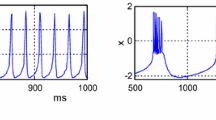
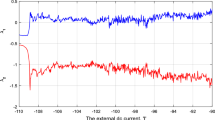
Abstract
This study presents experimental realizations of the HR neuron model with programmable hardware and synchronization applications. The HR neuron model exhibiting burst, spike, and chaotic dynamics has been implemented with both FPAA (Field Programmable Analog Array) and FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) devices. These devices provide flexible design possibilities such as reducing the complexity of design, real-time modification, software control and adjustment within the system. And it is also examined experimentally that how the synchronization of two HR neurons are able to achieve by using these hardware. The experimental results obtained from FPAA and FPGA based realizations agree with the numerical simulations very well.















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Online available: www.anadigm.com.
[Online]. Available: www.altera.com.
References
McCulloch, W.S., Pits, W.H.: A logical calculus of ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 5, 115–133 (1943)
Hodgkin, A., Huxley, A.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117, 500–544 (1952)
FitzHugh, R.: Mathematical models for excitation and propagation in nerve. In: Schawn, H.P. (ed.) Biological Engineering, vol. 1, pp. 1–85. McGraw-Hill, New York (1969)
Nagumo, J., Sato, S.: On a response characteristic of mathematical neuron model. Kybernetik 10, 155–164 (1972)
Wilson, H.R., Cowan, J.D.: Excitatory and inhibitory interactions in localized populations of model neurons. Biophys. J. 12(1), 1–24 (1972)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophysics J. 35, 193–213 (1981)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of neural bursting using three couple first order differential equations. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B, Biol. Sci. 221(1222), 87–102 (1984)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Simple model of spiking neurons. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 14(6) (2003)
Mishra, D., Yadav, A., Ray, S., Kalra, P.K.: Controlling synchronization of modified FitzHugh–Nagumo neurons under external electrical stimulation. NeuroQuantology 4(1), 50–67 (2006)
Checco, P., Righero, M., Biey, M., Kocerev, L.: Information processing in networks of coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons. In: International Symposium on Nonlinear Theory and its Applications (NOLTA 2006), Bologna-Italy, pp. 671–674 (2006)
Checco, P., Biey, M., Righero, M., Kocerev, L.: Synchronization and bifurcations in networks of coupled Hindmarsh-Rose neurons. In: IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2007, pp. 1541–1544 (2007)
Elson, R.C., Selverston, A.I., Huerta, R., Rulkov, N.F., Rabinovich, A.I., Abarbanel, H.D.I.: Synchronous behavior of two coupled biological neurons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81(25), 5692–5695 (1998)
Li, F., Liu, Q., Guo, H., Zhao, Y., Tang, J., Ma, J.: Simulating the electric activity of FitzHugh–Nagumo neuron by using Josephson junction model. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 2169–2179 (2012)
Shi, X.R.: Bursting synchronization of Hind–Rose system based on a single controller. Nonlinear Dyn. 59, 95–99 (2010)
Li, B., Li, Y. Rong, X.: Gait generation and transitions of quadruped robot based on Wilson–Cowan weakly neural networks. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), pp. 19–24 (2010)
Lu, J., Kim, Y.B., Ayers, J.: A low power 65 nm CMOS electronic neuron and synapse design for a biomimetic micro-robot. In: IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), pp. 1–4 (2011)
Lewis, E.R.: An electronic model of the neuron based on the dynamics of potassium and sodium ion fluxes. In: Reiss, R.F. (ed.) Neural Theory and Modeling, pp. 154–189. Stanford University Press, Stanford (1964)
Roy, G.: A simple electronic analog of the squid axon membrane: the neurofet. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 19(1), 60–63 (1972)
Merlat, L., Silvestre, N., Merckle, J.: A Hindmarsh and Rose-based electronic burster. In: Proceedings of Fifth International Conference on Microelectronics for Neural Networks, pp. 39–44 (1996)
Lee, Y.J., Lee, J., Kim, Y.B., Ayers, J., Volkovskii, A., Selverston, A., Abarbanel, H., Rabinovich, M.: Low power real time electronic neuron VLSI design using subthreshold technique. In: Proceedings of the 2004 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS ’04), vol. 4, pp. IV 744–747 (2004)
Poggi, T., Sciutto, A., Storace, M.: Piecewise linear implementation of nonlinear dynamical systems: from theory to practice. Electron. Lett. 45(19), 966–967 (2009)
