Abstract
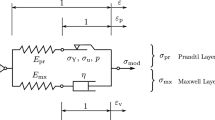
A series viscous-elastic-plastic (VEP) indentation model was expanded to include analysis of the common trapezoidal testing condition, consisting of constant loading—and unloading—rates with an intervening creep hold period. This full VEP model was applied to analyze nanoindentation test of three polymers and five different types of bone. The full VEP solution allows for direct determination of the viscous term as calculated from the creep hold, while the elastic and plastic material parameters were determined from a non-linear curve-fit of the unloading displacement-time data. Additionally, the use of the trapezoidal loading procedure permitted analysis of the unloading load-displacement data with traditional Oliver-Pharr analysis; the material properties from this analysis compared well with those obtained with VEP analysis. Using the full VEP solution and fitted material constants the loading and creep hold displacement-time curves were simulated and matched well to both polymer and bone experimental data. The full VEP solution shows great promise in for obtaining material parameters for many viscoelastic materials such as hydrated bone, polymers, and other biological tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bembey, A.K., Oyen, M.L., Bushby, A.J., Boyde, A.: Viscoelastic properties of bone as a function of hydration state determined by nanoindentation. Philos. Mag. 86(33–35), 5691–5703 (2006)
Briscoe, B.J., Fiori, L., Pelillo, E.: Nano-indentation of polymeric surfaces. J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys. 31(19), 2395–2405 (1998)
Chang, M.C., Ko, C.C., Liu, C.C., Douglas, W.H., DeLong, R., Seong, W.J., Hodges, J., An, K.N.: Elasticity of alveolar bone near dental implant-bone interfaces after one month’s healing. J. Biomech. 36(8), 1209–1214 (2003)
Cheng, Y.T., Ni, W.Y., Cheng, C.M.: Determining the instantaneous modulus of viscoelastic solids using instrumented indentation measurements. J. Mater. Res. 20(11), 3061–3071 (2005)
Chudoba, T., Richter, F.: Investigation of creep behaviour under load during indentation experiments and its influence on hardness and modulus results. Surf. Coat. Technol. 148, 191–198 (2001)
Feng, G., Ngan, A.H.W.: Effects of creep and thermal drift on modulus measurement using depth-sensing indentation. J. Mater. Res. 17(3), 660–668 (2002)
Ferguson, V.L.: Deformation partitioning provides insight into elastic, plastic, and viscous contributions to bone material behavior. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2(4), 364–374 (2009)
Ferguson, V.L., Bushby, A.J., Boyde, A.: Nanomechanical properties and mineral concentration in articular calcified cartilage and subchondral bone. J. Anat. 203(2), 191–202 (2003)
Liu, C.-K., Lee, S., Sung, L.-P., Nguyen, T.: Load-displacement relations for nanoindentation of viscoelastic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 100(3), 033503 (2006)
Oliver, W.C., Pharr, G.M.: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic-modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7(6), 1564–1583 (1992)
Oliver, W.C., Pharr, G.M.: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19(1), 3–20 (2004)
Oyen, M.L.: Analytical techniques for indentation of viscoelastic materials. Philos. Mag. 86(33–35), 5625–5641 (2006a)
Oyen, M.L.: Nanoindentation hardness of mineralized tissues. J. Biomech. 39(14), 2699–2702 (2006b)
Oyen, M.L.: Relating viscoelastic nanoindentation creep and load relaxation experiments. Int. J. Mater. Res. 99(8), 823–828 (2008)
Oyen, M.L., Cook, R.F.: Load-displacement behavior during sharp indentation of viscous-elastic-plastic materials. J. Mater. Res. 18(1), 139–150 (2003)
Oyen, M.L., Ko, C.: Examination of local variations in viscous, elastic, and plastic indentation responses in healing bone. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 18(4), 623–628 (2007)
Rho, J.Y., Roy, M.E., Tsui, T.Y., Pharr, G.M.: Elastic properties of microstructural components of human bone tissue as measured by nanoindentation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 45(1), 48–54 (1999a)
Rho, J.Y., Zioupos, P., Currey, J.D., Pharr, G.M.: Variations in the individual thick lamellar properties within osteons by nanoindentation. Bone 25(3), 295–300 (1999b)
Sakai, M.: The Meyer hardness: A measure for plasticity? J. Mater. Res. 14(9), 3630–3639 (1999)
Zhang, C.Y., Zhang, Y.W., Zeng, K.Y., Shen, L.: Nanoindentation of polymers with a sharp indenter. J. Mater. Res. 20(6), 1597–1605 (2005)
Zhang, C.Y., Zhang, Y.W., Zeng, K.Y., Shen, L.: Characterization of mechanical properties of polymers by nanoindentation tests. Philos. Mag. 86(28), 4487–4506 (2006)
Zysset, P.K., Guo, X.E., Hoffler, C.E., Moore, K.E., Goldstein, S.A.: Elastic modulus and hardness of cortical and trabecular bone lamellae measured by nanoindentation in the human femur. J. Biomech. 32(10), 1005–1012 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olesiak, S.E., Oyen, M.L. & Ferguson, V.L. Viscous-elastic-plastic behavior of bone using Berkovich nanoindentation. Mech Time-Depend Mater 14, 111–124 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-009-9098-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11043-009-9098-5