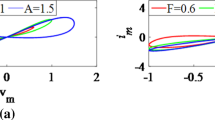
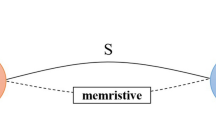
Abstract
The study of dynamics on artificial neurons and neuronal networks is of great significance to understand brain functions and develop neuromorphic systems. Recently, memristive neuron and neural network models offer great potential in the investigation of neurodynamics. Many chaotic dynamics including chaos, transient chaos, hyperchaos, coexisting attractors, multistability, and extreme multistability have been researched based on the memristive neurons and neural networks. In this review, we firstly introduce the basic definition of chaotic dynamics and review several traditional artificial neuron and neural network models. Then we categorize memristive neuron and neural network models with different biological function mechanisms into five types: memristive autapse neuron, memristive synapse-coupled bi-neuron network, memristive synaptic weight neural network, neuron under electromagnetic radiation, and neural network under electromagnetic radiation. The modeling mechanisms of each type are explained and described in detail. Furthermore, the pioneer works and some recent important papers related to those types are introduced. Finally, some open problems in this field are presented to further explore future work.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
References
Fell, J., Axmacher, N.: The role of phase synchronization in memory processes. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 12(2), 105–118 (2011)
Ma, J., Tang, J.: A review for dynamics in neuron and neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(3), 1569–1578 (2017)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 117(4), 500–544 (1952)
Fitzhugh, R.: Impulses and physiological states in theoretical models of nerve membrane. Biophys. J. 1(6), 445–466 (1961)
Nagumo, J., Arimoto, S., Yoshizawa, S.: An active pulse transmission line simulating nerve axon. Proc. IRE 50(10), 2061–2070 (1962)
Morris, C., Lecar, H.: Voltage oscillations in the barnacle giant muscle fiber. Biophys. J. 35(1), 193–213 (1981)
Hindmarsh, J.L., Rose, R.M.: A model of the nerve impulse using two first-order differential equations. Nature 296(5853), 162–164 (1982)
Chay, T.R.: Chaos in a three-variable model of an excitable cell. Physica D 16(2), 233–242 (1985)
Hopfield, J.J.: Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of 2-state neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81(10), 3088–3092 (1984)
Chua, L.O., Yang, L.: Cellular neural networks: theory. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 35(10), 1257–1272 (1988)
Maass, W.: Networks of spiking neurons: the third generation of neural network models. Neural Netw. 10, 659–1671 (1997)
Izhikevich, E.M.: Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 10(6), 1171–1266 (2000)
González, J.M.: Complex bifurcation structures in the Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 17(9), 3071–3083 (2007)
Yang, Z., Lu, Q.: Different types of bursting in Chay neuronal model. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 51(6), 687–698 (2008)
Hashemi, M., Valizadeh, A., Azizi, Y.: Effect of duration of synaptic activity on spike rate of a Hodgkin-Huxley neuron with delayed feedback. Phys. Rev. E 85(2), 21917 (2012)
Kang, Q., Huang, B., Zhou, M.: Dynamic behavior of artificial Hodgkin–Huxley neuron model subject to additive noise. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 46(9), 2083–2093 (2016)
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W.: Bipolar pulse-induced coexisting firing patterns in two-dimensional Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 29(1), 1950006 (2019)
Yan, B., Panahi, S., He, S., et al.: Further dynamical analysis of modified Fitzhugh–Nagumo model under the electric field. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(1), 1–9 (2020)
Strukov, D.B., Snider, G.S., Stewart, D.R., et al.: The missing memristor found. Nature 453(7191), 80–83 (2008)
Jo, S.H., Chang, T., Ebong, I., et al.: Nanoscale memristor device as synapse in neuromorphic systems. Nano Lett. 10(4), 1297–1301 (2010)
Lv, M., Wang, C., Ren, G., et al.: Model of electrical activity in a neuron under magnetic flow effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 85(3), 1479–1490 (2016)
Pershin, Y.V., Ventra, M.D.: Experimental demonstration of associative memory with memristive neural networks. Neural Netw. 23(7), 881–886 (2010)
