite indica plants expressing cryA(c) δ-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis are resistant against yellow stem borer (Scirpophaga incertulas). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:2111–2116
Pathak MD (1977) Insect pests of rice. The International Rice Research Institute, Manila, Philippines, pp 1–15
Ramesh S, Nagadhara D, Pasalu IC, Kumari AP, Sarma NP, Reddy VD, Rao KV (2004) Development of stem borer resistant transgenic parental lines involved in the production of hybrid rice. J Biotechnol 111:131–141
Roush RT (1998) Two-toxin strategies for management of insect resistant transgenic crops: can pyramiding succeed where pesticide mixtures have not?. Philos Trans Proc R Soc London Ser B 353:1777–1786
Sayyed AH, Haward R, Herrero S, Ferré J, Wright DJ (2000) Genetic and biochemical approach for characterization of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in a field population of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1509–1516
Shelton AM, Zhao JZ, Roush RT (2002) Economic, ecological, food, safety and social consequence of the deployment of Bt transgenic plants. Annu Rev Entomol 47:845–881
Stewart SD, Adamczyk JJ Jr, Knighten KS, Advis FM (2001) Impact of Bt cottons expressing one or two insecticidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner on growth and survival of noctuid (Lepidoptera) larvae. J Econ Entomol 94:752–760
Strizhov N, Keller M, Mathr J, Koncz KZ, Bosch D, Prdovsky E, Schell J, Sneh B, Koncz C, Zilberstein A (1996) A synthetic cryIC gene, encoding a Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin, confers Spodoptera resistance in alfalfa and tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:15012–15017
Tabashnik BE, Finson N, Groeters FR, Moar WJ, Johnson MW, Luo K, Adang MJ (1994) Reversal of resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis in Plutella xylostella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4120–4124
Tabashnik BE, Carri Y, Dennehy TJ, Morin S, Sisterson MS, Roush RT, Shelton AM, Zhao JZ (2003) Insect resistance to transgenic Bt crops: lessons from the laboratory and field. J Econ Entomol 96:1031–1038
Thompson CJ, Movva NR, Crameri R, Davvies JE, Lauwereys M, Botterman J (1987) Characterization of the herbicide-resistance gene Bar from streptomyces hygroscopicus. EMBO J 6:2519–2523
Tian YC, Zheng JB, Yu HM, Liang HY, Li CQ, Wang JM (2000) Studies of transgenic hybrid poplar 741 carrying two insect-resistant genes. Acta Bot Sinica 42:263–268
Tu JM, Zhang GA, Data K, Xu CG, He YQ, Zhang QF, Khush GS, Datta SK (2000) Field performance of transgenic elite commercial hybrid rice expressing Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin. Nat Biotechnol 18:1101–1104
Vaeck M, Reynaerts A, Höfte H, Jansens S, Beukeleer MD, Dean C, Zabeau M, Montagu MV, Leemans J (1987) Transgenic plants protected from insect attack. Nature 328:33–37
Wang Z, Shu Q, Ye G, Cui H, Wu D, Altosaar I, Xia Y (2002) Genetic analysis of resistance of Bt rice to stripe stem borer (Chilo suppressalis). Euphytica 123:379–386
Wu C, Fan Y, Zhang C, Oliva N, Datta SK (1997) Transgenic fertile japonica rice plants expressing a modified cry1A(b) gene resistant to yellow stem borer. Plant Cell Rep 17:129–132
Wünn J, Kloti A, Burkhardt PK, Biswas GCG, Launis K, Iglesias VA, Potrykus I (1996) Transgenic indica rice breeding line IR58 expressing a synthetic cryA(b) gene from Bacillus thuringiensis provides effective insect pest control. Biotechnology 14:171–176
Ye GY, Sh QY, Yao HW, Cui HR, Cheng XY, Hu C, Xia YW, Gao MW, Altosaar I (2001) Field evaluation of resistance of transgenic rice containing a synthetic cry1Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner to two stem borers. J Econ Entomol 94:271–276
Zhao JZ, Cao J, Li Y, Collins HL, Roush RT, Earle ED, Shelton AM (2003) Transgenic plants expressing two Bacillus thuringiensis toxins delay insect resistance evolution. Nat Biotechnol 21:1493–1487
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Program on Research and Development of Transgenic Plants and National Natural Science Foundation of P.R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, W., Chen, H., Xu, C. et al. Development of insect-resistant transgenic indica rice with a synthetic cry1C* gene. Mol Breeding 18, 1–10 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9002-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-006-9002-9