Abstract
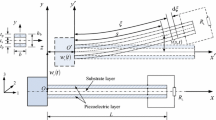
A global nonlinear distributed-parameter model for a piezoelectric energy harvester under parametric excitation is developed. The harvester consists of a unimorph piezoelectric cantilever beam with a tip mass. The derived model accounts for geometric, inertia, piezoelectric, and fluid drag nonlinearities. A reduced-order model is derived by using the Euler–Lagrange principle and Gauss law and implementing a Galerkin discretization. The method of multiple scales is used to obtain analytical expressions for the tip deflection, output voltage, and harvested power near the first principal parametric resonance. The effects of the nonlinear piezoelectric coefficients, the quadratic damping, and the excitation amplitude on the output voltage and harvested electrical power are quantified. The results show that a one-mode approximation in the Galerkin approach is not sufficient to evaluate the performance of the harvester. Furthermore, the nonlinear piezoelectric coefficients have an important influence on the harvester’s behavior in terms of softening or hardening. Depending on the excitation frequency, it is determined that, for small values of the quadratic damping, there is an overhang associated with a subcritical pitchfork bifurcation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gurav, S.P., Kasyap, A., Sheplak, M., Cattafesta, L., Haftka, R.T., Goosen, J.F.L., Van Keulen, F.: Uncertainty-based design optimization of a micro piezoelectric composite energy reclamation device. In: Proc. 10th AIAA/ISSSMO Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization Conference, pp. 3559–3570 (2004)
Muralt, P.: Ferroelectric thin films for micro-sensors and actuators: a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 10, 136–146 (2000)
Zhou, W., Liao, W.H., Li, W.J.: Analysis design of a self-powered piezoelectric microaccelerometer. In: Proc. Smart Structures and Materials Conference, pp. 233–240. SPIE, Bellingham (2005)
Inman, D.J., Grisso, B.L.: Towards autonomous sensing. In: Proc. Smart Structures and Materials Conference, p. 61740T. SPIE, Bellingham (2006)
Roundy, S., Wright, P.K.: A piezoelectric vibration-based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 809–823 (2005)
Capel, I.D., Dorrell, H.M., Spencer, E.P., Davis, M.W.: The amelioration of the suffering associated with spinal cord injury with subperception transcranial electrical stimulation. Spinal Cord 41, 109–117 (2003)
Priya, S., Popa, D., Lewis, F.: Energy efficient mobile wireless sensor networks. In: Proc. ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress Exposition, Chicago, IL (2006)
Williams, C.B., Yates, R.B.: Analysis of a micro-electric generator for microsystems. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 52, 8–11 (1996)
Arnold, D.: Review of microscale magnetic power generation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 3940–3951 (2007)
Mitcheson, P., Miao, P., Start, B., Yeatman, E., Holmes, A., Green, T.: MEMS electrostatic micro-power generator for low frequency operation. Sens. Actuators A, Phys. 115, 523–529 (2004)
Anton, S.R., Sodano, H.A.: A review of power harvesting using piezoelectric materials (2003–2006). Smart Mater. Struct. 16, 1–21 (2007)
Cook-Chennault, K.A., Thambi, N., Sastry, A.M.: Powering MEMS portable devices-a review of non-regenerative and regenerative power supply systems with emphasis on piezoelectric energy harvesting systems. Smart Mater. Struct. 17, 043001 (2008)
Beeby, S.P., Tudor, M.J., White, N.M.: Energy harvesting vibration sources for microsystems applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, 175–195 (2006)
Sodano, H.A., Inman, D.J., Park, G.: A review of power harvesting from vibration using piezoelectric materials. Shock Vib. Dig. 36, 197–205 (2004)
Priya, S.: Advances in energy harvesting using low profile piezoelectric transducers. J. Electroceram. 19, 167–184 (2007)
Sodano, H., Park, G., Inman, D.J.: Estimation of electric charge output for piezoelectric energy harvesting. Strain 40, 49–58 (2004)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: An experimentally validated bimorph cantilever model for piezoelectric energy harvesting from base excitations. Smart Mater. Struct. 18, 025009 (2009)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: On mechanical modeling of cantilevered piezoelectric vibration energy harvesters. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 19, 1311–1325 (2008)
Erturk, A., Inman, D.J.: A distributed parameter electromechanical model for cantilevered piezoelectric energy harvesters. J. Vib. Acoust. 130, 041002 (2008)
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H., Hajj, M.R.: Modeling and analysis of piezoaeroelastic energy harvesters. Nonlinear Dyn. (2011). doi:10.1007/s11071-011-0035-1
Daqaq, M.F., Stabler, C., Qaroush, Y., Seuaciuc-Osorio, T.: Investigation of power harvesting via parametric excitations. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 20, 545–557 (2009)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (1979)
Anderson, T.J., Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandar, B.: Experimental verification of the importance of the nonlinear curvature in the response of a cantilever beam. J. Vib. Acoust. 118, 21–28 (1996)
Arafat, H.N., Nayfeh, A.H., Chin, C.M.: Nonlinear nonplanar dynamics of parametrically excited cantilever beams. Nonlinear Dyn. 15, 31–61 (1997)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Nonlinear Interactions. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (2000)
Nayfeh, A.H., Pai, P.F.: Linear and Nonlinear Structural Mechanics. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (2004)
IEEE Standard on Piezoelectricity (1987)
Guyomar, D., Aurelle, N., Eyraud, L.: Piezoelectric ceramics nonlinear behavior Application to Langevin transducer. J. Phys., III 1, 1197–1208 (1997)
Guyomar, D., Aurelle, N., Richard, C., Gonnard, P., Eyraud, L.: Nonlinearities in Langevin transducers. In: Proc. IEEE, pp. 1051–0117 (1994)
Nayfeh, A.H., Lacarbonara, W.: On the discretization of distributed-parameter systems with quadratic and cubic nonlinearities. Nonlinear Dyn. 13, 203–220 (1997)
Nayfeh, A.H., Lacarbonara, W.: On the discretization of spatially continuous systems with quadratic and cubic nonlinearities. JSME Int. J. 41, 2–23 (1998)
Nayfeh, A.H., Arafat, H.N., Chin, C.M., Lacarbonara, W.: Multimode interactions in suspended cables. J. Vib. Control 8, 337–387 (2002)
Lacarbonara, W., Rega, G., Nayfeh, A.H.: Resonant nonlinear normal modes. Part I: Analytical treatment for one-dimensional structural systems. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 38, 851–872 (2003)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Reduced-order models of weakly nonlinear spatially continuous systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 16, 105–125 (1998)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Perturbation Methods. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (1973)
Nayfeh, A.H.: Introduction to Perturbation Techniques. Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelkefi, A., Nayfeh, A.H. & Hajj, M.R. Global nonlinear distributed-parameter model of parametrically excited piezoelectric energy harvesters. Nonlinear Dyn 67, 1147–1160 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0059-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-011-0059-6