Li, Q., Tang, S., Zeng, H., et al.: On hyperchaos in a small memristive neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 78, 1087–1099 (2014)
Lv, M., Ma, J.: Multiple modes of electrical activities in a new neuron model under electromagnetic radiation. Neurocomputing 205, 375–381 (2016)
Xu, Y., Jia, Y., Ma, J., et al.: Synchronization between neurons coupled by memristor. Chaos Soliton Fract. 104, 435–442 (2017)
Bao, B., Hu, A., Bao, H., et al.: Three-dimensional memristive Hindmarsh-Rose neuron model with hidden coexisting asymmetric behaviors. Complexity 3872573 (2018)
Hu, X., Liu, C., Liu, L., et al.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network under electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(3), 1541–1554 (2018)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Sun, Y., et al.: Firing multistability in a locally active memristive neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(4), 3667–3683 (2020)
Wu, F., Gu, H., Li, Y., et al.: Inhibitory electromagnetic induction current induces enhancement instead of reduction of neural bursting activities. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 79, 104924 (2019)
Wu, F., Gu, H.: Bifurcations of negative responses to positive feedback current mediated by memristor in a neuron model with bursting patterns. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 30(4), 2030009 (2020)
Zhang, J., Liao, X.: Synchronization and chaos in coupled memristor-based FitzHugh–Nagumo circuits with memristor synapse. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 75, 82–90 (2017)
Xu, F., Zhang, J., Fang, T., et al.: Synchronous dynamics in neural system coupled with memristive synapse. Nonlinear Dyn. 92(3), 1395–1402 (2018)
Lv, M., Ma, J., Yao, Y., et al.: Synchronization and wave propagation in neuronal network under field coupling. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62(3), 448–457 (2019)
Yamakou, M.E.: Chaotic synchronization of memristive neurons: Lyapunov function versus Hamilton function. Nonlinear Dyn. 101(1), 487–500 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Tan, Y.: Hidden extreme multistability with hyperchaos and transient chaos in a Hopfield neural network affected by electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2369–2386 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C.: Influences of electromagnetic radiation distribution on chaotic dynamics of a neural network. Appl. Math. Comput. 369, 124840 (2020)
Pham, V.T., Jafari, S., Vaidyanathan, S., et al.: A novel memristive neural network with hidden attractors and its circuitry implementation. Sci. China Technol. Sc. 59(3), 358–363 (2016)
Njitacke, Z.T., Doubla, I.S., Mabekou, S., et al.: Hidden electrical activity of two neurons connected with an asymmetric electric coupling subject to electromagnetic induction: coexistence of patterns and its analog implementation. Chaos Soliton Fract. 137, 109785 (2020)
Yu, Y., Shi, M., Kang, H., et al.: Hidden dynamics in a fractional-order memristive Hindmarsh–Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(1), 891–906 (2020)
Njitacke, Z.T., Matze, C.L., Tsotsop, M.F., et al.: Remerging feigenbaum trees, coexisting behaviors and bursting oscillations in a novel 3D generalized Hopfield neural network. Neural Process. Lett. 52(1), 267–289 (2020)
Bao, B., Qian, H., Xu, Q., et al.: Coexisting behaviors of asymmetric attractors in hyperbolic-type memristor based Hopfield neural network. Front. Comput. Neurosc. 11, 81 (2017)
Chen, C., Bao, H., Chen, M., et al.: Non-ideal memristor synapse-coupled bi-neuron Hopfield neural network: numerical simulations and breadboard experiments. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 111, 152894 (2019)
Bao, H., Liu, W., Hu, A.: Coexisting multiple firing patterns in two adjacent neurons coupled by memristive electromagnetic induction. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(1), 43–56 (2019)
Njitacke, Z.T., Doubla, I.S., Kengne, J., et al.: Coexistence of firing patterns and its control in two neurons coupled through an asymmetric electrical synapse. Chaos 30(2), 023101 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yao, W., et al.: Chaotic dynamics in a neural network with different types of external stimuli. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 90, 105390 (2020)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: Initial offset boosting coexisting attractors in memristive multi-double-scroll Hopfield neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(4), 2821–2841 (2020)
