Abstract
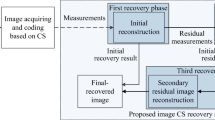
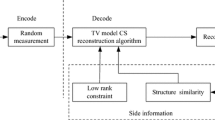
In the traditional reconstruction algorithm for compressed sensing, we use the measurement matrix and the corresponding observed image to recover the target image. In the application of remote sensing, there are many multi-source and multi-temporal reference images that have similar information to that of the target image. In this paper, we propose an algorithm to reconstruct the target image with information from multi-source and multi-temporal reference images to improve the image reconstruction accuracy, in other words, to improve the degree of similarity between the reconstructed image and the target image. The basic principle of our method is to construct a penalty term with the similarity of the target sparse coefficient and the reference sparse coefficient to constrain the reconstruction process. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich F, Sapatinas T, Silverman BW (1998) Wavelet thresholding via a bayesian approach. J R Stat Soc Ser B (Stat Methodol) 60:725–749
Basseville M, Benveniste A, Chou KC, Golden SA, Nikoukhah R, Willsky AS (1992) Modeling and estimation of multiresolution stochastic processes. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 38:766–784
Blumensath T, Davies ME (2009) Iterative hard thresholding for compressed sensing. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 27:265–274
Busch A, Boles WW, Sridharan S (2005) Texture for script identification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27:1720–1732
Chen SS, Donoho DL, Saunders MA (1998) Atomic decomposition by basis pursuit. SIAM J Sci Comput 20:33–61
Chipman HA, Kolaczyk ED, McCulloch RE (1997) Adaptive bayesian wavelet shrinkage. J Am Stat Assoc 92:1413–1421
Chou KC, Larry PH (1994) A multiscale stochastic modeling approach to the monitoring of mechanical systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-SP international symposium on Time-Frequency and Time-Scale Analysis, 1994, pp 25–27
Claude ES (1949) Communication in the presence of noise. Proc IRE 37(1):10–21
David L (2006) Donoho. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 52:1289–1306
John GD (1980) Two-dimensional spectral analysis of cortical receptive field profiles. Vis Res 20: 847–856
Figueiredo MAT, Nowak RD, Stephen JW (2007) Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction; Application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J SelTop Sign Proces 1: 586–597
Goldstein T, Osher S (2009) The split bregman method for l1-regularized problems. SIAM J Imag Sci 2:323–343
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1962) Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J Physiol 160:106
Kim SC, Kang TJ (2007) Texture classification and segmentation using wavelet packet frame and gaussian mixture model. Pattern Recogn 40:1207–1221
Kokare M, Biswas PK, Chatterji BN (2007) Texture image retrieval using rotated wavelet filters. Pattern Recogn Lett 28:1240–1249
Kokare M, Chatterji BN, Biswas PK (2002) M-band wavelet based texture features for content based image retrieval. In: ICVGIP
Kokare M, Chatterji BN, Biswas PK (2002) A survey on current content based image retrieval methods. IETE J Res 48:261–271
Kokare M, Chatterji BN, Biswas PK (2003) Comparison of similarity metrics for texture image retrieval. In: TENCON 2003. Conference on Convergent Technologies for the Asia-Pacific Region, vol 2 , pp 571–575
Lee N, Huynh Q, Schwartz S (1996) New method of linear time-frequency analysis for signal detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE-SP international symposium on Time-Frequency and Time-Scale Analysis, 1996, pp 13–16
Luettgen MR, Karl WC, Willsky AS, Tenney RR (1993) Multiscale representations of markov random fields. IEEE Trans Signal Process 41:3377–3396
Majumdar A, Ward RK. (2010) Compressed sensing of color images. Signal Process 90(12):3122–3127
Mallat SG, Zhang Z (1993) Matching pursuits with time-frequency dictionaries. IEEE Trans Signal Process 41:3397–3415
Mojsilovic A, Popovic MV, Rackov DM (2000) On the selection of an optimal wavelet basis for texture characterization. IEEE Trans Image Process 9(12):2043–2050
Muneeswaran K, Ganesan L, Arumugam S, Ruba Soundar K (2005) Texture classification with combined rotation and scale invariant wavelet features. Pattern Recogn 38:1495–1506
Nagesh P, Li B (2009) Compressed imaging of color images, pp 1261C1264
Needell D, Tropp JA (2009) Cosamp: Iterative signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate samples. Appl Comput Harmon Anal 26:301–321
Pesquet JC, Krim H, Leporini D, Hamman E (1996) Bayesian approach to best basis selection. In: 1996 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing, 1996. ICASSP-96. Conference Proceedings, vol 5, pp 2634–2637
Ravindran A (2006) Gintaras Victor Reklaitis, and Kenneth Martin Ragsdell. Engineering optimization: methods and applications. Wiley
Rubinstein R, Bruckstein AM, Elad M (2010) Dictionaries for sparse representation modeling. Proc IEEE 98:1045–1057
Simoncelli EP, Adelson EH (1996) Noise removal via bayesian wavelet coring. In: International Conference on Image Processing, 1996. Proceedings, vol 1, pp 379–382
Tropp JA, Gilbert AC (2007) Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 53:4655–4666
Zhang Z, Bhaskar D (2013) Extension of SBL algorithms for the recovery of block sparse signals with intra-block correlation. IEEE Trans Signal Process 61(8):2009–2015
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41471368 and No. 41571413).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, C., Wang, L., Liu, P. et al. Compressed sensing based remote sensing image reconstruction via employing similarities of reference images. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 12201–12225 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3004-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-3004-8