Abstract
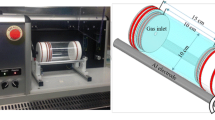
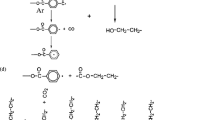
The plasma treatment of polymer surfaces is routinely used to enhance surface properties prior to adhesive bonding or biomolecule interaction. This study investigates the influence of plasma treatment conditions on the surface activation of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using the SurFx Atomflo™ 400L plasma source. In this study the effect of applied plasma power, processing speed, gas composition and plasma applicator nozzle to substrate distance were examined. The level of polymer surface activation was evaluated based on changes to the water contact angle (WCA) of PET samples after plasma treatment. PET surface properties were also monitored using surface energy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis. The heating effect of the plasma was monitored using thermal imaging and optical emission spectroscopy (OES) techniques. OES was also used as a diagnostic tool to monitor the change in atomic and molecular species intensity with changes in experimental conditions in both time and space. XPS analysis of the PET samples treated at different plasma powers indicated that increased oxygen content on samples surfaces accounted for the decreases observed in WCAs. For the first time a direct correlation was obtained between polymer WCA changes and the OES measurement of the atomic hydrogen Balmer Hα and molecular OH line emission intensities.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deilmann M, Halfmann H, Steves S, Bibinov N, Awakowicz P (2009) Silicon oxide permeation barrier coating and plasma sterilization of PET bottles and foils. Plasma Process Polym 6(S1):S695–S699
Topala I, Dumitrascu N, Pohoata V (2008) Influence of plasma treatments on the hemocompatibility of PET and PET plus TiO(2) films. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 28(4):535–551
Fang Z, Qiu Y, Wang H (2004) Surface treatment of polyethylene terephthalate film using atmospheric pressure glow discharge in air. Plasma Sci Technol 6(6):2576–2580
Pu FR, Williams RL, Markkula TK, Hunt JA (2002) Expression of leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion molecules on monocyte adhesion to human endothelial cells on plasma treated PET and PTFE in vitro. Biomaterials 23(24):4705–4718
Ademovic Z, Wei J, Winther-Jensen B, Hou X, Kingshott P (2005) Surface modification of PET films using pulsed AC plasma polymerisation aimed at preventing protein adsorption. Plasma Process Polym 2(1):53–63
Shenton MJ, Lovell-Hoare MC, Stevens GC (2001) Adhesion enhancement of polymer surfaces by atmospheric plasma treatment. J Phys D Appl Phys 34(18):2754–2760
Zanini S, Muller M, Riccardi C, Orlandi M (2007) Polyethylene glycol grafting on polypropylene membranes for anti-fouling properties. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27(4):446–457
Bigan M, Bigot J, Mutel B, Coqueret X (2008) Grafting of copolymer styrene maleic anhydride on poly(ethylene terephthalate) film by chemical reaction and by plasma method: optimization of the grafting reaction using experimental design. Appl Surf Sci 254(8):2300–2308
Thyen R, Weber A, Klages CP (1997) Plasma-enhanced chemical-vapour-deposition of thin films by corona discharge at atmospheric pressure. Surf Coat Technol 97(1):426–434
Żenkiewicz M, Richert J, Rytlewski P, Moraczewski K (2009) Some effects of corona plasma treatment of polylactide/montmorillonite nanocomposite films. Plasma Process Polym 6(S1):S387–S391
Onsuratoom S, Rujiravanit R, Sreethawong T, Tokura S, Chavadej S (2010) Silver loading on DBD plasma-modified woven PET surface for antimicrobial property improvement. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(1):191–206
Borris J, Dohse A, Hinze A, Thomas M, Klages C-P, Möbius A, Elbick D, Weidlich E-R (2009) Improvement of the adhesion of a galvanic metallization of polymers by surface functionalization using dielectric barrier discharges at atmospheric pressure. Plasma Process Polym 6(S1):S258–S263
Dowling DP, O’Neill FT, Langlais SJ, Law VJ (2011) Influence of dc pulsed atmospheric pressure plasma jet processing conditions on polymer activation. Plasma Process Polym 8(8):718–727
Oteyaka MO, Chevallier P, Turgeon S, Robitaille L, Laroche G (2012) Low pressure radio frequency ammonia plasma surface modification on poly(ethylene terephthalate) films and fibers: effect of the polymer forming process. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32(1):17–33
Orhan M, Kut D, Gunesoglu C (2012) Improving the antibacterial property of polyethylene terephthalate by cold plasma treatment. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 32(2):293–304
Yang S, Gupta MC (2004) Surface modification of polyethyleneterephthalate by an atmospheric-pressure plasma source. Surf Coat Technol 187(2):172–176
Dowling DP, Ramamoorthy A, Rahman M, Mooney DA, MacElroy JMD (2009) Influence of atmospheric plasma source and gas composition on the properties of deposited siloxane coatings. Plasma Process Polym 6(S1):S483–S489
Dowling DP, Twomey B, Byrne G, O’Neill L, O Hare L (2005) Deposition of functional coatings using an in-line atmospheric pressure plasma apparatus. In: Proceedings of the 48th annual conference—SVC, 2005. pp. 214–218
Lommatzsch U, Pasedag D, Baalmann A, Ellinghorst G, Wagner H-E (2007) Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment of polyethylene surfaces for adhesion improvement. Plasma Process Polym 4(S1):S1041–S1045