Li, Z., Zhou, H., Wang, M., et al.: Coexisting firing patterns and phase synchronization in locally active memristor coupled neurons with HR and FN models. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(2), 1455–1473 (2021)
Chen, C., Chen, J., Bao, H., et al.: Coexisting multi-stable patterns in memristor synapse-coupled Hopfield neural network with two neurons. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3385–3399 (2019)
Njitacke, Z.T., Kengne, J.: Complex dynamics of a 4D Hopfield neural networks (HNNs) with a nonlinear synaptic weight: coexistence of multiple attractors and remerging Feigenbaum trees. AEU-Int. J. Electron. C. 93, 242–252 (2018)
Xu, B., Lin, H., Wang, G.: Hidden multistability in a memristor-based cellular neural network. Adv. Math. Phys. 2020, 9708649 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Hong, Q., et al.: A multi-stable memristor and its application in a neural network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 67(12), 3472–3476 (2020)
Bao, H., Liu, W., Chen, M.: Hidden extreme multistability and dimensionality reduction analysis for an improved non-autonomous memristive FitzHugh–Nagumo circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(3), 1879–1894 (2019)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Fouda, H.P., et al.: Modulated wave formation in myocardial cells under electromagnetic radiation. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 32(14), 1850165 (2018)
Aram, Z., Jafari, S., Ma, J., et al.: Using chaotic artificial neural networks to model memory in the brain. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 44, 449–459 (2017)
Xiu, C., Zhou, R., Liu, Y.: New chaotic memristive cellular neural network and its application in secure communication system. Chaos Soliton Fract 141, 110316 (2020)
Wang, W., Yu, X., Luo, X., et al.: Finite-time synchronization of chaotic memristive multidirectional associative memory neural networks and applications in image encryption. IEEE Access 6, 35764–35779 (2018)
Guo, T., Wang, L., Zhou, M., et al.: A multi-layer memristive recurrent neural network for solving static and dynamic image associative memory. Neurocomputing 334, 35–43 (2019)
Ma, J., Yang, Z., Yang, L., et al.: A physical view of computational neurodynamics. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 20(9), 639–659 (2019)
Zhang, X., Wang, C., Yao, W., et al.: Chaotic system with bondorbital attractors. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(4), 2159–2174 (2019)
Chen, X., Qian, S., Yu, F., et al.: Pseudorandom number generator based on three kinds of four-wing memristive hyperchaotic system and its application in image encryption. Complexity 2020, 8274685 (2020)
Sarbadhikari, S.N., Chakrabarty, K.: Chaos in the brain: a short review alluding to epilepsy, depression, exercise and lateralization. Med. Eng. Phys. 23(7), 447–457 (2001)
Yousefpour, A., Jahanshahi, H., Munoz, P., et al.: A fractional-order hyper-chaotic economic system with transient chaos. Chaos Soliton Fract. 130, 109400 (2020)
Yu, F., Qian, S., Chen, X., et al.: Chaos-based engineering applications with a 6D memristive multistable hyperchaotic system and a 2D SF-SIMM hyperchaotic map. Complexity 2021, 6683284 (2021)
Jafari, S., Sprott, J.C., Nazarimehr, F.: Recent new examples of hidden attractors. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 224(8), 1469–1476 (2015)
Wang, Z., Wei, Z., Sun, K., et al.: Chaotic flows with special equilibria. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 229(6), 905–919 (2020)
Deng, Q., Wang, C.: Multi-scroll hidden attractors with two stable equilibrium points. Chaos 29(9), 93112 (2019)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Yu, F., et al.: An extremely simple multi-wing chaotic system: dynamics analysis, encryption application and hardware implementation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2020.3047012
Bayani, A., Rajagopal, K., Khalaf, A.J.M., et al.: Dynamical analysis of a new multistable chaotic system with hidden attractor: antimonotonicity, coexisting multiple attractors, and offset boosting. Phys. Lett. A 383(13), 1450–1456 (2019)
