Abstract
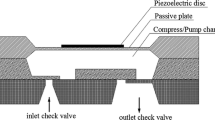
Diaphragm micropumps are the most common type among indirectly driven micropumps. The elastic diaphragm is deflected using a bias voltage and then driven to vibrate around its deflected position by a harmonic AC load to produce a flow rate. This paper investigates the nonlinear resonant behavior of a circular elastic diaphragm interacting with incompressible and inviscid liquids inside a cylindrical chamber containing a central discharge opening. The governing equations of the system are derived by taking into account the nonlinear electrostatic force and fluid pressure exerted upon the diaphragm which is formulated using the linear form of Bernoulli’s equation. In the modeling stage, the kinematic and compatibility conditions are incorporated into the elastic vibration of the diaphragm. The method of multiple scales is used to obtain an approximate analytical solution to the nonlinear resonant curves of the transverse oscillation amplitudes. It is shown that, as the DC voltage increases, the system exhibits softening behavior. The results also show that decreasing the discharge diameter further bends the frequency response cure to left side, which is an indication of increase in the system nonlinearity. The effects of micropump chamber height on the frequency curves were also studied and showed that softening behavior increases with decreasing chamber height. In addition, it was found that the electrical and inertial properties of the operating fluid can change the resonant curves significantly.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamahata, C., Vandevyver, C., Lacharme, F., Izewska, P., Vogel, H., Freitag, R., Gijs, M.A.: Pumping of mammalian cells with a nozzle–diffuser micropump. Lab Chip 5, 1083–1088 (2005)
Wang, S., Huang, X., Yang, C.: Valveless micropump with acoustically featured pumping chamber. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 8, 549–555 (2010)
Ma, H., Su, H., Wu, J.: Study of an innovative one-sided actuating piezoelectric valveless micropump with a secondary chamber. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 171, 297–305 (2011)
Nguyen, N.-T., Huang, X., Chuan, T.K.: MEMS-micropumps: a review. J. Fluids Eng. 124, 384–392 (2002)
Laser, D., Santiago, J.: A review of micropumps. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, R35 (2004)
Woias, P.: Micropumps—past, progress and future prospects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 105, 28–38 (2005)
Tsai, N.-C., Sue, C.-Y.: Review of MEMS-based drug delivery and dosing systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 134, 555–564 (2007)
Iverson, B.D., Garimella, S.V.: Recent advances in microscale pumping technologies: a review and evaluation. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 5, 145–174 (2008)
Nisar, A., Afzulpurkar, N., Mahaisavariya, B., Tuantranont, A.: MEMS-based micropumps in drug delivery and biomedical applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 130, 917–942 (2008)
Amirouche, F., Zhou, Y., Johnson, T.: Current micropump technologies and their biomedical applications. Microsyst. Technol. 15, 647–666 (2009)
Faris, W., Asrar, W., Omerbegovic, A.: Micropump modeling: current status and challenges. Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 6(1), 134–142 (2012)
Teymoori, M.M., Abbaspour-Sani, E.: Design and simulation of a novel electrostatic peristaltic micromachined pump for drug delivery applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 117, 222–229 (2005)
Feng, G.-H., Kim, E.S.: Micropump based on PZT unimorph and one-way parylene valves. J. Micromech. Microeng. 14, 429 (2004)
Dario, P., Croce, N., Carrozza, M., Varallo, G.: A fluid handling system for a chemical microanalyzer. J. Micromech. Microeng. 6, 95 (1996)
Schomburg, W., Vollmer, J., Bustgens, B., Fahrenberg, J., Hein, H., Menz, W.: Microfluidic components in LIGA technique. J. Micromech. Microeng. 4, 186 (1994)
Yang, Y., Zhou, Z., Ye, X., Jiang, X.: Bimetallic thermally actuated micropump. In: Proceedings of the 1996 ASME International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Atlanta, GA, USA, 11/17-22/96, pp. 351–354
Makino, E., Mitsuya, T., Shibata, T.: Fabrication of TiNi shape memory micropump. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 88, 256–262 (2001)
Sim, W.Y., Yoon, H.J., Jeong, O.C., Yang, S.S.: A phase-change type micropump with aluminum flap valves. J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 286 (2003)
Younis, M., Nayfeh, A.: A study of the nonlinear response of a resonant microbeam to an electric actuation. Nonlinear Dyn. 31, 91–117 (2003)
Borwick III, R.L., Stupar, P.A., DeNatale, J.F., Anderson, R., Erlandson, R.: Variable MEMS capacitors implemented into RF filter systems. Microw. Theory Tech. IEEE Trans. 51, 315–319 (2003)
Rochus, V., Rixen, D.J., Golinval, J.-C.: Electrostatic coupling of MEMS structures: transient simulations and dynamic pull-in. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 63, e1619–e1633 (2005)
Krylov, S.: Lyapunov exponents as a criterion for the dynamic pull-in instability of electrostatically actuated microstructures. Int. J. Non Linear Mech. 42, 626–642 (2007)
Nayfeh, A.H., Younis, M.I., Abdel-Rahman, E.M.: Dynamic pull-in phenomenon in MEMS resonators. Nonlinear Dyn. 48, 153–163 (2007)
Xie, W., Lee, H., Lim, S.: Nonlinear dynamic analysis of MEMS switches by nonlinear modal analysis. Nonlinear Dyn. 31, 243–256 (2003)
Zand, M.M., Ahmadian, M., Rashidian, B.: Semi-analytic solutions to nonlinear vibrations of microbeams under suddenly applied voltages. J. Sound Vib. 325, 382–396 (2009)
Faris, W.F., Abdel Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.F.: Mechanical behavior of an electrostatically actuated micropump, AIAA, 1303, New York (2002)
Shabani, R., Hatami, H., Golzar, F.G., Tariverdilo, S., Rezazadeh, G.: Coupled vibration of a cantilever micro-beam submerged in a bounded incompressible fluid domain. Acta Mech. 224, 841–850 (2013)
Paidoussis, M.P.: Fluid–Structure Interactions: Slender Structures and Axial Flow. Academic Press, London (1998)
Bao, M., Yang, H.: Squeeze film air damping in MEMS. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 136, 3–27 (2007)
Nayfeh, A.H., Mook, D.T.: Nonlinear Oscillations. Wiley, New York (1979)
Caruntu, D.I., Martinez, I., Taylor, K.N.: Voltage–amplitude response of alternating current near half natural frequency electrostatically actuated MEMS resonators. Mech. Res. Commun. 52, 25–31 (2013)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhlou, M., Shabani, R. & Rezazadeh, G. Nonlinear analysis of electrostatically actuated diaphragm-type micropumps. Nonlinear Dyn 83, 951–961 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2379-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-015-2379-4