Abstract
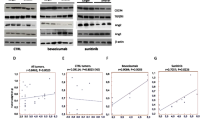
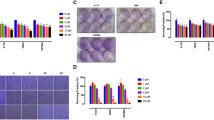
Glioblastomas are among the most aggressive human cancers, and prognosis remains poor despite presently available therapies. Angiogenesis is a hallmark of glioblastoma, and the resultant vascularity is associated with poor prognosis. The proteins that mediate angiogenesis, including vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling proteins, have emerged as attractive targets for therapeutic development. Since VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR-2) is thought to be the primary receptor mediating angiogenesis, direct inhibition of this receptor may produce an ideal therapeutic effect. In this context, we tested the therapeutic effect of CT322, a selective inhibitor of VEGFR-2. Using an intracranial murine xenograft model (U87-EGFRvIII-luciferase), we demonstrate that CT322 inhibited glioblastoma growth in vivo and prolonged survival. Of note, the anti-neoplastic effect of CT322 is augmented by the incorporation of temozolomide or temozolomide with radiation therapy. Immunohistochemical analysis of CT322 treated tumors revealed decreased CD31 staining, suggesting that the tumoricidal effect is mediated by inhibition of angiogenesis. These pre-clinical results provide the foundation to further understand long term response and tumor escape mechanisms to anti-angiogenic treatments on EGFR over-expressing glioblastomas.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walker MD, Alexander E Jr, Hunt WE, MacCarty CS, Mahaley MS Jr, Mealey J Jr, Norrell HA, Owens G, Ransohoff J, Wilson CB, Gehan EA, Strike TA (1978) Evaluation of BCNU and/or radiotherapy in the treatment of anaplastic gliomas. A cooperative clinical trial. J Neurosurg 49:333–343. doi:10.3171/jns.1978.49.3.0333
Stupp R, Mason WP, Bent MJvd, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJB, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann Jr, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Quick A, Patel D, Hadziahmetovic M, Chakravarti A, Mehta M (2010) Current therapeutic paradigms in Glioblastoma. Rev Recent Clin Trials 5:14–27
Schmidt NO, Westphal M, Hagel C, Ergun S, Stavrou D, Rosen EM, Lamszus K (1999) Levels of vascular endothelial growth factor hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in human gliomas and their relation to angiogenesis. Int J Cancer 84:10–18. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19990219)84:1<10:AID-IJC3>3.0.CO;2-L
Plate K, Breier G, Weich H, Mennel H, Risau W (1994) Vascular endothelial growth factor and glioma angiogenesis: coordinate induction of VEGF receptors, distribution of VEGF protein and possible in vivo regulatory mechanisms. Int J Cancer 59:520–529
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359:845–848. doi:10.1038/359845a0
Feldkamp MM, Lau N, Rak J, Kerbel RS, Guha A (1999) Normoxic and hypoxic regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by astrocytoma cells is mediated by Ras. Int J Cancer 81:118–124. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19990331)81:1<118:AID-IJC20>3.0.CO;2-5
Zhou Y-H, Tan F, Hess KR, Yung WKA (2003) The expression of PAX6 PTEN, vascular endothelial growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor in gliomas: relationship to tumor grade and survival. Clin Cancer Res 9:3369–3375
Leon SP, Folkerth RD, Black PM (1996) Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with astroglial brain tumors. Cancer 77:362–372. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19960115)77:2<362:AID-CNCR20>3.0.CO;2-Z
Wick W, Weller M, Weiler M, Batchelor T, Yung AWK, Platten M (2011) Pathway inhibition: emerging molecular targets for treating glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncol 13:566–579. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nor039
Norden AD, Drappatz J, Muzikansky A, David K, Gerard M, McNamara MB, Phan P, Ross A, Kesari S, Wen PY (2008) An exploratory survival analysis of anti-angiogenic therapy for recurrent malignant glioma. J Neurooncol 92:149–155. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9745-8
Kerbel RS (2008) Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 358:2039–2049. doi:10.1056/NEJMra0706596
Veikkola T, Alitalo K (1999) VEGFs, receptors and angiogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 9:211–220
Baldwin ME, Catimel B, Nice EC, Roufail S, Hall NE, Stenvers KL, Karkkainen MJ, Alitalo K, Stacker SA, Achen MG (2001) The specificity of receptor binding by vascular endothelial growth factor-D is different in mouse and man. J Biol Chem 276:19166–19171. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100097200
Millauer B, Wizigmann-Voos S, Schnürch H, Martinez R, Møller NPH, Risau W, Ullrich A (1993) High affinity VEGF binding and developmental expression suggest Flk-1 as a major regulator of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Cell 72:835–846
Veikkola T, Jussila L, Makinen T, Karpanen T, Jeltsch M, Petrova TV, Kubo H, Thurston G, McDonald DM, Achen MG, Stacker SA, Alitalo K (2001) Signalling via vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 is sufficient for lymphangiogenesis in transgenic mice. The EMBO. J. 20: 1223–1231. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.6.1223
Oka N, Soeda A, Inagaki A, Onodera M, Maruyama H, Hara A, Kunisada T, Mori H, Iwama T (2007) VEGF promotes tumorigenesis and angiogenesis of human glioblastoma stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 360:553–559. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.06.094
Gan HK, Kaye AH, Luwor RB (2009) The EGFRvIII variant in glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Neurosci 16:748–754
