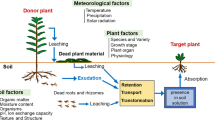
Abstract
Current evidence illustrates the significance of soil microbes in influencing the bioavailability of allelochemicals. This review discusses (i) the significance of soil microorganisms in influencing allelopathic expression, (ii) different ways of avoiding microbial degradation of putative allelochemicals, and (iii) the need of incorporating experiments on microbial modification of allelochemicals in laboratory bioassays for allelopathy. Several climatic and edaphic factors affect the soil microflora; therefore, allelopathy should be assessed in a range of soil types. Allelopathy can be better understood in terms of soil microbial ecology, and appropriate methodologies are needed to evaluate the roles of soil microorganisms in chemically-mediated interactions between plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T H Anderson K H Domsch (1985) ArticleTitleDetermination of eco-physiological maintanence carbon requirements of soil microorganisms in a dormant site Biol. Fert. Soils 1 81–89 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00255134 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XitVKisL4%3D
S Armstrong T R Patel (1993) ArticleTitle1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene biodegradation by Rhodococcus sp. BPG-8 Can. J. Microbiol. 39 175–179 Occurrence Handle8467418 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXit12qs7o%3D
O Barazani J Friedman (1999) Allelopathic bacteria Inderjit K M M Dakshini CL Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRG Press Boca Raton, FL 149–163
U Blum (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of microbial utilization of phenolic acids and their phenolic acid breakdown products on allelopathic interactions J. Chem. Ecol. 24 685–708 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022394203540 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXivVajs78%3D
U Blum S R Shafer (1988) ArticleTitleMicrobial populations and phenolic acids in soils Soil Biol. Biochem. 20 793–800 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(88)90084-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhtFelsrc%3D
U Blum T M Gerig A D Worsham L D King (1993) ArticleTitleModification of allelopathic effects of p-Coumaric acid on morning-glory seedling biomass by glucose, methionine, and nitrate J. Chem. Ecol. 19 2791–2811 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00980584 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhsF2itr8%3D
U Blum S R Shafer M E Lehman (1999) ArticleTitleEvidence for inhibitory allelopathic interactions involving phenolic acids in field soils: concepts vs. experimental model Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 18 673–693 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXntVCmtLo%3D
U Blum K L Staman L J Flint S R Shafer (2000) ArticleTitleInduction and/or selection of phenolic acid-utilizing bulk-soil and rhizosphere bacteria and their influence on phenolic acid phytotoxicity J. Chem. Ecol. 26 2059–2078 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFaitr4%3D
W R Chase M G Nair A R Putnam S K Mishra (1991) ArticleTitle2, 2′-oxo-1, 1′-azobenzene: microbial transformation of rye (Secale cereale L.) allelochemicals in field soils by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus: III J. Chem. Ecol. 17 1575–1584 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmtVaqur8%3D
H H Cheng (1995) Characterization of the mechanisms of allelopathy: Modeling and experimental approaches Inderjit K M M Dakshini F A Einhellig (Eds) Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications American Chemical Society Washington, DC 132–141
D N Choesin R E J Boerner (1991) ArticleTitleAllyl isothiocyanate release and the allelopathic potential of Brassica napus (Brassicaceae) Am. J. Bot. 78 1083–1090 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXmt1yntL4%3D
B R Dalton (1989) ArticleTitlePhysicochemical and biological processes affecting the recovery of exogenously applied ferulic acid from tropical forest soils Plant Soil 115 13–22 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02220689 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXkslKqtrk%3D
B R Dalton (1999) The occurrence and behavior of plant phenolic acids in soil environment and their potential involvement in allelochemical interference interactions: methodological limitations in establishing conclusive proof of allelopathy Inderjit K M M Dakshini C L Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 57–74
N H Fischer G B Williamson J D Weidenhamer D R Richardson (1994) ArticleTitleIn search of allelopathy in the Florida scrub: the role of terpenoids J. Chem. Ecol. 20 1355–1380 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02059812 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXksFequrc%3D
C L Foy (1999) How to make bioassays for allelopathy more relevant to field conditions with particular reference to cropland weeds Inderjit K M M Dakshini C L Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 25–33
R W Gagliardo W S Chilton (1992) ArticleTitleSoil transformation of 2(3H)- benzoxazolone of rye into phytotoxic 2-amino-3H-phenoxazin-3-one J. Chem. Ecol. 18 1683–1691 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XmsFSls70%3D
E Gand J R Hanson H Nasir (1995) ArticleTitleThe biotransformation of 8-epicedrol and some relatives by Cephalosporium aphicola Phytochemistry 39 1081–1084 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0031-9422(95)00120-V Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXnsFSnsL4%3D Occurrence HandleA1995RN58900022
W D Grant (1976) ArticleTitleMicrobial degradation of condensed tannins Science 193 1137–1138 Occurrence Handle959828 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE28Xltl2mu78%3D Occurrence HandleA1976CC91600027
J R Hanson H. Nasir (1993) ArticleTitleBiotransformation of sesquiterpenoid, cedrol, by Cephalosporium aphidicola Phytochemistry 33 835–837 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXmsVGit7g%3D Occurrence HandleA1993LN33700019
