Abstract
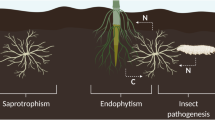
This review examines the symbiotic, evolutionary, proteomic and genetic basis for a group of fungi that occupy a specialized niche as insect pathogens as well as endophytes. We focus primarily on species in the genera Metarhizium and Beauveria, traditionally recognized as insect pathogenic fungi but are also found as plant symbionts. Phylogenetic evidence suggests that these fungi are more closely related to grass endophytes and diverged from that lineage ca. 100 MYA. We explore how the dual life cycles of these fungi as insect pathogens and endophytes are coupled. We discuss the evolution of insect pathogenesis while maintaining an endophytic lifestyle and provide examples of genes that may be involved in the transition toward insect pathogenicity. That is, some genes for insect pathogenesis may have been co-opted from genes involved in endophytic colonization. Other genes may be multifunctional and serve in both lifestyle capacities. We suggest that their evolution as insect pathogens allowed them to effectively barter a specialized nitrogen source (i.e. insects) with host plants for photosynthate. These ubiquitous fungi may play an important role as plant growth promoters and have a potential reservoir of secondary metabolites.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagga S, Hu G, Screen SE, St. Leger RJ (2004) Reconstructing the diversification of subtilisins in the pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene 324:159–169
Behie SW, Bidochka MJ (2014) Ubiquity of insect-derived nitrogen transfer to plants by endophytic insect-pathogenic fungi: an additional branch of the soil nitrogen cycle. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:1553–1560
Behie SW, Zelisko PM, Bidochka MJ (2012) Endophytic insect-parasitic fungi translocate nitrogen directly from insects to plants. Science 336:1576–1577
Behie SW, Jones SJ, Bidochka MJ (2015) Plant tissue localization of the endophytic insect pathogenic fungi Metarhizium and Beauveria. Fungal Ecol 13:112–119
Blanford S, Chan BHK, Jenkins N, Sim D, Turner RJ, Read AF, Thomas MB (2005) Fungal pathogen reduces potential for malaria transmission. Science 308:1638–1641
Bonfante P, Genre A (2010) Mechanisms underlying beneficial plant–fungus interactions in mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nat Commun 1:48
Bordallo JJ, Lopez-Llorca LV, Jansson HB, Salinas J, Persmark L, Asensio L (2002) Colonization of plant roots by egg-parasitic and nematode-trapping fungi. New Phytol 154:491–499
Carollo CA, Calil ALA, Schiave LA, Guaratini T, Roberts DW, Lopes NP, Braga GU (2010) Fungal tyrosine betaine, a novel secondary metabolite from conidia of entomopathogenic Metarhizium spp. fungi. Fungal Biol 114:473–480
Castrillo LA, Griggs MH, Ranger CM, Reding ME, Vandenberg JD (2011) Virulence of commercial strains of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium brunneum (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) against adult Xylosandrus germanus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and impact on brood. Biol Control 58:121–126
Chandler D (1997) Selection of an isolate of the insect pathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae virulent to the lettuce root aphid, Pemphigus bursarius. Biocontrol Sci Technol 7:95–104
Clark RB, Zeto SK (2000) Mineral acquisition by arbuscular mycorrhizal plants. J Plant Nutr 23:867–902
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Deising HB, Werner S, Wernitz M (2000) The role of fungal appressoria in plant infection. Microbes Infect 13:1631–1641
Elena GJ, Beatriz PJ, Alejandro P, Lecuona RE (2011) Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschnikoff) Sorokin promotes growth and has endophytic activity in tomato plants. Adv Biol Res 5:22–27
Fang W, St. Leger RJ (2010) Mrt, a gene unique to fungi, encodes an oligosaccharide transporter and facilitates rhizosphere competency in Metarhizium robertsii. Plant Physiol 154:1549–1557
