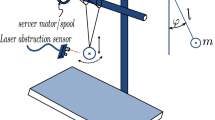
Abstract
In this paper, a novel online motion planning method for double-pendulum overhead cranes is proposed. The proposed trajectory is made up of two parts: anti-sway component and trolley positioning component. The objective of the first part is to suppress and eliminate the swings of hook and payload. Lyapunov techniques, LaSalle’s invariance theorem, and Barbalat’s lemma are used to demonstrate that the trolley can be driven to arrive at the desired position, while the unexpected hook swing and payload swing are damped out simultaneously with the proposed trajectory. Numerical simulation results indicate that the proposed control trajectory achieves superior performance and admits strong robustness against parameter variations and external disturbances.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In this paper, we refer to the term ‘offline’ as calculating the trajectory commands in advance of implementation. By contrast, the term ‘online’ implies that the trajectory commands are generated real time to the system. For example, assume that the control period is 5 ms, and then the trajectory commands for the next control action are calculated within the current 5 ms.
References
Blajer, W., Kolodziejczyk, K.: Motion planning and control of gantry cranes in cluttered work environment. IET Control Theory Appl. 1(5), 1370–1379 (2007)
Wu, Z., Xia, X., Zhu, B.: Model predictive control for improving operational efficiency of overhead cranes. Nonlinear Dyn. 79, 2639–2657 (2015)
Ngo, Q.H., Hong, K.S.: Sliding-mode anti-sway control if an offshore container crane. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 17(2), 201–209 (2012)
Abdel-Rahman, E.M., Nayfeh, A.H., Masoud, Z.N.: Dynamics and control of cranes: a review. J. Vib. Control 9(7), 863–908 (2003)
Joshua, V., Dooroo, K., William, S.: Control of tower cranes with double-pendulum payload dynamics. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 18(6), 1345–1357 (2010)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, B.: A novel kinematic coupling-based trajectory planning method for overhead cranes. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 17(1), 166–173 (2012)
Fang, Y., Wang, P., Sun, N., Zhang, Y.: Dynamics analysis and nonlinear control of an offshore boom crane. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 59(1), 414–427 (2012)
Lu, X., Ma, W.X., Yu, J., Lin, F.H., Khalique, C.M.: Envelope bright- and dark-soliton solutions for the Gerdjikov–lvanov model. Nonlinear Dyn. 82(3), 1211–1220 (2015)
Lu, X.: Madelung fluid description on a generalized mixed nonlinear Schrodinger equation. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(1–2), 239–247 (2015)
Vaughan, J., Yoo, J., Knight, N., Singhose, W.: Multi-input shaping control for multi-hoist cranes. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference, pp. 3449–3454. Washington, DC (2013)
Lee, H.H., Liang, Y., Segura, D.: A sliding-mode antiswing trajectory control for overhead cranes with high-speed load hoisting. ASME J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 128(4), 842–845 (2006)
Gao, D., Guo, W., Yi, J.: Dynamics and GA-based stable control for a class of underactuated mechanical systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 6(1), 35–43 (2008)
Lee, L.H., Huang, P.H., Shih, Y.C., Chiang, T.C., Chang, C.Y.: Parallel neural network combined with sliding mode control in overhead crane control system. J. Vib. Control 20(5), 749–760 (2014)
Uchiyama, N.: Robust control of rotary crane by partial-state feedback with integrator. Mechatronics 19(8), 1294–1302 (2009)
Uchiyama, N., Ouyang, H., Sano, S.: Simple rotary crane dynamics modeling and open-loop control for residual load sway suppression by only horizontal boom motion. Mechatronics 23(8), 1223–1236 (2013)
Garrido, S., Abderrahim, M., Giménez, A., Diez, R., Balaguer, C.: Anti-swinging input shaping control of an automatic construction crane. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 5(3), 549–557 (2008)
Blackburn, D., Singhose, W., Kitchen, J., Patrangenaru, V., Lawrence, J., Kamoi, T., Taura, A.: Command shaping for nonlinear crane dynamics. J. Vib. Control 16(4), 477–501 (2010)
Sorensen, K., Singhose, W., Dickerson, S.: A controller enabling precise positioning and sway reduction in bridge and gantry cranes. Control Eng. Pract. 15(7), 825–837 (2007)
Wu, Z., Xia, X.: Optimal motion planning for overhead cranes. IET Control Theory Appl. in press, doi:10.1049/iet-cta.2014.0069
Zhang, X., Fang, Y., Sun, N.: Minimum-time trajectory planning for underactuated overhead crane systems with state and control constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 61(12), 6915–6925 (2014)
Piazzi, A., Visioli, A.: Optimal dynamic-inversion-based control of an overhead crane. IEE Control Theory Appl. 149(5), 405–411 (2002)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Wu, X.: An enhanced coupling nonlinear control method for bridge cranes. IET Control Theory Appl. 8(13), 1215–1223 (2014)