Charles, G., Gordon, C., Alexander, W.E.: An implementation of a biological neural model using analog-digital integrated circuits. In: IEEE International Behavioral Modeling and Simulation Workshop (BMAS 2008), pp. 78–83 (2008)
Gotthans, T., Petrzela, J., Hrubos, Z.: Analysis of Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model and novel circuitry realization. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems (MIXDES), pp. 576–580 (2011)
Linaro, D., Poggi, T., Storace, M.: Experimental bifurcation diagram of a circuit-implemented neuron model. Phys. Lett. A 374, 4589–4593 (2010)
Steur, E.: On synchronization of electromechanical Hindmarsh–Rose oscillators. Master thesis, Eindhoven University of Technology (2007)
Pinto, R.D., Varona, P., Volkovskii, A.R., Szücs, A., Abarbanel, H.D.I., Rabinovich, M.I.: Synchronous behavior of two coupled electronic neurons. Phys. Rev., E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Topics 62, 2644–2656 (2000) (2000)
Jacquir, S., Binczak, S., Bilbault, J.M., Kazantsev, V., Nekorkin, V.: Synaptic coupling between two electronic neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 44, 29–36 (2006)
Zhao, J., Kim, Y.B.: Circuit implementation of Fitz–Hugh–Nagumo neuron model using field programmable analog arrays. In: 50th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS 2007), pp. 772–775 (2007)
Sekerli, M., Butera, R.J.: An implementation of a simple neuron model in field programmable analog arrays. In: 26th Annual International Conference of the IEEE on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (IEMBS ’04), pp. 4564–4567 (2004)
Rice, K.L., Bhuiyan, M.A., Taha, T.M., Vutsinas, C.N., Smith, M.C.: FPGA implementation of Izhikevich spiking neural networks for character recognition. In: International Conference on Reconfigurable Computing and FPGAs (ReConFig ’09), pp. 451–456 (2009)
Weinstein, R.K., Lee, R.H.: Architectures for high-performance FPGA implementations of neural models. J. Neural Eng. 3, 21–34 (2006)
Bizzarri, F., Linaro, D., Storace, M.: PWL approximation of the Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model in view of its circuit implementation. In: 18th European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD 2007), pp. 878–881 (2007)
Gonzàlez-Mıranda, J.M.: Complex bifurcation structures in the Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos Appl. Sci. Eng. 17(9), 3071–3083 (2007)
Storace, M., Linaro, D., Lange, E.: The Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model: bifurcation analysis and piecewise-linear approximations. Chaos 18(3), 033128 (2008)
Innocenti, G., Genesio, R.: On the dynamics of chaotic spiking-bursting transition in the Hindmarsh–Rose neuron. Chaos 19(2), 023124 (2009)
Danca, M.F., Wang, Q.: Synthesizing attractors of Hindmarsh–Rose neuronal systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 62(1–2), 437–446 (2010)
Kandel, E.R., Schwartz, J.H., Jessell, T.M.: Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York (2000) ISBN 0-8385-7701-6
Bal, T., Nagy, F., Moulins, M.: The pyloric central pattern generator in Crustacea: a set of conditional neuronal oscillators. J. Comp. Physiol. 163(6), 715–727 (1988)
Miller, J.P., Selverston, A.I.: Mechanisms underlying pattern generation in lobster stomatogastric ganglion as determined by selective inactivation of identified neurons. II. Oscillatory properties of pyloric neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 48(6), 1378–1391 (1982)
Wu, Y., Xu, J., Jin, W.: Synchronous behaviors of two coupled neurons. In: Neural Networks (ISNN 2005), Lecture Notes in Computer Science Advances, vol. 3496, pp. 121–130 (2005)
Shi, Y., Wang, J., Deng, B., Liu, Q.: Chaotic synchronization of coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons using adaptive control. In: 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI ’09), pp. 1–5 (2009)
Che, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, J., Cui, S., Han, C., Deng, B., Wei, X.: Synchronization of inhibitory coupled Hindmarsh–Rose neurons via adaptive sliding mode control. In: 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP), vol. 2, pp. 1134–1139 (2011)
Shi, X., Wang, Z.: Adaptive synchronization of time delay Hindmarsh–Rose neuron system via self-feedback. Nonlinear Dyn. 69(4), 2147–2153 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahasert, N., Öztürk, İ. & Kiliç, R. Experimental realizations of the HR neuron model with programmable hardware and synchronization applications. Nonlinear Dyn 70, 2343–2358 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0618-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-012-0618-5