Fang W, Pava-Ripoll M, Wang S, Leger RS (2009) Protein kinase A regulates production of virulence determinants by the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Fungal Genet Biol 46:277–285
Faria MR, Wraight SP (2007) Mycoinsecticides and mycoacaricides: a comprehensive list with worldwide coverage and international classification of formulation types. Biol Control 43:237–256
Freimoser FM, Screen S, Bagga S, Hu G, St. Leger RJ (2003) Expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis of two subspecies of Metarhizium anisopliae reveals a plethora of secreted proteins with potential activity in insect hosts. Microbiology 149:239–247
Gao Q, Jin K, Ying SH et al (2011) Genome sequencing and comparative transcriptomics of the model entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. acridum. PLoS Genet. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1001264
Garyali S, Reddy MS (2013) Taxol production by an endophytic fungus, Fusarium redolens, isolated from Himalayan yew. J Microbiol Biotechnol 23:1372–1380
Geremia RA, Goldman GH, Jacobs D, Ardiles W, Vila SB, Van Montagu M, Herrera-Estrella A (1993) Molecular characterization of the proteinase-encoding gene, prbl, related to mycoparasitism by Trichoderma harzianum. Mol Microbiol 8:603–613
Gibson DM, Donzelli BG, Krasnoff SB, Keyhani NO (2014) Discovering the secondary metabolite potential encoded within entomopathogenic fungi. Nat Prod Rep 31:1287–1305
Govindarajulu M, Pfeffer P, Philip E et al (2005) Nitrogen transfer in the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Nature 435:819–823
Grogan GJ, Holland HL (2000) The biocatalytic reactions of Beauveria spp. J Mol Catal B Enzym 9:1–32
Guether M, Neuhäuser B, Balestrini R et al (2009) A mycorrhizal specific ammonium transporter from Lotus japonicus acquires nitrogen. Plant Physiol 150:73–83
Hallsworth JE, Magan N (1996) Culture age, temperature, and pH affect the polyol and trehalose contents of fungal propagules. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:2435–2442
Holder DJ, Keyhani NO (2005) Adhesion of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria (Cordyceps) bassiana to substrata. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:5260–5266
Holder DJ, Kirkland BH, Lewis MW, Keyhani NO (2007) Surface characteristics of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria (Cordyceps) bassiana. Microbiology 153:3448–3457
Hu G, St. Leger RJ (2002) Field studies using a recombinant mycoinsecticide (Metarhizium anisopliae) reveal that it is rhizosphere competent. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6383–6387
Hu X, Xiao G, Zheng P et al (2014) Trajectory and genomic determinants of fungal-pathogen speciation and host adaptation. PNAS 111:16796–16801
Humber RA (2008) Evolution of entomopathogenicity in fungi. J Invertebr Pathol 98:262–266
Kabaluk JT, Ericsson JD (2007) Seed treatment increases yield of field corn when applied for wireworm control. Agron J 99:1377–1381
Khan AL, Hamayun M, Khan SA, Kang SM, Shinwari ZK, Kamran M, Rehman S, Kim JG, Lee IJ (2012) Pure culture of Metarhizium anisopliae LHL07 reprograms soybean to higher growth and mitigates salt stress. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:1483–1494
Kosuta S, Chabaud M, Lougnon G, Gough C, Dénarié J, Barker DG, Bécard G (2003) A diffusible factor from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi induces symbiosis-specific MtENOD11 expression in roots of Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 131:952–962
Lewis MW, Robalino IV, Keyhani NO (2009) Uptake of the fluorescent probe FM4-64 by hyphae and haemolymph-derived in vivo hyphal bodies of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Microbiology 155:3110–3120
Liao X, O’Brien TR, Fang W, St. Leger RJ (2014) The plant beneficial effects of Metarhizium species correlate with their association with roots. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:7089–7096
