Abstract
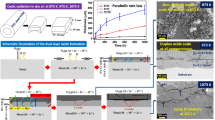
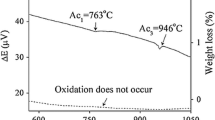
The effect of Si content (in the range of 0.01–1.91 wt%) on scale formation of electrical steels in dry air at temperatures ranging from 850 to 1200 °C was investigated. The effect of applied tensile strain on oxidation behavior was also explored. A thermo-mechanical simulator (Gleeble machine) was employed to conduct the oxidation tests at different load conditions. The experimental results showed that at 1000 °C the oxidation rate decreased with increasing Si content in the steel. The formation of an inner scale, mainly consisting of amorphous silica, was responsible for the improved oxidation resistance. However, a substantial increase in oxidation rate due to the formation of molten eutectic fayalite (Fe2SiO4) was observed when the temperature was raised to 1200 °C. Under straining conditions at a very short oxidation time, the inner scale structure was slightly modified though the scale thickness remained almost unchanged for the steel containing 1.91 wt% Si.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Fukagawa, H. Okada, and Y. Maehara, Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International 34, 906 (1994).
H. Okada, T. Fukagawa, H. Ishihara, A. Okamoto, M. Azuma, and Y. Matsuda, Tetsu-to-Hagane 80, 849 (1994).
I. Svedung and N. G. Vannerberg, Corroion Science 14, 391 (1974).
C. W. Tuck, in Proceedings of the First International Congress of Metallic Corrosion, London, 1961, p. 221.
T. Adachi and G. H. Meier, Oxidation of Metals 27, 347 (1987).
Y. L. Yang, C. H. Yang, S. L. Lin, C. H. Chen, and W. T. Tsai, Materials Chemistry and Physics 112, 566 (2008).
K. Kusabiraki, R. Watanabe, T. Ikehata, M. Takeda, T. Onishi, and X. Guo, Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International 47, 1329 (2007).
L. Suarez, J. Schneider, and Y. Houbaert, Defect and Diffusion Forum 273–276, 655 (2008).
L. Suarez, J. Schneider, and Y. Houbaert, Defect and Diffusion Forum 273–276, 661 (2008).
M. Diéz-Ercilla, T. Ros-Yáñez, R. Petrov, Y. Houbaert, and R. Colás, Corrosion Engineering, Science and Technology 39, 295 (2004).
J. Païdassi, Acta Metallurgica 6, 184 (1958).
R. D. Shaw and R. Rolls, Corrosion Science 14, 443 (1974).
R. Y. Chen and W. Y. D. Yuen, Oxidation of Metals 57, 53 (2002).
C. W. Tuck, Corrosion Science 5, 631 (1965).
A. Atkinson and J. W. Gardner, Corrosion Science 21, 49 (1981).
P. Wu, G. Eriksson, A. D. Pelton, and M. Blander, Iron and Steel Institute of Japan International 33, 26 (1993).
S. Taniguchi, K. Yamamoto, D. Megumi, and T. Shibata, Materials Science and Engineering A 308, 250 (2001).
M. Okita, A. Nagai, I. Sinagawa, and K. Horinouchi, in Current Advances in Materials and Processes: Report of the ISIJ Meeting, Vol. 2 (1989), p. 1509.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, CH., Lin, SN., Chen, CH. et al. Effects of Temperature and Straining on the Oxidation Behavior of Electrical Steels. Oxid Met 72, 145–157 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-009-9152-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-009-9152-3