Dong, Y., Wang, G., Iu, H.H.C., et al.: Coexisting hidden and self-excited attractors in a locally active memristor-based circuit. Chaos 30(10), 103123 (2020)
Li, C., Sprott, J.C., Hu, W., et al.: Infinite multistability in a self-reproducing chaotic system. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 27(10), 1750160 (2017)
Wang, N., Zhang, G., Kuznetsov, N., et al.: Hidden attractors and multistability in a modified Chua’s circuit. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 92, 105494 (2021)
Mezatio, B.A., Motchongom, M.T., Tekam, B.R.W., et al.: A novel memristive 6D hyperchaotic autonomous system with hidden extreme multistability. Chaos Soliton Fract. 120, 100–115 (2019)
Lai, Q., Kuate, P.D.K., Liu, F., et al.: An extremely simple chaotic system with infinitely many coexisting attractors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 67(6), 1129–1133 (2020)
Chang, H., Li, Y., Chen, G., et al.: Extreme multistability and complex dynamics of a memristor-based chaotic system. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 30(08), 2030019 (2020)
Baysal, V., Sarac, Z., Yilmaz, E.: Chaotic resonance in Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 97(2), 1275–1285 (2019)
Davison, E.N., Aminzare, Z., Dey, B., et al.: Mixed mode oscillations and phase locking in coupled FitzHugh–Nagumo model neurons. Chaos 29(3), 33105 (2019)
Xing, M., Song, X., Yang, Z., et al.: Bifurcations and excitability in the temperature-sensitive Morris–Lecar neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(3), 2687–2698 (2020)
Yang, Y., Liao, X.: Filippov Hindmarsh–Rose neuronal model with threshold policy control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 30(1), 306–311 (2019)
Etémé, A.S., Tabi, C.B., Mohamadou, A., et al.: Long-range memory effects in a magnetized Hindmarsh–Rose neural network. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 84, 105208 (2020)
Zhu, F., Wang, R., Aihara, K., et al.: Energy-efficient firing patterns with sparse bursts in the Chay neuron model. Nonlinear Dyn. 100(3), 2657–2672 (2020)
Lin, H., Wang, C., Chen, C., et al.: Neural bursting and synchronization emulated by neural networks and circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I. Reg. Pap. 68(8), 3397–3410 (2021)
Wang, L., Liu, W., Shi, H., et al.: Cellular neural networks with transient chaos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 54(5), 440–444 (2007)
Chua, L.: Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 18(5), 507–519 (1971)
Adhikari, S.P., Sah, M.P., Kim, H., et al.: Three fingerprints of memristor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 60(11), 3008–3021 (2013)
Chua, L.O.: Everything you wish to know about memristors but are afraid to ask. Radioengineering 24(2), 89–157 (2015)
Zhu, M., Wang, C., Deng, Q., et al.: Locally active memristor with three coexisting pinched hysteresis loops and its emulator circuit. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 30(13), 2050184 (2020)
Tan, Y., Wang, C.: A simple locally active memristor and its application in HR neurons. Chaos 30(5), 53118 (2020)
Xie, W., Wang, C., Lin, H.: A fractional-order multistable locally active memristor and its chaotic system with transient transition, state jump. Nonlinear Dyn. 104(4), 4523–4541 (2021)
Sah, M.P., Kim, H., Chua, L.O.: Brains are made of memristors. IEEE Circ. Syst. Mag. 14(1), 12–36 (2014)
Cai, W., Ellinger, F., Tetzlaff, R.: Neuronal synapse as a memristor: modeling pair-and triplet-based STDP rule. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 9(1), 87–95 (2014)
Li, Y., Zhong, Y., Xu, L., et al.: Ultrafast synaptic events in a chalcogenide memristor. Sci. Rep. 3(1), 1–7 (2013)
Liu, L., Xiong, W., Liu, Y., et al.: Designing high-performance storage in HfO2/BiFeO3 memristor for artificial synapse applications. Adv. Electron. Mater. 6(2), 1901012 (2020)
Wang, C., Guo, S., Xu, Y., et al.: Formation of autapse connected to neuron andits biological function. Complexity 5436737 (2017)
Guo, S., Tang, J., Ma, J., et al.: Autaptic modulation of electrical activity in a network of neuron-coupled astrocyte. Complexity 4631602 (2017)
Kim, S., Du, C., Sheridan, P., et al.: Experimental demonstration of a second-order memristor and its ability to biorealistically implement synaptic plasticity. Nano Lett. 15(3), 2203–2211 (2015)
