Abstract
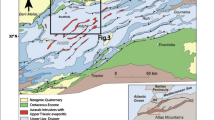
Big landslides are one of the main natural hazards in Kyrgyzstan, which are concentrated in the foothills of the high mountain ranges along the Eastern rim of the Fergana Basin. Because of the high number of landslides and their occurrence over large areas there is a strong need for effective and objective landslide hazard assessment at a regional scale. In Kyrgyzstan satellite remote sensing data represent the only source of multitemporal information about surface conditions covering large areas. Against this background the goal is the development of a satellite remote sensing and GIS-based system for quantitatively oriented and spatially differentiated hazard assessment. During the presented pilot investigations in the area of the Upper Maili Suu river basin a methodological framework has been developed incorporating remote sensing and GIS techniques for various levels of information extraction. So far, methodological investigations have been focused on the potential of satellite remote sensing data from different optical (Landsat-(E)TM, ASTER, MOMS-2P) and radar (ERS-1/2) systems for the creation of an improved knowledge basis for hazard assessment. This includes landslide identification, generation of topographic information and characterization of the geological setting. The derived primary information have been analyzed in a GIS environment to gain an improved process understanding as a main prerequisite for successful hazard assessment. The results show that currently available satellite remote sensing data are suitable for landslide investigation in Kyrgyzstan. Full exploitation of their information potential requires combined analysis with other thematic information based on methods of interactive and automated information extraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitmatov I., Koshogulov K., Nikolskaya O. (1999) Geomechanics of Landslide Processes, Ilim Bishkek, 210 pp. (in Russian)
A. Carrara M. Cardinali R. Detti F. Guzzetti V. Pasqui P. Reichenbach (1991) ArticleTitleGIS techniques and statistical models in evaluating landslide hazard Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 16 427–445
A. Carrara F. Guzzetti M. Cardinali P. Reichenbach (1999) ArticleTitleUse of GIS technology in the prediction and monitoring of landslide hazard Nat. Hazards 20 117–135 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008097111310
Ch. Chung A. Fabbri C. Van Westen (1995) Multivariate regression analysis for landslide hazard zonation A. Carrara F. Guzzetti (Eds) Geographical Information Systems in Assessing Natural Hazard Kluwer Academic Publisher Dordrecht, The Netherlands 107–133
L. Donati M. Turrini (2002) ArticleTitleAn objective method to rank the importance of factors predisposing to landslides with the GIS methodology: Application to an area of the Apennines (Valneria; Perugia, Italy) Eng. Geol. 63 277–289 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00087-4
Eyers R., Moore-J McM., Hervas J., Liu J. (1998). Integrated use of Landsat TM and SPOT panchromatic imagery for landslide mapping: Case histories from southeast Spain, In: Geohazards in Engineering Geology, Geological Society Special Publication, 15 pp. 133–140
B. Fruneau J. Achache C. Delacourt (1996) ArticleTitleObservation and modelling of the Saint-Etienne-de-Tinee landslide using SAR interferometry Tectonophysics 265 181–190 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0040-1951(96)00047-9
E. Garcia-Melendez I. Molina M. Ferre-Julia J. Aguirre (1998) ArticleTitleMultisensor data integration and GIS analysis for natural hazard mapping in a semiarid area (southeast Spain) Adv. Space. Res. 21 493–499 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0273-1177(97)00886-7
F. Guzzetti A. Carrara M. Cardinali P. Reichenbach (1999) ArticleTitleLandslide evaluation: A review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study, Central Italy Geomorphology 31 181–216 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00078-1
F. Guzzetti M. Cardinali P. Reichenbach A. Carrara (2000) ArticleTitleComparing landslide maps: A case study in the Upper Tiber River basin, Central Italy Environ. Manag. 25 247–263 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002679910020
