Abstract
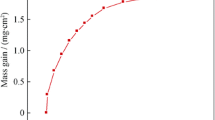
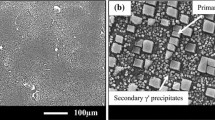
Ni-base superalloy IN 718 was cyclically oxidized in laboratory air at temperatures ranging from 750 to 950 °C for up to 12 cycles (14 h/cycle). The kinetic behaviour as well as the surface morphology, and the oxide phases of the scales were characterized by means of weight gain measurements, cyclic oxidation kinetics, scanning electron microscopy equipped with energy dispersive spectroscopy (SEM-EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis techniques. The results showed that as the oxidation temperature increased, the oxidation rate, the external scale thickness, and internal oxidation zone increased. It was suggested that the oxidation rate was controlled by the diffusion of substrate elements in the alloy and the inward diffusion of oxygen through the oxide scale. The oxidation kinetics followed a sub-parabolic rate law and, the activation energy of oxidation was 249 ± 20 kJ mol−1. The scaling process was controlled mainly by the diffusion of chromium, titanium, manganese, and oxygen ions through the chromia scale. IN 718 showed low weight gain and very slow reaction rates of substrate elements at 750 °C. At 850 °C, a continuous and very thin oxide scale was formed. At 950 °C, XRD and EDS-elemental mapping analysis revealed that a complex oxide scale had formed. It consisted of an outermost layer of TiO2–MnCr2O4 spinels, inner layer of Cr2O3, and the inner most layer composed of Ni3Nb enriched with Nb, Ti and Al oxides underneath the chromia layer. The oxide scale at this temperature seemed to be thicker layer, significant spallation and volatilization had apparently occurred, and greater internal corrosion was identified. The doping effect of titanium was observed, where it was found to be diffused through the chromia scale to form TiO2 at the oxide-gas interface as well as internally and at the oxide alloy interface. The amount of rutile (TiO2) at the oxide surface increased with temperature. In view of Mn contents in the alloy, the manganese–chromium spinel oxide was inferred to have played an important role in cyclic oxidation behaviour of IN 718, where the change in oxidation kinetic was noted. The Al contents would cause internal Al-rich oxide formation at grain boundaries.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. S. Pampana, MSc. Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, August 2004.
www.specialmetals.com. Accessed 2001.
X. S. Xie, J. X. Dong and M. C. Zhang, Materials Science Forum 539–543, 262 (2007).
Il. Ho Kim and S. I. Kwun, Materials Science Forum 486–487, 109 (2005).
H. Park, H. Kim, Y. Huh, M. Kim, S. Park, J. Koo and C. Seok, Key Engineering Materials 353–358, 523 (2007).
L. Zhou, Computational Materials Science 7(3), 336 (1997).
S. Gossé, T. Alpettaz, S. Chatain and C. Guéneau, Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power 131, 062901 (2009).
J. Zurek, D. J. Young, E. Essuman, M. Hänsel, H. J. Penkalla, L. Niewolak and W. J. Quadakkers, Materials Science and Engineering A 477, 259 (2008).
F. J. Perez, M. J. Cristobal, M. P. Hierro and F. Pedraza, Surface and Coatings Technology 120–121, 442 (1999).
G. R. Holcomb and D. E. Alman, Scripta Materialia 54, 1821 (2006).
M. P. Brady, W. J. Brindley, J. L. Smialek and I. E. Locci, Journal of Meterology 48, 46 (1996).
I. C. I. Okafor and R. G. Reddy, Journal of Meterology 51, 35 (1999).
S. Chevalier, G. Bonnet, K. Przybylski, J. C. Colson and J. P. Larpin, Oxidation of Metals 54, 527 (2000).
S. Taniguchi, Y. Shibata and A. Murakami, Oxidation of Metals 41, 103 (1994).
H. Kawaura, H. Kawahara, K. Nishino and T. Saito, Materials Science and Engineering A329, 589 (2002).
V. B. Trindade, U. Krupp, B. Z. Hangari, S. Yang and H. Christ, Materials Research 8, 371 (2005).
V. B. Trindade, U. Krupp, B. Z. Hangari, S. Yang, R. Borin and H. Christ, Materials Research 8, 365 (2005).
D. Caplan and M. Cohen, Corrosion Science 6, 321 (1966).
C. Ostwald and H. J. Grabke, Corrosion Science 46, 1113 (2004).
J. M. Rakowski, G. H. Meier and F. S. Pettit, Scripta Materialia 35, 1417 (1996).
H. J. Grabke, E. M. Muller-Lorenz, S. Strauss, E. Pippel and J. Woltersdorf, Oxidation of Metals 50, 241 (1998).
P. S. N. Stokes, F. H. Stott and G. C. Wood, Material Science and Engineering A 121, 549 (1989).
A. Atkinson and R. I. Taylor, Philosophical Magazine A 39, 581 (1979).
F. A. Khalid and S. E. Benjamin, Electron Microscopy 2, 183 (1998).
T. L. Wolfsdorf, W. H. Bender and P. W. Voorhees, Acta Metallurgica 45, 2279 (1997).
G. A. Greene and C. C. Finfrock, Oxidation of Metals 55, 505 (2001).
H. Singh, D. Puri, and S. Prakash, International Symposium of Research Students on Materials Science and Engineering, Chennai, India, December 20–22, 2004.