Luo F, Wang Q, Yin C et al (2015) Differential metabolic responses of Beauveria bassiana cultured in pupae extracts, root exudates and its interactions with insect and plant. J Invertebr Pathol. doi:10.1016/j.jip.2015.01.003
Madelin MF (1963) Diseases caused by hyphomycetous fungi. In: Steinhaus E (ed) Insect pathology: an advanced treatise, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 233–272
Maillet F, Poinsot V, André O et al (2011) Fungal lipochitooligosaccharide symbiotic signals in arbuscular mycorrhiza. Nature 469:58–63
Mayerhofer MS, Fraser E, Kernaghan G (2015) Acid protease production in fungal root endophytes. Mycologia 107:1–11
Nicholson RL, Epstein L (1991) Adhesion of fungi to the plant surface: prerequisite for pathogenesis. In: Cole GT, Hoch HC (eds) The fungal spore and disease initiation in plants and animals. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3–23
Oldroyd GED, Harrison MJ, Paszkowski U (2009) Reprogramming plant cells for endosymbiosis. Science 324:753–754
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2013) Action on the surface: entomopathogenic fungi versus the insect cuticle. Insects 4:357–374
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Keyhani NO (2015) Stress response signaling and virulence: insights from entomopathogenic fungi. Curr Genet 61:239–249
Ortiz-Urquiza A, Luo Z, Keyhani NO (2015) Improving mycoinsecticides for insect biological control. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:1057–1068
Ownley BH, Griffin MR, Klingeman WE, Gwinn KD, Moulton JK, Pereira RM (2008) Beauveria bassiana: endophytic colonization and plant disease control. J Invertebr Pathol 98:267–270
Ownley BH, Gwinn KD, Vega FE (2010) Endophytic fungal entomopathogens with activity against plant pathogens: ecology and evolution. Ecol Fungal Entomopathog 55:113–128
Pava-Ripoll M, Angelini C, Fang W, Wang S, Posada FJ, St. Leger RJ (2011) The rhizosphere-competent entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae expresses a specific subset of genes in plant root exudate. Microbiology 157:47–55
Pedrini N, Ortiz-Urquiza A, Huarte-Bonnet C et al (2013) Targeting of insect epicuticular lipids by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana: hydrocarbon oxidation within the context of a host-pathogen interaction. Front Microbiol 4:1–18
Pekrul S, Grula EA (1979) Mode of infection of the corn earworm (Heliothus zea) by Beauveria bassiana as revealed by scanning electron microscopy. J Invertebr Pathol 34:238–247
Reddy PV, Lam CK, Belanger FC (1996) Mutualistic fungal endophytes express a proteinase that is homologous to proteases suspected to be important in fungal pathogenicity. Plant Physiol 111:1209–1218
Sasan RK, Bidochka MJ (2012) The insect-pathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii (Clavicipitaceae) is also an endophyte that stimulates plant root development. Am J Bot 99:101–107
Sasan RK, Bidochka MJ (2013) Antagonism of the endophytic insect pathogenic fungus Metarhizium robertsii against the bean plant pathogen Fusarium solani f. sp. phaseoli. Can J Plant Pathol 35:288–293
Schrank A, Vainstein MH (2010) Metarhizium anisopliae enzymes and toxins. Toxicon 56:1267–1274
Screen SE, St. Leger RJ (2000) Cloning, expression, and substrate specificity of a fungal chymotrypsin—evidence for lateral gene transfer from an actinomycete bacterium. J Biol Chem 275:6689–6694
Small CLN, Bidochka MJ (2005) Up-regulation of Pr1, a subtilisin-like protease, during conidiation in the insect pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae. Mycol Res 109:307–313
Spatafora JW, Sung GH, Sung HM, Hywel-Jones L, White JF (2007) Phylogenetic evidence for an animal pathogen origin of ergot and the grass endophytes. Mol Ecol 16:1701–1711
St. Leger RJ, Staples RC, Roberts DW (1992a) Cloning and regulatory analysis of starvation-stress gene, ssgA, encoding a hydrophobin-like protein from the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. Gene 120:119–124