Arefi-Khonsari F, Tatoulian M, Bretagnol F, Bouloussa O, Rondelez F (2005) Processing of polymers by plasma technologies. Surf Coat Technol 200(1):14–20
Arefi-Khonsari F, Kurdi J, Tatoulian M, Amouroux J (2001) On plasma processing of polymers and the stability of the surface properties for enhanced adhesion to metals. Surf Coat Technol 142–444:437–448
Yang L, Chen J, Guo Y, Zhang Z (2009) Surface modification of a biomedical polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by air plasma. Appl Surf Sci 255(8):4446–4451
Nwankire C, Law V, Nindrayog A, Twomey B, Niemi K, Milosavljević V, Graham W, Dowling D (2010) Electrical, thermal and optical diagnostics of an atmospheric plasma jet system. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 30(5):537–552
Vesel A, Mozetic M, Zalar A (2007) XPS study of oxygen plasma activated PET. Vacuum 82(2):248–251
Vesel A (2011) Activation of polymer polyethylene terephthalate (PET) by exposure to Co2 and O2 plasma. Mater Technol 45(2):121–124
Junkar I, Vesel A, Cvelbar U, Mozetifç M, Strnad S (2009) Influence of oxygen and nitrogen plasma treatment on polyethylene terephthalate (PET) polymers. Vacuum 84(1):83–85
Carosio F, Alongi J, Frache A (2011) Influence of surface activation by plasma and nanoparticle adsorption on the morphology, thermal stability and combustion behavior of PET fabrics. Eur Polym J 47(5):893–902
Hocine D, Belkaid MS, Pasquinelli M, Escoubas L, Simon JJ, Rivière GA, Moussi A (2013) Improved efficiency of multicrystalline silicon solar cells by TiO2 antireflection coatings derived by APCVD process. Mater Sci Semicon Proc 16(1):113–117
Wang J, Chen JY, Yang P, Leng YX, Wan GJ, Sun H, Zhao AS, Huang N, Chu PK (2006) In vitro platelet adhesion and activation of polyethylene terephthalate modified by acetylene plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition. Nucl Instrum Meth B 242(1–2):12–14
Yang M-R, Chen K-S, Tsai J-C, Tseng C–C, Lin S-F (2002) The antibacterial activities of hydrophilic-modified nonwoven PET. Mater Sci Eng C 20(1–2):167–173
Vassallo E, Cremona A, Ghezzi F, Ricci D (2010) Characterization by optical emission spectroscopy of an oxygen plasma used for improving PET wettability. Vacuum 84(7):902–906
Kravets L, Dmitriev S, Gilman A, Drachev A, Dinescu G (2005) Water permeability of poly(ethylene terephthalate) track membranes modified by DC discharge plasma polymerization of dimethylaniline. J Membr Sci 263(1–2):127–136
Dowling DP, Tynan J, Ward P, Hynes AM, Cullen J, Byrne G (2012) Atmospheric pressure plasma treatment of amorphous polyethylene terephthalate for enhanced heatsealing properties. Int J Adhes Adhes 35:1–8
Lam YL, Kan CW, Yuen CW (2011) Effect of oxygen plasma pretreatment and titanium dioxide overlay on flame retardant finished cotton fabrics. BioResources 6(2):1454–1474
Gonzalez E 2nd, Barankin MD, Guschl PC, Hicks RF (2008) Remote atmospheric-pressure plasma activation of the surfaces of polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene naphthalate. Langmuir 24(21):12636–12643
Li Y, Sun J, Yao L, Ji F, Peng S, Gao Z, Qiu Y (2012) Influence of moisture on effectiveness of plasma treatments of polymer surfaces. J Adhes Sci Technol 26(8–9):1123–1139
Homola T, Matousek J, Hergelova B, Kormunda M, Wu LYL, Cernak M (2012) Activation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) surfaces by atmospheric pressure plasma. Polym Degrad Stab 97(11):2249–2254
Kostov KG, dos Santos ALR, Honda RY, Nascente PAP, Kayama ME, Algatti MA, Mota RP (2010) Treatment of PET and PU polymers by atmospheric pressure plasma generated in dielectric barrier discharge in air. Surf Coat Technol 204(18–19):3064–3068
Pellerin S, Cormier JM, Richard F, Musiol K, Chapelle J (1996) A spectroscopic diagnostic method using UV OH band spectrum. J Phys D Appl Phys 29(3):726–739
Mortazavi M, Nosonovsky M (2012) A model for diffusion-driven hydrophobic recovery in plasma treated polymers. Appl Surf Sci 258(18):6876–6883
Strom G, Fredriksson M, Stenius P (1987) Contact angles, work of adhesion, and interfacial tensions at a dissolving Hydrocarbon surface. J Colloid Interf Sci 119(2):352–361
Owens DK, Wendt RC (1969) Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 13(8):1741–1747
Milosavljevic V, Ellingboe AR, Daniels S (2011) Influence of plasma chemistry on oxygen triplets. Eur Phys J D 64(2–3):437–445
Stallard C, McDonnell K, Onayemi O, O’Gara J, Dowling D (2012) Evaluation of protein adsorption on atmospheric plasma deposited coatings exhibiting superhydrophilic to superhydrophobic properties. Biointerphases 7(1–4):1–12
Acknowledgement
This material is based upon works supported by the Science Foundation Ireland under Grant No. 08/SRC/I1411. V. Milosavljević is grateful to the Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Serbia under Grant No. OI171006. The authors would also like to acknowledge the significant support of Proxy Biomedical Ltd. in the carrying out of this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donegan, M., Milosavljević, V. & Dowling, D.P. Activation of PET Using an RF Atmospheric Plasma System. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 33, 941–957 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9474-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-013-9474-4