Mamluk R, Carvajal IM, Morse BA, Wong H, Abramowitz J, Aslanian S, Lim AC, Gokemeijer J, Storek MJ, Lee J, Gosselin M, Wright MC, Camphausen RT, Wang J, Chen Y, Miller K, Sanders K, Short S, Sperinde J, Prasad G, Williams S, Kerbel R, Ebos J, Mutsaers A, Mendlein JD, Harris AS, Furfine ES (2010) Anti-tumor effect of CT-322 as an adnectin inhibitor of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2. Monoclon Antib 2: 199–208
Lipovsek D (2010) Adnectins: engineered target-binding protein therapeutics. Prot Eng Des Sel 24:3–9. doi:10.1093/protein/gzq097
Tolcher AW, Sweeney CJ, Papadopoulos K, Patnaik A, Chiorean EG, Mita AC, Sankhala K, Furfine E, Gokemeijer J, Iacono L, Eaton C, Silver BA, Mita M (2011) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of CT-322 (BMS-844203), a targeted adnectin inhibitor of VEGFR-2 based on a domain of human fibronectin. Clin Cancer Res 17:363–371. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-1411
Murphy GJ, Mostoslavsky G, Kotton DN, Mulligan RC (2006) Exogenous control of mammalian gene expression via modulation of translational termination. Nat Med 12:1093–1099. doi:10.1038/nm1376
Shapiro WR (1974) The chemotherapy of intracerebral vs subcutaneous murine gliomas: a comparative study of the effect of VM 26. Arch Neurol 30:222–226
Kerbel RS (2006) Antiangiogenic therapy: a universal chemosensitization strategy for cancer? Science 312:1171–1175. doi:10.1126/science.1125950
Hudis CA (2005) Clinical implications of antiangiogenic therapies. Oncology 19:26–31
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62. doi:10.1126/science.1104819
Kamoun WS, Ley CD, Farrar CT, Duyverman AM, Lahdenranta J, Lacorre DA, Batchelor TT, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Fukumura D, Sorensen AG, Jain RK (2009) Edema control by cediranib, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-targeted kinase inhibitor, prolongs survival despite persistent brain tumor growth in mice. J Clin Oncol 27:2542–2552. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.19.9356
Gerstner ER, Duda DG, Tomaso Ed, Ryg PA, Loeffler JS, Sorensen AG, Ivy P, Jain RK, Batchelor TT (2009) VEGF inhibitors in the treatment of cerebral edema in patients with brain cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6:229–236. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.14
Gerstner ER, Frosch MP, Batchelor TT (2010) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging detects pathologically confirmed, nonenhancing tumor progression in a patient with recurrent glioblastoma receiving bevacizumab. J Clin Oncol 28:e91–e93
Cohen MH, Shen YL, Keegan P, Pazdur R (2009) FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin(R)) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Oncologist 14:1131–1138. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2009-0121
Batchelor TT, Duda DG, di Tomaso E, Ancukiewicz M, Plotkin SR, Gerstner E, Eichler AF, Drappatz J, Hochberg FH, Benner T, Louis DN, Cohen KS, Chea H, Exarhopoulos A, Loeffler JS, Moses MA, Ivy P, Sorensen AG, Wen PY, Jain RK (2010) Phase II Study of Cediranib, an oral pan-vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in Patients with recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28:2817–2823. doi:10.1200/jco.2009.26.3988
de Groot JF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Gilbert MR, Cloughesy TF, Aldape K, Yao J, Jackson EF, Lieberman F, Robins HI, Mehta MP, Lassman AB, DeAngelis LM, Yung WKA, Chen A, Prados MD, Wen PY (2011) Phase II Study of aflibercept in recurrent malignant glioma: a North American brain tumor consortium study. J Clin Oncol 29:2689–2695. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.34.1636
Lai A, Tran A, Nghiemphu PL, Pope WB, Solis OE, Selch M, Filka E, Yong WH, Mischel PS, Liau LM, Phuphanich S, Black K, Peak S, Green RM, Spier CE, Kolevska T, Polikoff J, Fehrenbacher L, Elashoff R, Cloughesy T (2010) Phase II study of bevacizumab plus temozolomide during and after radiation therapy for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 29:142–148. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.30.2729
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Neyns B, Goldbrunner R, Schlegel U, Paul MJ Clement, Grabenbauer GG, Ochsenbein AF, Simon M, Dietrich PY, Pietsch T, Hicking C, Tonn JC, Diserens AC, Pica A, Hermisson M, Krueger S, Picard M, Weller M (2010) Phase I/IIa study of cilengitide and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy followed by cilengitide and temozolomide maintenance therapy in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 28
Beal K, Abrey LE, Gutin PH (2011) Antiangiogenic agents in the treatment of recurrent or newly diagnosed glioblastoma: analysis of single-agent and combined modality approaches. Radiat Oncol 6:2. doi:10.1186/1748-717X-6-2
Schiff DRD, Kesari S, Mikkelsen T, De Groot JF, Fichtel L, Coyle TE, Wong EEC, Silver B (2010) Phase II study of CT-322, a targeted biologic inhibitor of VEGFR-2 based on a domain of human fibronectin, in recurrent glioblastoma (rGBM) [abstract]. J Clin Oncol 28:182s
Acknowledgment
Grant Support: Adnexus, a Bristol-Myers Squibb R&D Company.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
J. Dawn Waters, Carlos Sanchez, Ayguen Sahin contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waters, J.D., Sanchez, C., Sahin, A. et al. CT322, a VEGFR-2 antagonist, demonstrates anti-glioma efficacy in orthotopic brain tumor model as a single agent or in combination with temozolomide and radiation therapy. J Neurooncol 110, 37–48 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0948-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0948-7