Abstract
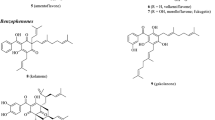
Bioactive natural compounds from garlic and onions have been the focus of researches for decades, firstly due to their pharmacological effects, and secondly due to their defence properties against plant diseases. In fact, garlic and onion, belonging to Allium genus, are among the oldest food plants known since ancient times and used as ingredient of many recipes and for therapeutic properties. These plants are well known to produce bioactive apolar sulphur compounds but less is known about their polar natural compounds, such as phenols, sapogenins and saponins, that are more stable to cooking, So, we continued our work on the discovery of polar bioactive metabolites from Allium with the isolation of a number of sapogenins and saponins from the wild onion species Allium elburzense, Allium hirtifolium, Allium atroviolaceum, and Allium minutiflorum, and, more recently, from the cultivated white onion, Allium cepa, and garlic, Allium sativum. In particular, the sapogenins and saponins isolated from A. elburzense and A. hirtifolium, named elburzensosides and hirtifoliosides respectively, exhibited significant antispasmodic properties. In addition, the saponins named minutosides isolated from A. minutiflorum showed promising antimicrobial activity. More recently the phytochemical analysis of A. cepa and A. sativum has been undertaken and afforded the characterization of saponins, phenols and N-cynnamic amides which showed significant antifungal activity.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adao CR, Pereira da Silva B, Tinoco LW, Parente JP (2012) Haemolytic activity and immunological adjuvant effect of a new steroidal saponin from Allium ampeloprasum var. porrum. Chem Biodiv 9:58–67
Agrawal PK (1992) NMR spectroscopy in the structural elucidation of oligosaccharides and glycosides. Phytochemistry 57:3307–3330
Avato P, Bucci R, Tava A, Vitali C, Rosato A, Bialy Z, Jurzysta M (2006) Antimicrobial activity of saponins from Medicago sp.: structure-activity relationship. Phytother Res 20:454–457
Barile E, Zolfaghari B, Sajjadi SE, Lanzotti V (2004) Saponins of Allium elburzense. J Nat Prod 67:2037–2042
Barile E, Capasso R, Izzo AA, Lanzotti V, Sajjadi SE, Zolfaghari B (2005) Structure-activity relationships for saponins from Allium hirtifolium and Allium elburzense and their antispasmodic activity. Planta Med 71:1010–1018
Barile E, Bonanomi G, Antignani V, Zolfaghari B, Sajjadi SE, Scala F, Lanzotti V (2006) Saponins from Allium minutiflorum with antifungal activity. Phytochemistry 68:596–603
Block E (1985) The chemistry of garlic and onions. Sci Am 252:114–119
Bowyer P, Clarke BR, Lunness P, Daniels MJ, Osbourn AE (1995) Host range of a plant pathogenic fungus determined by a saponins detoxifying enzyme. Science 267:371–374
Breitmaier E, Voelter W (1987) Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy. VCH, Weinheim
Carotenuto A, Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Magno S, Carnuccio R, D’Acquisto F (1997) 12-keto-porrigenin and the unique 2,3-seco-Porrigenin, New Antiproliferative Sapogenins from Allium porrum. Tetrahedron 53:3401–3406
Carotenuto A, Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Magno S (1999) Spirostanol Saponins of Allium porrum L. Phytochemistry 51:1077–1082
Chen H, Wang G, Wang N, Yang M, Wang Z, Wang X, Yao X (2007) New furostanol saponins rom the bulbs of Allium macrostemon Bunge and their cytotoxic activity. Pharmazie 62:544–548
Chen HF, Wang GH, Luo Q, Wang NL, Yao XS (2009) Two new steroidal saponins from Allium macrostemon Bunge and their cytotoxicity on different cell lines. Molecules 14(2246):2253
Cioaca C, Margineanu C, Cucu V (1978) The saponins of Hedera helix with antibacterial activity. Pharmazie 33:609–610
Cordes E-H, Bull H-G (1974) Mechanism and catalysis for hydrolysis of acetals, ketals, and ortho esters. Chem Rev 74:581–603
Corea G, Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V (2003) Saponins and flavonoids of Allium triquetrum. J Nat Prod 66:1405–1411
Corea G, Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Capasso R, Izzo AA (2005) Antispasmodic saponins form bulbs of red onion, Allium cepa L. Var. Tropea. J Agric Food Chem 53:935–940
Curir P, Dolci M, Corea G, Galeotti F, Lanzotti V (2006) The plant antifungal isoflavone genistein is metabolized by Armillaria mellea Vahl to give non-fungitoxic products. Plant Biosyst 140:156–162
Di Carlo G, Mascolo N, Izzo A–A, Capasso F (1999) Flavonoids: old and new aspects of a class of natural therapeutic drugs. Life Sci 65:337–353
Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Magno S, Taglialatela-Scafati O (1998) Sapogenins of Allium porrum L. J Agric Food Chem 46:4904–4908
Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Taglialatela-Scafati O (1999) Antifungal N-feruloyl amides from roots of Allium species. Plant Biosyst 133:199–203
Fattorusso E, Lanzotti V, Magno S, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Di Rosa M, Ianaro A (2000) Cytotoxic Saponins from Bulbs of Allium porrum L. J Agric Food Chem 46:4904–4908
Fattorusso E, Iorizzi M, Lanzotti V, Taglialatela-Scafati O (2002) Chemical composition of shallot (Allium ascalonicum Hort.). J Agric Food Chem 50:5686–5690
Gorovits MB, Khristulas FS, Abubakirov NK (1971) Alliogenin and alliogenin-β-D-glucopyranoside from Allium giganteum. Khim Prir Soedin 7:434–442
Harman GE, Howell CR, Viterbo A, Chet I, Lorito M (2004) Trichoderma species-opportunistic, avirulent plants symbionts. Nat Rev 2:43–56
Hu G, Mao R, Ma Z (2009) A new steroidal saponin from the seeds of Allium tuberosum. Food Chem 113:1065–1068
Iwakami S, Shibuta M, Tseng C, Hanaoka F, Sankawa U (1986) Inhibition of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase by phenolic compounds. Chem Pharm Bull 34:3960–3963
Jabrane A, Jannet HB, Miyamoto T, Mirjolet JF, Duchamp O, Harzallah-Skhiri F, Lacaille-Dubois MA (2011) Spirostane and cholestane glycosides from the bulbs of Allium nigrum L. Food Chem 125:447–455
Kang LP, Liu ZJ, Zhang L, Tan DW, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Chen HB, Ma BP (2007) New furostanol saponins from Allium ascalonicum. Magn Res Chem 45:725–733
Khristulas FS, Gorovits MB, Luchanskaya VN, Abubakirov NK (1970) New steroidal sapogenin from Allium giganteum. Khim Prir Soedin 6:489–490
Lai W, Wu Z, Lin H, Li T, Sun L, Chai Y, Chen W (2010) Anti-ischemica steroidal saponins from the seeds of Allium fistulosum. J Nat Prod 73:1053–1057
Lanzotti V (2005) Bioactive Saponins from Allium and Aster plants. Phytochem Rev 4:95–110
Lanzotti V (2006) The analysis of onion and garlic. J Chromat A 1112:3–22
Lanzotti V, Romano A, Bonanomi G, Lanzuise S, Scala F (2012a) Antifungal saponins from bulbs of white onion, Allium cepa L. Phytochemistry 74:133–138
Lanzotti V, Barile E, Bonanomi G, Antignani V, Scala F (2012b) Antifungal saponins from bulbs of garlic, Allium sativum L. var. Voghiera. Phytochemistry 78:126–134
Mandala P, Sinha Babub SP, Mandal NC (2005) Antimicrobial activity of saponins from Acacia auriculiformis. Fitoterapia 76:462–465
Mathew GEA, Stephen T (1957) 7-Dehydroagapanthagenin and 8(14)-dehydroagapanthagenin, two new spirostan sapogenins from Agapanthus africanus. J Chem Soc 262–264
Mimaki Y, Kuroda M, Sashida Y (1999) Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Allium ampeloprasum. Nat Med 53:88–93
Morrissey JP, Osbourn AE (1999) Fungal resistance to plant antibiotics as a mechanism of pathogenesis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:708–724
Mskhiladze L, Legault J, Lavoie S, Mshvildadze V, Kuchukhidze J, Elias R, Pichette A (2008) Cytotoxic steroidal saponins from flowers of Allium leucanthum. Molecules 13:2925–2934
Nicol RW, Traquair JA, Bernards MA (2002) Ginensosides as host resistance factors in American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius). Can J Bot 80:557–562
Ou WC, Chen HF, Zhong Y, Liu BR, Liu SM, Chen KJ (2012) Inhibition of platelet activation and aggregation by furostanol saponins isolated from bulbs of Allium macrostemon Bunge. Am J Med Sci PMID 2222–2335
Roldán-Arjona T, Pérez-Espinosa A, Ruiz-Rubio M (1999) Tomatinase from Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici defines a new class of saponinases. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 12:852–861
Sandrock RW, Van Etten HD (1998) Fungal sensitivity to and enzymatic degradation of the phytoanticipin α-tomatine. Phytopathology 88:137–143
Sang S, Mao S, Lao A, Chen Z, Ho C-T (2003) Steroidal saponins from the bulbs of Allium aflatunense. Food Chem 83:499–506
Wang Y, McAllister TA, Yanke LJ, Cheeke PR (2000) Effect of steroidal saponin from Yucca schidigera extract on ruminal microbes. J Appl Microbiol 88:887–896
Yuan L, Ji TF, Li CJ, Wang AG, Yang JB, Su YL (2009) Two new steroidal saponins from the seeds of Allium cepa L. J As Nat Prod Res 11:213–218
Zimmer DE, Pedersen MW, McGuire DF (1967) A bioassay for alfalfa saponins using the fungus Trichoderma viride. Pers Ex Fr Crop Sci 7:223–224
Zolfaghari B, Barile E, Capasso R, Izzo AA, Sajjadi SE, Lanzotti V (2006) The sapogenin atroviolagenin and its diglycoside atroviolaceoside from Allium atroviolaceum. J Nat Prod 69:191–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lanzotti, V. Bioactive polar natural compounds from garlic and onions. Phytochem Rev 11, 179–196 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-012-9247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-012-9247-3