Abstract
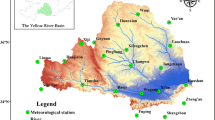
Drought is one of the most harmful natural hazards in Gansu Province in Northwest China. The changes of precipitation affect the severity of drought. In order to recognize the trend of precipitation and understand the effect of rainfall change on water resources management and drought severity, Mann–Kendall test was used. Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) was calculated to reconstruct the drought at different time scales and analyze the frequency of drought occurrence in the recent 50 years. The results show that the SPI is applicable in Gansu Province. The number of severe droughts differs among regions: it is more obvious as a 3-month drought in the Yellow River Basin and the Yangtze River Basin than in the Inland River Basin, and other droughts at 6-, 9-, and 12-month time scales have the same effect in the three regions. Mann–Kendall test results show that there is an upward trend in the summer periods and a downward trend in the autumn-winter-spring intervals ranging from 10.5 mm/10 years to −37.4 mm/10 years, which affect the local water resources management, droughts mitigation, and agriculture decision making. This situation poses challenges for future study.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramowitz M, Stegun I (eds) (1965) Handbook of mathematical functions with formulas, graphs, and mathematical table. Dover Publications, New York
Chow V, Maidment R, Mays W (1988) Applied hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Edwards D, McKee T (1997) Characteristics of 20th century drought in the United States at multiple scale. Atmospheric Science Paper No. 634, May 1–30
Guttman N (1998) Comparing the Palmer drought index and the standardized precipitation index. J Am Water Resour Assoc 34(1):113–121. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1998.tb05964.x
Guttman N (1999) Accepting the standardized precipitation index: a calculation algorithm. J Am Water Resour Assoc 35(2):311–322. doi:10.1111/j.1752-1688.1999.tb03592.x
Hayes M, Svoboda M, Wilhite D et al (1999) Monitoring the 1996 drought using the standardized precipitation index. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 80:429–438. doi 10.1175/1520-0477(1999)080<0429:MTDUTS>2.0.CO;2
Hirsch R, Helsel D, Cohn T, Gilroy E (1993) Statistical analysis of hydrologic data. In: Maidment D (ed) Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York
Hisdal H, Stahl K, Tallaksen L et al (2001) Have streamflow droughts in Europe become more severe or frequent? Int J Climatol 21:317–333. doi:10.1002/joc.619
Husak G, Michaelsen J, Funk C (2007) Use of gamma distribution to represent monthly rainfall in Africa for drought monitoring applications. Int J Climatol 27:935–944. doi:10.1002/joc.1441
Kangas R, Brown T (2007) Characteristics of US drought and pluvials from a high-resolution spatial dataset. Int J Climatol 27:1303–1325. doi:10.1002/joc.1473
Łabędzki L (2007) Estimation of local drought frequency in central Poland using the Standardized Precipitation Index SPI. Irrig Drain 56:67–77. doi:10.1002/ird.285
Li Q, Liu X, Li X (2002) Drought trend in North in recent half century. J Nat Disasters 11(3):50–56 (in Chinese)
Li Y, Yu Y, Luo X, Ma X, Zhang A, Wang R (2004) Study on climatic prediction of sandstorm in east of Hexi Corridor. Plateau Meteorol 23(6):851–856 (in Chinese)
Ma Z, Dan L (2005) Dry/wet variation and its relationship with regional warming in arid regions of northern China. Chin J Geophys 48(5):1091–1099
Ma Z, Fu C (2006) Some evidence of drying trend over northern China from 1951 to 2004. Chin Sci Bull 51(23):2913–2925. doi:10.1007/s11434-006-2159-0
McKee T, Doesken N, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scale. In: 8th conference on applied climatology, pp 179–184
Morid S, Smakhtin S, Moghaddasi M (2006) Comparison of seven meteorological indices for drought monitoring in Iran. Int J Climatol 26:971–985. doi:10.1002/joc.1264
Ntale H, Thian Y (2003) Drought indices and their application to East Africa. Int J Climatol 23:1335–1357. doi:10.1002/joc.931
Paulo A, Pereira L (2006) Drought concepts and characterization: comparing drought indices applied at local and regional scales. Water Int 31(1):37–49