Sun, N., Fang, Y.: New energy analytical results for the regulation of underactuated overhead cranes: an end-effector motion-based approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 29(12), 4723–4734 (2012)
Sun, N., Fang, Y.: A partially saturated nonlinear controller for overhead cranes with experimental implementation. In: Proceedings of the Karlsruhe, Germany, IEEE International Conference on Robotics Automation, pp. 4473–4478 (2013)
Fang, Y., Dixon, W.E., Dawson, D.M., Zergeroglu, E.: Nonlinear coupling control laws for an underactuated overhead crane system. IEEE Trans. Mechatron. 8(3), 418–423 (2003)
Le, T.A., Kim, G.H., Kim, M.Y., Lee, S.G.: Partial feedback linearization control of overhead cranes with varying cable lengths. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 13(4), 501–507 (2012)
Zhang, M., Ma, X., Rong, X., Tian, X., Li, Y.: Adaptive tracking control for double-pendulum overhead cranes subject to tracking error limitation, parameteric uncertainties and external disturbances. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. (2016). doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2016.02.013
Burg, T., Dawson, D., Rahn, C., Rbodes,W.: Nonlinear control of an overhead crane via the saturating control approach of Teel. In: Proceedings of the Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, IEEE International Conference on Robotics Automation, pp. 3155–3160 (1996)
Ma, B., Fang, Y., Zhang, Y.: Switching-based emergency braking control for an overhead crane system. IET Control Theory Appl. 4(9), 1739–1747 (2010)
Hu, G., Makkar, C., Dixon, W.E.: Energy-based nonlinear control of underactuated Euler–Lagrange systems subject to impacts. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52(9), 1742–1748 (2007)
Chwa, D.: Nonlinear tracking control of 3-D overhead crane s against the initial swing angle and the variation of payload weight. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 17(4), 876–883 (2009)
Fang, Y., Ma, B., Wang, P., Zhang, X.: A motion planning-based adaptive control method for an underactuated crane system. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 20(1), 241–248 (2012)
Hua, Y.J., Shine, Y.K.: Adaptive coupling control for overhead crane systems. Mechatronics 17(2–3), 143–152 (2007)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Zhang, X., Yuan, Y.: Phase plane analysis based motion planning for underactuated overhead cranes. In: Proceedings of the Shanghai, China, IEEE International Conference on Robotics Automation, pp. 3283–3488 (2011)
Sun, N., Fang, Y., Zhang, X., Yuan, Y.: Transportation task-oriented trajectory planning for underactuated overhead cranes using geometric analysis. IET Control Theory Appl. 6(10), 1410–1423 (2012)
Sun, N., Fang, Y.: An efficient online trajectory generating method for underactuated crane systems. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 24, 1653–1663 (2014)
Kim, D.J., Wang, Z., Behal, A.: Motion segmentation and control design for UCF-MANU-An intelligent assistive robotic manipulator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 17(5), 936–948 (2012)
You, C., Han, J.: Trajectory planning of manipulator for a hitting task with autonomous incremental learning. In: Proceedings of the Sanya, China, IEEE International Conference on Robotics Biomimetics, pp. 1446–1450 (2007)
Huang, J., Liang, Z., Zang, Q.: Dynamics and swing control of double-pendulum bridge cranes with distributed-mass beams. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 54–55, 357–366 (2015)
Masoud, Z., Nayfeh, A.: Sway reduction on container cranes using delayed feedback controller. Nonlinear Dyn. 34, 347–358 (2003)
Al-Sweiti, Y., Söffker, D.: Modeling and control of an elastic ship-mounted crane using variable gain model-based controller. J. Vib. Control 13(5), 657–685 (2007)
Guo, W., Liu, D., Yi, J., Zhao, D.: Passivity-based-control for double-pendulum-type overhead cranes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference Analog Digital Techniques in Electrical Engineering, Chiang Mai, Thailand, pp. D546–D549 (2004)
Tuan, L.A., Lee, S.G.: Sliding mode controls of double-pendulum crane systems. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 27(6), 1863–1873 (2013)
Liu, D., Guo, W., Yi, J.: GA-based composite sliding mode fuzzy control for double-pendulum- type overhead crane. In: Proceedings of the Changsha, China, International Conference on Fuzzy System Knowledge Discovery, pp. 792–801 (2005)
Adeli, M., Zarabadipour, H., Aliyari Shoorehdeli, M.: Anti-swing control of a double- pendulum-type overhead crane using parallel distributed fuzzy LQR controller. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Instrumentation and Automation, pp. 401–406 (2011)
Khalil, H.K.: Nonlinear Systems, 3rd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2002)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Ma, X., Chai, H. et al. A novel online motion planning method for double-pendulum overhead cranes. Nonlinear Dyn 85, 1079–1090 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2745-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2745-x