H. Kaufmann D. Meißner J. Bodechtel F.-J. Behr (1989) ArticleTitleDesign of spectral and panchromatic bands for the German MOMS-02 sensor Photogramm. Eng. Rem. S. 55 875–881
Koshogulov K., Nikolskaja O., Meleshko A. (1999). Special characteristics of the formation and activation of landslide processes in the Maili Suu river basin, In: Questions of Geomechanics and Reprocessing of Deposits of Mineral Resources, Ilim Bishkek, pp. 292–301 (in Russian)
W. Kornus M. Lehner H. Ebner H. Froeba T. Ohlhof (1999) ArticleTitlePhotogrammetric point determination and DEM generation using MOMS-2P/PRIRODA three-line imagery Geo-Informations-Systeme (GIS) 6 28–36
C. Lee H. Ye M. Yeung X. Shan G. Chen (2001) ArticleTitleAIGIS-based methodology for natural terrain landslide susceptibility mapping in Hong Kong Episodes 24 150–159
Lehner M., Gill R. (1992). Semi-automatic Derivation of Digital Elevation Models from Stereoscopic 3-line Scanner Data. IAPRS, 29, Part B4, Washington, USA, pp. 68–75
F. Mantovani R. Soeters C. Van Westen (1996) ArticleTitleRemote sensing techniques for landslide studies and hazard zonation in Europe Geomorphology 15 213–225 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0169-555X(95)00071-C
D. Massonnet K. Feigl (1998) ArticleTitleRadar interferometry and its application to changes in the earth’s surface Rev. Geophys. 36 441–500 Occurrence Handle10.1029/97RG03139
J. McKean S. Buechel L. Gaydos (1991) ArticleTitleRemote sensing and landslide hazard assessment Photogramm. Eng. Rem. S. 57 1185–1193
Moldobekov B., Sarangoev A., Usupaev Sh., Meleshko A. (1997). Prognosis of Natural Hazards on the Territory of the Kyrgyz Republic, All-Press Bishkek, 172 pp. (in Russian)
Roessner S., Wetzel H.-U., Kaufmann H., Kornus W., Lehner M., Reinartz P., and Mueller R. (2000). Landslide Investigations in Southern Kyrgyzstan Based on a Digital Elevation Model derived from MOMS-2P Data, IAPRS, 33, B7, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, pp. 1259–1266
V. Singhroy K. Mattar A. Gray (1998) ArticleTitleLandslide characteristics in Canada using interferometric SAR and combined SAR and TM images Adv. Space Res. 21 465–476
B. Temesgen M. Mohammed T. Korme (2001) ArticleTitleNatural hazard assessment using GIS and remote sensing methods, with particular reference to the landslides in the Wondogenet area, Ethiopia Phys. Chem. Earth (C) 26 665–675
Toutin Th., and Cheng Ph. (2001). DEM Generation with ASTER stereo data. Earth Observation Magazine, 10: 6, http://www.eomonline.com/Common/currentissues/~June01/tableofcontents.htm (online)
Torgoev Yu., Aleshin B., Moldobekov B., Meleshko A. (1999). Genetic factors of the development of landslides in the Maili-Suu river basin. In: Questions of Geomechanics and Reprocessing of Deposits of Mineral Resources, Ilim Bishkek (in Russian)
Van Westen C.J. (1993). Application of Geographical Information System to Landslide Hazard Zonation. ITC Publication no. 15, ITC Enschede, The Netherlands, 245 pp
C.J. Van Westen A. Seijmonsbergen F. Mantovani (1999) ArticleTitleComparing landslide hazard maps Nat. Hazards 20 137–158
Varnes D.J., International Association of Engineering Geology Commission on Landslides and Other Movements on Slopes (1984). Landslide Hazard Zonation–A Review of Principles and Practice, UNESCO, Natural Hazard Series, 3, 63 pp
H.-U. Wetzel S. Roessner A. Sarnagoev (2000) Remote sensing and GIS based geological mapping for assessment of landslide hazard in Southern Kyrgyzstan (Central Asia) C. Brebbia P. Pascolo (Eds) Management Information Systems 2000 – GIS and Remote Sensing WIT-Press Southampton, Boston 355–366
Xia Y. (2001). INSAR activities in Central Asia using a mobile SAR receiving station. IEEE IGARSS 2001 Proceedings, Sydney, Australia (CD-ROM)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roessner, S., Wetzel, HU., Kaufmann, H. et al. Potential of Satellite Remote Sensing and GIS for Landslide Hazard Assessment in Southern Kyrgyzstan (Central Asia). Nat Hazards 35, 395–416 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-004-1799-0
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-004-1799-0