J. Huang, H. Fang, X. Fu, F. Huang, H. Wan, Q. Zhang, S. Deng and J. Zu, Oxidation of Metals 53, 273 (2000).
F. Rabbani, L. P. Ward, and K. N. Strafford, Oxidation of Metals 54(1/2), 139 (2000).
P. Kofstad, High Temperature Corrosion, (Elsevier, London, 1988).
B. Pieraggi, Material Science and Engineering 88, 199 (1987).
S. Esmaeili, C. C. Engler-Pinto Jr., B. Ilschner and F. Rézaï-Aria, Scripta Materialia 32, 1777 (1995).
B. D. Prasad, S. N. Sankran, K. E. Wiedermann and D. E. Glass, Thin Solid Films 345, 255 (1999).
B. Gleeson, and B. Li, Corrosion 2001, NACE International, Houston, TX, March 11–16, 2001.
F. Abe, H. Araki, M. Okada and H. Yoshida, Transactions of the Iron and Steel Institute of Japan 25, 424 (1985).
M. Shindo and T. Kondo, Tetsu-lo-Hagane 68, 1628 (1982).
H. Buscail, S. Perrier, and C. Josse, Materials and Corrosion, 2010 (61).
H. Buscail, S. El Messki, F. Riffard, S. Perrier, R. Cueff, E. Caudron and C. Issartel, Materials, Chemistry and Physics 111, 491 (2008).
L. Kumar, R. Venkataramani, M. Sundaraman, P. Mukhopadhyay and S. P. Garg, Oxidation of Metals 45, 221 (1996).
R. E. Lobnig, H. P. Schmidt, K. Hennesen and H. J. Grabke, Oxidation of Metals 37, 81 (1992).
H. Buscail, S. El Messki, F. Riffard, S. Perrier, R. Cueff and C. Issartel, Journal of Materials Science 43, 6960 (2008).
G. Ben Abderrazik, G. Moulin and M. Huntz, Oxidation of Metals 33, 191 (1990).
T. Sun Jo, D. Kim and S. Kim, Metals and Materials International 14, 739 (2008).
M. G. E. Cox, B. McEnany and V. D. Scott, Philosophical Magazine 26, 839 (1972).
C. Berthier, J. M. Lameille, M. Lenglet, D. Abida, J. Lopitaux and E. Beucher, Materials Science Forum 251–254, 1997 (1997).
C. Berthier, J. M. Lameille, M. Lenglet, D. Abida, J. Lopitaux and E. Beucher, Materials Science Forum 89, 251 (1996).
L. Antoni and B. Baroux, Review Meteorology (Paris) 99, 177 (2002).
F. Rouillard, C. Cabet, K. Wolski and M. Pijolat, Oxidation of Metals 68, 133 (2007).
D. M. England and A. V. Virkar, Journal of the Electrochemical Society 146, 3196 (1996).
F. Riffard, H. Buscail, E. Caudron, R. Cueff, C. Issartel and S. Perrier, Corrosion Science 45, 2867 (2003).
L. Jian, P. Jian, H. Bing and G. Xie, Journal of Power Sources 159, 641 (2006).
N. Hussain, K. A. Shahid, I. H. Khan and S. Rahman, Oxidation of Metals 43, 363 (1995).
A. M. Huntz, Journal of Physics III 5, 1729 (1995).
M. Landkof, A. V. Levy, D. H. Boone, R. Gray and E. Yaniv, Corrosion Science 41, 344 (1985).
C. S. Tedmon, Journal of Electrochemical Society 113, 766 (1966).
E. N. _dah, M. P. Hierro, K. Borrero and F. J. Perez, Oxidation of Metals 68, 9 (2007).
F. Delaunay, C. Berthier, M. Lenglet and J. Lameille, Mikrochimica Acta 132, 337 (2000).
P. Elliot and A. F. Hampton, Oxidation of Metals 14, 449 (1980).
D. Kim, C. Jang and W. Ryu, Oxidation of Metals 71, 271 (2009).
Acknowledgments
The work has been funded to a large extent by German Academic Exchange Service (Deutscher Akademisher Austaausch DAAD) under code number: A/09/08208, which is gratefully acknowledged by the authors. Mr. H.-G. Kleinheider (Metallographic examinations), Mrs. K. Mey (SEM & XRD analysis) are thanked for the Characterization work. Dr. U. Krupp, Mr. M. Kantehm, and Mr. A.Giertler are thanked for their support as well as all the staff of the Mechanical Engineering Department-University of Applied Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-hatab, K.A., Al-bukhaiti, M.A., Krupp, U. et al. Cyclic Oxidation Behavior of IN 718 Superalloy in Air at High Temperatures. Oxid Met 75, 209–228 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-010-9230-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11085-010-9230-6