Zhang, G., Guo, D., Wu, F., et al.: Memristive autapse involving magnetic coupling and excitatory autapse enhance firing. Neurocomputing 379, 296–304 (2020)
Bao, H., Hu, A., Liu, W., et al.: Hidden bursting firings and bifurcation mechanisms in memristive neuron model with threshold electromagnetic induction. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 31(2), 502–511 (2020)
Zhang, G., Wang, C., Alzahrani, F., et al.: Investigation of dynamical behaviors of neurons driven by memristive synapse. Chaos Solitons Fractals 108, 15–24 (2018)
Liu, Y., Nazarimehr, F., Khalaf, A.J.M., et al.: Detecting bifurcation points in a memristive neuron model. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 1943–1950 (2019)
Zhang, J., Liao, X.: Effects of initial conditions on the synchronization of the coupled memristor neural circuits. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(2), 1269–1282 (2019)
Xu, Q., Tan, X., Zhu, D., et al.: Synchronous behavior for memristive synapse-connected Chay twin-neuron network and hardware implementation. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 8218740 (2020)
Bao, B., Yang, Q., Zhu, D., et al.: Initial-induced coexisting and synchronous firing activities in memristor synapse-coupled Morris–Lecar bi-neuron network. Nonlinear Dyn. 99(3), 2339–2354 (2020)
Ren, G., Xu, Y., Wang, C.: Synchronization behavior of coupled neuron circuits composed of memristors. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(2), 893–901 (2017)
Bao, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, W., et al.: Memristor synapse-coupled memristive neuron network: synchronization transition and occurrence of chimera. Nonlinear Dyn. 100, 937–950 (2020)
Parastesh, F., Jafari, S., Azarnoush, H., et al.: Chimera in a network of memristor-based Hopfield neural network. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 228(10), 2023–2033 (2019)
Wang, Z., Parastesh, F., Rajagopal, K., et al.: Delay-induced synchronization in two coupled chaotic memristive Hopfield neural networks. Chaos Soliton Fract. 134, 109702 (2020)
Leng, Y., Yu, D., Hu, Y., et al.: Dynamic behaviors of hyperbolic-type memristor-based Hopfield neural network considering synaptic crosstalk. Chaos 30(3), 33108 (2020)
Rajagopal, K., Hussain, I., Rostami, Z., et al.: Magnetic induction can control the effect of external electrical stimuli on the spiral wave. Appl. Math. Comput. 390, 125608 (2021)
Wu, F., Wang, C., Jin, W., et al.: Dynamical responses in a new neuron model subjected to electromagnetic induction and phase noise. Physica A 469, 81–88 (2017)
Ge, M., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., et al.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 515–523 (2018)
Liu, Y., Ma, J., Xu, Y., et al.: Electrical mode transition of hybrid neuronal model induced by external stimulus and electromagnetic induction. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 29(11), 1950156 (2019)
Wu, J., Ma, S.: Coherence resonance of the spiking regularity in a neuron under electromagnetic radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 96(3), 1895–1908 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Xu, Y., Yao, Z., et al.: A feasible neuron for estimating the magnetic field effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(3), 1849–1867 (2020)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: A novel no-equilibrium HR neuron model with hidden homogeneous extreme multistability. Chaos Solitons Fractals 145, 110761 (2021)
Bao, H., Liu, W., Ma, J., et al.: Memristor initial-offset boosting in memristive HR neuron model with hidden firing patterns. Int. J. Bifurcat. Chaos 30(10), 2030029 (2020)
Parastesh, F., Rajagopal, K., Karthikeyan, A., et al.: Complex dynamics of a neuron model with discontinuous magnetic induction and exposed to external radiation. Cogn. Neurodyn. 12(6), 607–614 (2018)
Zhang, S., Zheng, J., Wang, X., et al.: Multi-scroll hidden attractor in memristive HR neuron model under electromagnetic radiation and its applications. Chaos 31(1), 011101 (2021)
Takembo, C.N., Mvogo, A., Fouda, H.P.E., et al.: Effect of electromagnetic radiation on the dynamics of spatiotemporal patterns in memristor-based neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(2), 1067–1078 (2019)
Qu, L., Du, L., Hu, H., et al.: Pattern control of external electromagnetic stimulation to neuronal networks. Nonlinear Dyn. 102(4), 2739–2757 (2020)