Pereira L, Cordery I, Iacovides I (2002) Coping with water scarcity. UNESCO IHP VI, Technical Documents in Hydrology No. 58, UNESCO, Paris, p 269
Ren H, Zhang P, Li W, Gao L (2006) Low-frequency oscillation characteristics of precipitation and water vapor transport in the eastern part of Northwest China in spring. Plateau Meteorol 25(2):285–292 (in Chinese)
Salas J (1993) Analysis and modeling of hydrologic time series. In: Maidment D (ed) Handbook of hydrology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 19.1–19.72
Shi Y, Shen Y, Li D, Zhang G, Ding Y, Hu R, Kang E (2003) Discussion on the present climate change from warm-dry to warm-wet in northwest China. Quat Sci 23(2):152–164 (in Chinese)
Silva V (2005) On climate variability in Northeast of Brazil. J Arid Environ 58(4):575–596
Sneyers R (1990) On the statistical analysis of series of observations. WMO Technical Note 43, World Meteorological Organization, Geneva
Tate E, Gustard A (2000) Drought definition: a hydrological perspective. In: Vogt J, Somma F (eds) Drought and drought mitigation in Europe. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 23–48
Thom H (1966) Some methods of climatological analysis. WMO Technical Note Number 81, Secretariat of the World Meteorological Organization, Geneva, p 53
Wang Z, Zhai P (2003) Climate change in drought over northern China during 1950–2000. Acta Geogr Sin 58(Supplement):61–68 (in Chinese)
Wang Q, Ding Y, Jiang Y (1998) Relationship between Asian Monsoon activities and the precipitation over China mainland. Quat J Appl Meteorol 9(Supplement):84–89 (in Chinese)
Wilhite D, Glantz M (1985) Understanding the drought phenomenon: the role of definition. Water Int 10:111–120
Wu H, Hayes M, Weiss A, Hu Q (2001) An evaluation of the standardized precipitation index, the China-Z index and the statistical Z-Score. Int J Climatol 21:745–758. doi:10.1002/joc.658
Wu H, Hayes M, Wilhite D, Svoboda M (2005) The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int J Climatol 25:505–520. doi:10.1002/joc.1142
Wu H, Svoboda M, Hayes M, Wilhite D, Wen F (2007) Appropriate application of the Standardized Precipitation Index in arid locations and dry seasons. Int J Climatol 27:65–79. doi:10.1002/joc.1371
Xu X, Tao S, Wang J, Chen L, Zhou L, Wang X (2002) The relationship between water vapor transport features of Tibetan Plateau-Monsoon “large triangle” affecting region and drought-flood abnormality of China. Acta Meteorol Sin 60(3):257–266 (in Chinese)
Yin X, Deng Z, Xu Q, Dong A (2005) Study on drought disasters in Gansu Province since recent 50 years. Arid Zone Res 22(1):120–124 (in Chinese)
Yu Y, Zou S, Whittemore D (1993) Non-parametric trend analysis of water quality data of rivers in Kansas. J Hydrol (Amst) 150:61–80. doi:10.1016/0022-1694(93)90156-4
Zhang Q (1998) Research on determination of drought index in north China and its application. J Catastrophol 13(4):34–38 (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Chen L (1991) Variations of dryness and wetness in China during 1951–1980. Sci Atmos Sin 15(5):72–81 (in Chinese)
Zhang Q, Wei J, Tao S (2003) The decadal and interannual variations of drought in the northern China and association with the circulation. Clim Environ Res 8(3):307–318 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 40671010; 40725001). The authors greatly appreciate the help of the China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System (http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/) and the Hydrology and Water Resources Survey Administration of the Gansu Province for providing valuable pluviometric data. The authors also acknowledge the comments and advice from Dr. Chansheng He at the Department of Geography, Western Michigan University. We also thank two anonymous reviewers for providing constructive comments in reviewing this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, L., Feng, Q. Spatial and temporal pattern of precipitation and drought in Gansu Province, Northwest China. Nat Hazards 49, 1–24 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-008-9274-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-008-9274-y