St. Leger RJ, Frank DC, Roberts DW, Staples RC (1992b) Molecular cloning and regulatory analysis of the cuticle-degrading protease structural gene from the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Eur J Biochem 204:991–1001
St. Leger RJ, Joshi L, Bidochka MJ, Rizzo NW, Roberts DW (1996) Characterization and ultrastructural localization of chitinases from Metarhizium anisopliae, M. flavoviride, and Beauveria bassiana during fungal invasion of host (Manduca sexta) cuticle. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:907–912
St. Leger RJ, Joshi L, Roberts D (1998) Ambient pH is a major determinant in the expression of cuticle-degrading enzymes and hydrophobin by Metarhizium anisopliae. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:709–713
St. Leger RJ, Nelson JO, Screen SE (1999) The entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae alters ambient pH, allowing extracellular protease production and activity. Microbiology 145:2691–2699
Tunlid A, Rosen SEB, Rask L (1994) Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology 140:1687–1695
Vega FE (2008) Insect pathology and fungal endophytes. J Invertebr Pathol 98:277–279
Wagner BL, Lewis LC (2000) Colonization of corn, Zea mays, by the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:3468–3473
Wanchoo A, Lewis MW, Keyhani NO (2009) Lectin mapping reveals stage-specific display of surface carbohydrates in in vitro and haemolymph-derived cells of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana. Microbiology 155:3121–3133
Wang C, St. Leger RJ (2005) Developmental and transcriptional responses to host and nonhost cuticles by the specific locust pathogen Metarhizium anisopliae var. acridum. Eukaryot Cell 4:937–947
Wang C, St. Leger RJ (2006) A collagenous protective coat enables Metarhizium anisopliae to evade insect immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6647–6652
Wang C, St. Leger RJ (2007a) The MAD1 adhesin of Metarhizium anisopliae links adhesion with blastospore production and virulence to insects, and the MAD2 adhesin enables attachment to plants. Eukaryot Cell 6:808–816
Wang C, St. Leger RJ (2007b) The Metarhizium anisopliae perilipin homolog MPL1 regulates lipid metabolism, appressorial turgor pressure, and virulence. J Biol Chem 282:21110–21115
Wang Q, Xu L (2012) Beauvericin, a bioactive compound produced by fungi: a short review. Molecules 17:2367–2377
Wang C, Hu G, St. Leger RJ (2005) Differential gene expression by Metarhizium anisopliae growing in root exudate and host (Manduca sexta) cuticle or hemolymph reveals mechanisms of physiological adaptation. Fungal Genet Biol 42:704–718
Wang C, Duan Z, St. Leger RJ (2008) MOS1 osmosensor of Metarhizium anisopliae is required for adaptation to insect host hemolymph. Eukaryot Cell 7:302–309
Wyrebek M, Bidochka MJ (2013) Variability in the insect and plant adhesins, Mad1 and Mad2, within the fungal genus Metarhizium suggest plant adaptation as an evolutionary force. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059357
Wyrebek M, Huber C, Sasan RK, Bidochka MJ (2011) Three sympatrically occurring species of Metarhizium show plant rhizosphere specificity. Microbiology 157:2904–2911
Xiao G, Ying SH, Zheng P et al (2012) Genomic perspectives on the evolution of fungal entomopathogenicity in Beauveria bassiana. Sci Rep 2:1–10
Zhang S, Xia YX, Kim B, Keyhani NO (2011) Two hydrophobins are involved in fungal spore coat rodlet layer assembly and each play distinct roles in surface interactions, development and pathogenesis in the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana. Mol Microbiol 80:811–826
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barelli, L., Moonjely, S., Behie, S.W. et al. Fungi with multifunctional lifestyles: endophytic insect pathogenic fungi. Plant Mol Biol 90, 657–664 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0413-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-015-0413-z