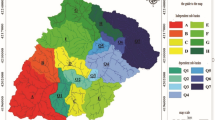
Abstract
Flood disaster is an important threat to the safe operation of reservoirs. Accurate flood forecasting can provide important information for optimal reservoir operation. Generally, the characteristic of precipitation spatial distribution is analyzed based on observation of several discreet preset stations. This cannot catch the rainstorm center all the time and will lead to deviation in the characteristic of precipitation spatial distribution. Therefore, it can hardly arrive at optimal sub-watershed delineation and flood modeling. Therefore, a novel method is proposed for analysis of characteristic of precipitation spatial distribution in consideration of rainfall distribution and the delay of rainfall–runoff concentration. Based on the analysis results of precipitation spatial distribution, several key sub-basins which have significant impact on the flood process can be recognized. And then the elaborate sub-watershed delineation and flood modeling approach is put forward consequently on these key sub-basins. The efficacy of the proposed method is estimated on the flood forecasting of Zhexi reservoir watershed. The results verify that the proposed method can significantly improve the flood forecasting precision, which can provide important decision-making basis for reservoir operation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsenault R, Latraverse M, Duchesne T (2016) An efficient method to correct under-dispersion in ensemble stream flow prediction of inflow volumes for reservoir optimization. Water Resour Manag 30:1–18
Badrzadeh H, Sarukkalige R, Jayawardena AW (2015) Hourly runoff forecasting for flood risk management: application of various computational intelligence models. J Hydrol 529:1633–1643
Chen L, Singh VP, Guo S et al (2013) A new method for identification of flood seasons using directional statistics. Hydrol Sci J 58:1–13
Cheng CT, Niu WJ, Feng ZK et al (2015) Daily reservoir runoff forecasting method using artificial neural network based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Water 7:4232–4246
Dolcine L, Andrieu H, Sempere-Torres D et al (2015) Flash flood forecasting with coupled precipitation model in mountainous mediterranean basin. J Hydrol Eng 6:1–10
Duan J (1995) Overview of Zhexi reservoir hydrological forecast and operation. Cent China Electr Power 8:50–54
Jiao W, Long H (2015) Applicability analysis of modified distributed hydrological model in Weihe river basin. Water Resour Power 33:22–27
Kong F, Wang X (2009) A semi-distributed hydrological model based on DEM. Eng J Wuhan Univ 42:596–600
Li Q, Ouyang S (2015) Research on multi-objective joint optimal flood control model for cascade reservoirs in river basin system. Nat Hazards 77:2097–2115
Li C, Duan J, Xiao S et al (2005) Application of digital hydrological model to the flood forecast of Zhexi hydropower station. Hydrol Auto Dam Monit 29:48–51
Li H, Zhang Y, Chiew FHS et al (2009) Predicting runoff in ungauged catchments by using Xinanjiang model with MODIS leaf area index. J Hydrol 370:155–162
Li J, Shen B, Jie J et al (2010) Hydrological forecasting preferred and combination based on multi-attribute group decision. Syst Eng Theory Pract 30:2315–2320
Liu Z, Hou A, Wang X (2015) Flood forecasting for small-and medium-sized rivers based on distributed hydrological modeling. J China Hydrol 35:1–6
Liu Z, Guo S, Zhang H et al (2016) Comparative study of three updating procedures for real-time flood forecasting. Water Resour Manag 30:2111–2126
Luo W, Yu S, Wang X et al (2006) Anti-error researching of flood forecasting project of double mutual inflow reservoir. Eng J Wuhan Univ 39:1–5
Peng Y, Sun X, Zhang X et al (2017) A flood forecasting model that considers the impact of hydraulic projects by the simulations of the aggregate reservoir’s retaining and discharging. Water Resour Manag 31:1031–1045
Rahman M, Lu M (2015) Model spin-up behaviour for wet and dry basins: a case study using Xinanjiang model. Water 7:4256–4273
Shen H, Xie J, Li J et al (2012) Hydrological combined forecasting method based-on vector angular cosine. Syst Eng Theory Pract 32:1591–1597
Shu D, Cheng G, Lin S (2004) Spatial discretization of digital watershed based on DEM for the upper reach of minjiang river. J Sichuan Univ (Eng Sci Edit) 36:6–11
Song X, Kong F, Zhan C et al (2012) A hybrid optimization rainfall–runoff simulation based on Xinanjiang model and artificial neural network. J Hydrol Eng 17:1033–1041
Tang Q (2006) Application of digital hydrological model for flood-forecast in Zhexi reservoir. Hunan Electr Power 26(18–20):23
Wang J, Liang Z, Jiang X et al (2016) Bayesian theory based self-adapting real-time correction model for flood forecasting. Water 8:75
Wu X, Liu C, Hao F et al (2004) Storm-runoff simulation of distributed hydrological model in the Yellow River basin. Adv Water Sci 15:511–516
Xu X, Zhang X, Fang H et al (2017) A real-time probabilistic channel flood-forecasting model based on the Bayesian particle filter approach. Environ Model Softw 88:151–167
Yan B, Guo S, Chen L (2014) Estimation of reservoir flood control operation risks with considering inflow forecasting errors. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 28:359–368
Zhang J, Chen L, Singh VP et al (2015) Determination of the distribution of flood forecasting error. Nat Hazards 1:1389–1402
Zhao R, Liu X, Singh VP (1995) The Xinanjiang model. Proc Oxf Symp Hydrol Forecast IAHS Publ 135:371–381
Zheng H, Wang Z, Liu C et al (2004a) GIS/RS based distributed hydrological modeling 1. Model theories and structures. Adv Water Sci 15:501–505
Zheng H, Wang Z, Liu C et al (2004b) GIS/RS based distributed hydrological modeling 2. Model test and application. Adv Water Sci 15:506–510
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Key Project of State Grid Hunan Electric Power Corporation of China (Grant No. 5216A514003Z). Special thanks are given to the anonymous reviewers and editors for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, J., Guo, J., Yang, L. et al. Research of reservoir watershed fine zoning and flood forecasting method. Nat Hazards 89, 1291–1306 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3017-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3017-x