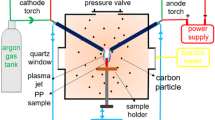
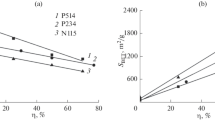
Abstract
A direct current thermal plasma system was developed and applied to synthesize ultrafine carbon black by using PS (polystyrene) and HDPE (high density polyethylene) as carbon sources. The precursors were pyrolyzed at different temperatures and the pyrolysis products were employed to investigate the actual synthesis of carbon black through the plasma jet. Spherical carbon nanoparticles with a high degree of turbostratic structure were obtained, showing a fingerprint graphite structure with a large surface area and ultrafine particle size. The carbon black was characterized by transmission and scanning electron microscopy, powder X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and nitrogen physisorption. Particle size distribution and dispersion stability in solvents were also investigated.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hyeon T, Han S, Sung YE, Park KW, Kim YW (2003) Angew Chem Int Ed 42:4352
Frysz CA, Shui X, Chung DDL (1996) J Power Sour 58:41
Miranda-Hernández M, Ayala JA, Rincón ME (2003) J Solid State Electrochem 7:264
Gao T, Woodka MD, Brunschwig BS, Lewis NS (2006) Chem Mater 18:5193
Zhu M, Weber CJ, Yang Y, Konuma M, Starke U, Kern K, Bittner AM (2008) Carbon 46:1829
Qian JJ, Chen AP, Liu ZX, Li CZ (2009) Adv Mater Res 66:139
Kim JS, Kim BS, Lee JG, Cho JP, Park BW (2005) J Power Sour 139:289
Carmona F, Ravier J (2002) J Carbon 40:151
Whitney, Lynn C (1988) Plast Eng 44:29
Merlo-Sosa L, Cota-Sanchez G, Soucy G (2001) Production of carbon black using induction plasma technology. In: Proceedings of the 15th Int. Symp. on Plasma Chemistry, vol VII, 2879
Kim KS, Lee KS, Ju WT, Hong SH (2005) Synthesis of nanostructured carbonaceous materials by thermal decomposition of methane using DC thermal plasmas 17th Int. Symp. on Plasma Chemistry CD-ROM
Fulcheri L, Probst N, Flamant G, Fabry F, Grivei E, Bourrat X (2002) Carbon 40:169
Lynum S, Myklebust N, Hox K (2000) US Patent 6068827
Fulcheri L, Schwob Y (1995) Int J Hydrogen Energy 20:197
Fabry F, Flamant G, Fulcheri L (2001) Chem Eng Sci 56:2123
Fincke JR, Anderson RP, Hyde TA, Detering BA (2002) Ind Eng Chem Res 41:1425
Pfender E (1999) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 19:1
Sarangi D, Godon C, Granier A, Moalic R, Goullet A, Turban G (2001) Appl Phys A 73:765
Maksimova NI, Krivoruchko OP, Mestl G, Zaikovskii VI, Chuvilin AL, Salanov AN (2000) J Mol Catal A 158:301
Chung Y-H, Jou S (2005) Mater Chem Phys 92:256
Nishino H, Nishida R, Matsui T, Kawase N, Mochida I (2003) Carbon 41:2819
Jou S, Hsu CK (2004) Mater Sci Eng B B106:275
Arena U, Mastellone ML, Camino G, Boccaleri E (2006) Polym Degrad Stabil 91:763
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, surface area and porosity. London, Academic Press, p 41
Barrett EP, Joyner LG, Halenda PP (1951) J Am Chem Soc 73:373
Fitzer E, Rozpłoch F (1988) High Temp High Press 20:449
Shimodaira N, Masui A (2002) J Appl Phys 92:902
Ferrari AC, Robertson J (2000) Phys Rev B 61:14095
Jawhari T, Roid A, Casado J (1995) Carbon 33:1561
Lee JW, Kim MH, Hong CK, Shim SE (2007) Meas Sci Technol 18:3707
Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing K (1999) Adsorption by powders & porous solids. San Diego, Academic Press, p 93
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, XF., Kim, GJ. Synthesis of Ultrafine Carbon Black by Pyrolysis of Polymers Using a Direct Current Thermal Plasma Process. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30, 75–90 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-009-9198-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-009-9198-7