Abstract
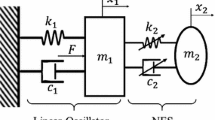
A general, nonlinear, multi-d.o.f. structure, excited by harmonic external force in 1:1 resonance with one of the modes of the system, is considered. The structure is attached to an essentially nonlinear oscillator, with small mass and damping (Nonlinear Energy Sink, NES). The scope of the NES is to passively control the amplitude of vibrations of the main structure. A mixed Multiple Scale/Harmonic Balance Method (MSHBM) is proposed to get the differential equations describing the slow- and fast-flow dynamics of the whole structure. The main advantage of the procedure is that no complexification-averaging is required, so that the analysis is reconducted in the framework of the classical perturbation techniques.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vakakis, A.F., Gendelman, O.V., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M., Kerschen, G., Lee, Y.S.: Nonlinear Targeted Energy Transfer in Mechanical and Structural Systems I. Springer, New York (2008a)
Vakakis, A.F., Gendelman, O.V., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M., Kerschen, G., Lee, Y.S.: Nonlinear Targeted Energy Transfer in Mechanical and Structural Systems II. Springer, New York (2008b)
Maniadis, P., Kopidakis, G., Aubry, S.: Classical and quantum targeted energy transfer between nonlinear oscillators. Physica D 188, 153–177 (2004)
Kerschen, G., Kowtko, J.J., McFarland, D.M., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Theoretical and experimental study of multimodal targeted energy transfer in a system of coupled oscillators. Nonlinear Dyn. 47, 285–309 (2007)
Panagopoulos, P.N., Gendelman, O., Vakakis, A.F.: Robustness of nonlinear targeted energy transfer in coupled oscillators to changes of initial conditions. Nonlinear Dyn. 47, 377–387 (2007)
Aubry, S., Kopidakis, G., Morgante, A.M., Tsironis, G.P.: Analytic conditions for targeted energy transfer between nonlinear oscillators or discrete breathers. Physica B 296, 222–236 (2001)
Tsakirtzis, S., Panagopoulos, P.N., Kerschen, G., Gendelman, O., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A.: Complex dynamics and targeted energy transfer in linear oscillators coupled to multi-degree-of-freedom essentially nonlinear attachments. Nonlinear Dyn. 48, 285–318 (2007)
Guckenheimer, J., Hoffman, K., Weckesser, W.: Bifurcations of relaxation oscillations near folded saddles. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 15, 3411–3421 (2005)
Guckenheimer, J., Wechselberger, M., Young, L.-S.: Chaotic attractors of relaxation oscillators. Nonlinearity 19, 701–720 (2006)
Gendelman, O.V., Starosvetsky, Y., Feldman, M.: Attractors of harmonically forced linear oscillator with attached nonlinear energy sink i: description of response regimes. Nonlinear Dyn. 51, 31–46 (2008)
Starosvetsky, Y., Gendelman, O.V.: Response regimes of linear oscillator coupled to nonlinear energy sink with harmonic forcing and frequency detuning. J. Sound Vib. 315, 746–765 (2008)
Vaurigaud, B., Savadkoohi, A.T., Lamarque, C.-H.: Targeted energy transfer with parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Part I: design theory and numerical results. Nonlinear Dyn. 66(4), 763–780 (2011a)
Savadkoohi, A.T., Vaurigaud, B., Lamarque, C.-H., Pernot, S.: Targeted energy transfer with parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Part II: theory and experiments. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(1), 37–46 (2012)
Lamarque, C.-H., Gendelman, O.V., Savadkoohi, A.T., Etcheverria, E.: Targeted energy transfer in mechanical systems by means of non-smooth nonlinear energy sink. Acta Mech. 221, 175–200 (2011)
Gendelman, O.V., Vakakis, A.F., Bergman, L.A., McFarland, D.M.: Asymptotic analysis of passive nonlinear suppression of aeroelastic instabilities of a rigid wing in subsonic flow. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70(5), 1655–1677 (2010)
Vaurigaud, B., Manevitch, L.I., Lamarque, C.-H.: Passive control of aeroelastic instability in a long span bridge model prone to coupled flutter using targeted energy transfer. J. Sound Vib. 330, 2580–2595 (2011b)
Manevitch, L.: The description of localized normal modes in a chain of nonlinear coupled oscillators using complex variables. Nonlinear Dyn. 25, 95–109 (2001)
Gendelman, O.V.: Targeted energy transfer in systems with non-polynomial nonlinearity. J. Sound Vib. 315, 732–745 (2008)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley, New York (1979)
Jiang, X., McFarland, D.M., Bergman, L.A., Vakakis, A.F.: Steady state passive nonlinear energy pumping in coupled oscillators: theoretical and experimental results. Nonlinear Dyn. 33, 87–102 (2003)
Malatkar, P., Nayfeh, A.H.: Steady-state dynamics of a linear structure weakly coupled to an essentially nonlinear oscillator. Nonlinear Dyn. 47, 167–179 (2007)
Doedel, E.J., Oldeman, B.E.: AUTO-07P: continuation and bifurcation software for ordinary differential equation (2012). URL http://cmvl.cs.concordia.ca/auto/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix: Coefficients of the equations
Appendix: Coefficients of the equations
The mode u is assumed normalized to get unitary modal mass (u T Mu=1). The expression of the coefficients of Eq. (19) are:
In Eq. (20), the column matrices w j (j=1,…,6) are the solutions of the following singular algebraic problems in which, however, compatibility is satisfied:






The solution is made unique by the normalization condition \(\mathbf {w}_{j}^{T}\mathbf {u}=0\).
Moreover, w j (j=7,8) are the solutions of the following non-singular algebraic:


Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luongo, A., Zulli, D. Dynamic analysis of externally excited NES-controlled systems via a mixed Multiple Scale/Harmonic Balance algorithm. Nonlinear Dyn 70, 2049–2061 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0597-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0597-6