Abstract
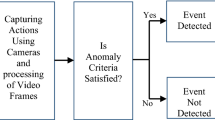
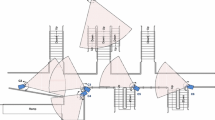
This paper presents a spatio-temporal grid-based framework to deal with the complexity of structured and unstructured motion flows that can effectively group optical flows in the field of view into crowds. This approach utilizes motion flows of the features based on a grid in a scene. In order to detect abnormal events in crowded scenes, the proposed method measures motion features including the speed and direction of moving objects based on a spatio-temporal grid-based approach for flow representation. Experiments have been conducted on several different videos in three domains that are crosswalks, escalators, and highways. To evaluate and compare the performance of our method to other methods, ROC curves are plotted which take into consideration both detection rate and false alarm rate for multiple threshold values.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade EL, Blunsden S, Fisher RB (2006) Hidden markov models for optical flow analysis in crowds. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition—volume 01, ICPR ’06. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 460–463. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2006.621
Ali S, Shah M (2007) A lagrangian particle dynamics approach for crowd flow segmentation and stability analysis. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and patten recognition, pp 1–6. doi:ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.382977
Bertini M, Del Bimbo A, Seidenari L (2012) Scene and crowd behaviour analysis with local space-time descriptors. In: 2012 5th International Symposium on Communications Control and Signal Processing (ISCCSP), pp 1–6. doi:10.1109/ISCCSP.2012.6217857
Cho SH, Nam Y, Hong S, Cho W (2011) Sector based scanning and adaptive active tracking of multiple objects. TIIS 5(6):1166–1191
Cong Y, Yuan J, Liu J (2011) Sparse reconstruction cost for abnormal event detection. In: 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp 3449–3456. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2011.5995434
Gupta A, Srinivasan P, Shi J, Davis L (2009) Understanding videos, constructing plots learning a visually grounded storyline model from annotated videos. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2009, pp 2012–2019. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206492
Ihaddadene N, Djeraba C (2008) Real-time crowd motion analysis. In: 19th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR 2008), 8–11 December 2008. IEEE, Tampa, Florida, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2008.4761041
Li J, Gong S, Xiang T (2008) Global behaviour inference using probabilistic latent semantic analysis. In: BMVC’08, p 10
Lin L, Gong H, Li L, Wang L (2009) Semantic event representation and recognition using syntactic attribute graph grammar. Pattern Recogn Lett 30(2):180–186. Video-based Object and Event Analysis. doi:10.1016/j.patrec.2008.02.023. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0167865508000937
Lin L, Lu Y, Pan Y, Chen X (2012) Integrating graph partitioning and matching for trajectory analysis in video surveillance. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4844–4857. doi:10.1109/TIP.2012.2211373
Liu X, Lin L, Yan S, Jin H, Tao W (2011) Integrating spatio-temporal context with multiview representation for object recognition in visual surveillance. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 21(4):393–407. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2010.2087570
Mehran R, Oyama A, Shah M (2009) Abnormal crowd behavior detection using social force model. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 935–942. doi:ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2009.5206641
Nam Y, Rho S, Park J (2012) Intelligent video surveillance system: 3-tier context-aware surveillance system with metadata. Multimed Tools Appl 57:315–334. doi:10.1007/s11042-010-0677-x
Nam Y, Rho S, Park JH (2012) Inference topology of distributed camera networks with multiple cameras. Multimed Tools Appl 1–21. doi:10.1007/s11042-012-0997-0
Over P, Awad G, Rose RT, Fiscus JG, Kraaij W, Smeaton AF (eds) (2008) TRECVID 2008 workshop participants notebook papers, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, November 2008. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Ozturk O, Yamasaki T, Aizawa K (2010) Detecting dominant motion flows in unstructured/structured crowd scenes. In: Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, ICPR ’10. IEEE Computer Society, Washington, DC, pp 3533–3536. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.862
Sharif M, Ihaddadene N, Djeraba C (2008) Crowd behaviour monitoring on the escalator exits. In: 11th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, 2008. ICCIT 2008, pp 194–200. doi:10.1109/ICCITECHN.2008.4803051
Tang S, Li J-T, Li M, Xie C, Liu Y, Tao K, Xu S-X (2008) Trecvid 2008 participation by mcg-ict-cas. In: TRECVID’08, pp 1–1
Umn: Unusual Crowd Activity Dataset of University of Minnesota. Umndataset.mha.cs.umn.edu/movies/crowd-activity-all.avi
Wang X, Ma X, Grimson WEL (2009) Unsupervised activity perception in crowded and complicated scenes using hierarchical bayesian models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal Mach Intell 31:539–555. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2008.87. URL: http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1512152.1512378
Xiang T, Gong S (2005) Video behaviour profiling and abnormality detection without manual labelling. In: 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. ICCV 2005, vol 2, pp 1238–1245. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2005.248
Xiang T, Gong S (2008) Video behavior profiling for anomaly detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(5):893–908. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70731
Zhang D, Gatica-Perez D, Bengio S, McCowan I (2005) Semi-supervised adapted hmms for unusual event detection. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2005, vol 1. IEEE, pp 611–618
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nam, Y. Crowd flux analysis and abnormal event detection in unstructured and structured scenes. Multimed Tools Appl 72, 3001–3029 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1593-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-013-1593-7