Abstract
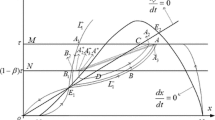
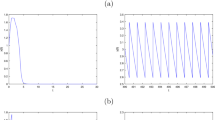
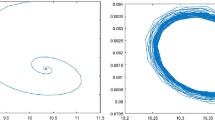
In this article, we investigate a prey– predator model with Allee effect and state-dependent impulsive harvesting. We obtain the sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of order-1 periodic solution of system (1.2) by means of the geometry theory of semicontinuous dynamic system and the method of successor function. We also obtain that system (1.2) exhibits the phenomenon of heteroclinic bifurcation about parameter \(\alpha \). The methods used in this article are novel and prove the existence of order-1 periodic solution and heteroclinic bifurcation.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berec, L., Angulo, E., Courchamp, F.: Multiple Allee effects and population management. Trends Ecol. Evol. 22, 185–191 (2007)
Courchamp, F., Clutton-Brock, T., Grenfell, B.: Inverse density dependence and the Allee effect. Trends Ecol. Evol. 14, 405–410 (1999)
Guo, H.J., Chen, L.S., Song, X.Y.: Mathematical models of restoration and control of a single species with Allee effect. Appl. Math. Model. 34, 3264–3272 (2010)
Allee, W.C.: Animal Aggregations: A Study in General Sociology. University of Chicago Press (1931)
Groom, M.J.: Allee effects limit population viability of an annual plant. Am. Nat. 151, 487–496 (1998)
Stephens, P.A., Sutherland, W.J.: Consequences of the Allee effect for behaviour: ecology and conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 14, 401–404 (1999)
Kent, A., Doncaster, C.P., Sluckin, T.: Consequences for predators of rescue and Allee effects on prey. Ecol. Model. 162, 233–245 (2003)
Van Voorn, G.A.K., Hemerik, L., Boer, M.P., Kooi, B.W.: Heteroclinic orbits indicate overexploitation in predator-prey systems with a strong Allee effect. Math. Bios. 209, 451–469 (2007)
Clark, C.W.: Mathematical Bioeconomics: The Optimal Management of Renewable Resources. Wiley, New York (1990)
Clark, C.W.: Bioeconomic Modelling and Fisheries Management. Wiley, New York (1985)
Mesterton-Gibbons, M.: A technique for finding optimal two species harvesting policies. Ecol. Model. 92, 235–244 (1996)
Chaudhuri, K.S.: A bioeconomic model of harvesting a multispecies fishery. Ecol. Model. 32, 267–279 (1986)
Gu, E.G., Tian, F.: Complex dynamics analysis for a duopoly model of common fishery resource. Nonlinear Dyn. 61, 579–590 (2010)
Rojas-Palma, A., Gonzalez-Olivares, E.: Optimal harvesting in a predator-prey model with Allee effect and sigmoid functional response. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 1864–1874 (2012)
Xiao, D., Jennings, L.: Bifurcations of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system with constant rate harvesting. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 65, 737–753 (2005)
Pei, Y.Z., Li, C.G., Chen, L.S.: Continuous and impulsive harvesting strategies in a stage-structured predator-prey model with time-delay. Math. Comput. Simul. 10, 2994–3008 (2009)
Zhao, Z., Zhang, X.Q., Chen, L.S.: The effect of pulsed harvesting policy on the inshore-offshore fishery model with the impulsive diffusion. Nonlinear Dyn. 57, 135–142 (2009)
Wei, C.J., Chen, L.S.: Periodic solution of prey-predator model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and impulsive state feedback control. J. Appl. Math. Article ID 607105, 17 pages (2012)
Liu, B., Tian, Y., Kang, B.: Dynamics on a Holling II predator-prey model with state-dependent impulsive control. Int. J. Biomath. 5, 1260006 (2012)
Chen, L.S.: Pest control and geometric theory of semi-continuous dynamical system. J. Beihua Univ. 12, 1–9 (2011)
Huang, M.Z., Li, J.X., Song, X.Y., Guo, H.J.: Modeling impulsive injections of insulin: towards artificial pancreas. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 72, 1524–1548 (2012)
Guo, H.J., Chen, L.S.: Periodic solution of a chemostat model with Monod growth rate and impulsive feedback control. J. Theor. Biol. 260, 502–509 (2009)
Li, Z.X., Chen, L.S., Liu, Z.J.: Periodic solution of a chemostat model with variable yield and impulsive state feedback control. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 1255–1266 (2012)
Dai, C.J., Zhao, M., Chen, L.S.: Homoclinic bifurcation in semi-continuous dynamic system. Int. J. Biomath. 5, 1250059 (2012)
Acknowledgments
Supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11301216,11171284), Fujian Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (2012J01012), the Fujian Provincial Education Fundation (JA12198) and the Scientific Research Foundation of Jimei University of China (ZC2011003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, C., Chen, L. Periodic solution and heteroclinic bifurcation in a predator–prey system with Allee effect and impulsive harvesting. Nonlinear Dyn 76, 1109–1117 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1194-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-013-1194-z