Hu, X., Liu, C.: Bursting and synchronization of coupled neurons under electromagnetic radiation. Complexity 2019, 4835379 (2019)
Mostaghimi, S., Nazarimehr, F., Jafari, S., et al.: Chemical and electrical synapse-modulated dynamical properties of coupled neurons under magnetic flow. Appl. Math. Comput. 348, 42–56 (2019)
Liddelow, S.A., Guttenplan, K.A., Clarke, L.E., et al.: Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 541(7638), 481–487 (2017)
Merlini, M., Rafalski, V.A., Ma, K., et al.: Microglial Gi-dependent dynamics regulate brain network hyperexcitability. Nat. Neurosci. 24(1), 19–21 (2021)
Zeeuw, C.I.D., Lisberger, S.G., Raymond, J.L.: Diversity and dynamism in the cerebellum. Nat. Neurosci. 24(2), 160–167 (2021)
Wu, F., Ma, J., Zhang, G.: Energy estimation and coupling synchronization between biophysical neurons. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 63(4), 1–12 (2020)
Yao, Z., Wang, C., Zhou, P., et al.: Regulating synchronous patterns in neurons and networks via field coupling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 95, 105583 (2021)
Zhu, Z., Ren, G., Zhang, X., et al.: Effects of multiplicative-noise and coupling on synchronization in thermosensitive neural circuits. Chaos Soliton Fract 151, 111203 (2021)
Zhou, P., Yao, Z., Ma, J., et al.: A piezoelectric sensing neuron and resonance synchronization between auditory neurons under stimulus. Chaos Soliton Fract 145, 110751 (2021)
Lv, M., Ma, J., Yao, Y.G., et al.: Synchronization and wave propagation in neuronal network under field coupling. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 62(3), 448–457 (2019)
Bao, B., Zhu, Y., Ma, J., et al.: Memristive neuron model with an adapting synapse and its hardware experiments. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 64(5), 1107–1117 (2021)
Yao, W., Wang, C., Sun, Y., et al.: Exponential multistability of memristive Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with stochastic parameter perturbations. Appl. Math. Comput. 386, 125483 (2020)
Yao, W., Wang, C., Sun, Y., et al.: Synchronization of inertial memristive neural networks with time-varying delays via static or dynamic event-triggered control. Neurocomputing 404, 367–380 (2020)
Zhou, C., Wang, C., Sun, Y., et al.: Weighted sum synchronization of memristive coupled neural networks. Neurocomputing 403, 211–223 (2020)
Yao, W., Wang, C., Cao, J., et al.: Hybrid multisynchronization of coupled multistable memristive neural networks with time delays. Neurocomputing 363, 281–294 (2019)
Lakshmi, C., Thenmozhi, K., Rayappan, J.B., et al.: Hopfield attractor-trusted neural network: an attack-resistant image encryption. Neural Comput. Appl. 32(15), 11477–11489 (2020)
Njitacke, Z.T., Isaac, S.D., Nestor, T., et al.: Window of multistability and its control in a simple 3D Hopfield neural network: application to biomedical image encryption. Neural Comput. Appl. 33(12), 6733–6752 (2021)
Liu, L., Zhang, L., Jiang, D., et al.: A simultaneous scrambling and diffusion color image encryption algorithm based on Hopfield chaotic neural network. IEEE Access 7, 185796–185810 (2019)
Pan, C., Hong, Q., Wang, X.: A novel memristive chaotic neuron circuit and its application in chaotic neural networks for associative memory. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aid D 40(3), 521–532 (2021)
Hong, Q., Yan, R., Wang, C., et al.: Memristive circuit implementation of biological nonassociative learning mechanism and its applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 14(5), 1036–1050 (2020)
Carro-Pérez, I., Sánchez-López, C., González-Hernández, H.G.: Experimental verification of a memristive neural network. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(4), 1823–1840 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by The Major Research Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (91964108), The National Natural Science Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020JJ4218) Foundation of China (61971185), The Open Fund Project of Key Laboratory in Hunan Universities (18K010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Wang, C., Deng, Q. et al. Review on chaotic dynamics of memristive neuron and neural network. Nonlinear Dyn 106, 959–973 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06853-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06853-x