Y Hashidoko M Urashima T Yoshida J Mizutani (1993) ArticleTitleDecarboxylative conversion of hydrocinnamic acids by Klebsiella oxytoca and Erwinia uredovora, epiphytic bacteria of Polymnia sonchifolia leaf, possibly associated with formation of microflora on the damaged leaves Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 57 215–219 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXitV2iu7g%3D Occurrence Handle10.1271/bbb.57.215
S Hattori I Noguchi (1959) ArticleTitleMicrobial degradation of rutin Nature 184 1145–1146 Occurrence Handle13852047 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3cXksFaltQ%3D%3D Occurrence HandleA1959ZQ02500040
M E K Henderson (1956) ArticleTitleA study of the metabolism of phenolic compounds by soil fungi using spore suspension J. Gen. Microbiol. 14 684–691 Occurrence Handle13346030 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG28XntFWrtg%3D%3D
J Holowczak J Kuc E G Williams (1960) ArticleTitleMetabolism in vitro of phloridzin and other host compounds by Venturia inaequalis Phytopathology 50 640 Occurrence HandleA1960WN77200086
P M Huang M C Wang M K Wang (1999) Catalytic transformation of phenolic compounds in the soil Inderjit K M M Dakshini CL Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 287–306
InstitutionalAuthorNameInderjit (1996) ArticleTitlePlant phenolics in allelopathy Bot. Rev. 62 186–202
InstitutionalAuthorNameInderjit (1998) ArticleTitleInfluence of Pluchea lanceolata on some selected soil properties Am. J. Bot. 85 64–69
InstitutionalAuthorNameInderjit (2001) ArticleTitleSoils: environmental effect on allelochemical activity Agron J 93 79–84 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitl2mu7s%3D
Inderjit R M Callaway (2003) ArticleTitleExperimental designs for the study of allelopathy Plant Soil 256 1–11 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXot1ClsL8%3D
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1991) ArticleTitleInvestigations on some aspects of chemical ecology of cogongrass, Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv J. Chem. Ecol. 17 343–352 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhsVSis7w%3D
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1994a) ArticleTitleAllelopathic effect of Pluchea lanceolata (Asteraceae) on characteristics of four soils and tomato and mustard growth Am. J. Bot. 81 799–804
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1994b) ArticleTitleAllelopathic potential of phenolics from the roots of Pluchea lanceolata Physiol. Plant. 92 571–576 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXivVSls7w%3D
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1995a) Quercetin and quercitrin from Pluchea lanceolata and their effects on growth of asparagus bean Inderjit K M M Dakshini F A Einhellig (Eds) Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications American Chemical Society Washington, DC 86–95
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1995b) ArticleTitleOn laboratory bioassays in allelopathy Bot. Rev. 61 28–44 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02897150
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1996b) ArticleTitleAllelopathic potential of Pluchea lanceolata: comparative study of cultivated fields Weed Sci. 44 393–396 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjtVCgtrs%3D
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1999a) ArticleTitleAllelopathic potential of well water from Pluchea lanceolata-infested cultivated fields J. Chem. Ecol. 22 1123–1131
Inderjit S O Duke (2003) ArticleTitleEcophysiological aspects of allelopathy Planta 217 529–539 Occurrence Handle12811559 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmtVWgsrY%3D Occurrence Handle000185256300001
Inderjit S Kaur K M M Dakshini (1996) ArticleTitleDetermination of allelopathic potential of a weed Pluchea lanceolata through a multi-faceted approach Can. L. J. Bot. 74 1445–1450
Inderjit R M Callaway (2003) ArticleTitleExperimental designs for the study of allelopathy Plant Soil 256 IssueID1 1–11 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXot1ClsL8%3D
Del Inderjit R Moral (1997) ArticleTitleIs separating resource competition from allelopathy realistic? Bot. Rev. 63 221–230
Inderjit K M M Dakshini (1999) Bioassay for allelopathy: interactions of soil organic and inorganic constituents Inderjit K M M Dakshini C L Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 35–44
Inderjit C L Foy (1999) ArticleTitleNature of the interference potential of mugwort (Artemisia vulgaris) Weed Technol. 13 176–182
Inderjit K I Keating (1999) ArticleTitleAllelopathy: principles, procedures, processes, and promises for biological control Adv. Agron. 67 141–231 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXlt1Snt7c%3D
Inderjit E T Nilsen (2003) ArticleTitleBioassays and field studies for allelopathy in terrestrial plants: progress and problems Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 22 221–238
Inderjit J Weiner (2001) ArticleTitlePlant allelochemical interference or soil chemical ecology? Persp.Plant Ecol. Evol. Syste. 4 3–12
Inderjit H H Cheng H Nishimura (1999a) Plant phenolics and terpenoids: transformation, degradation, and potential for allelopathic interactions Inderjit K M M Dakshini C L Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 255–266
Inderjit C Asakawa K M M Dakshini (1999b) ArticleTitleAllelopathic potential of Verbesina encelioides root leachate in soil Can. J. Bot. 77 1419–1424 Occurrence Handle10.1139/cjb-77-10-1419 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXht12jsLk%3D
Inderjit, Rawat D S, Foy C L, 2004 Multifaceted approach to determine rice straw phytotoxicity. Can. J. Bot. 82, 168--176.
S Jose (2002) Black walnut allelopathy: current state of the science Inderjit A U Mallik (Eds) Chemical Ecology of Plants: Allelopathy in Aquatic and Terrestrial Ecosystems Birkhauser-Verlag AG Basal 149–172
S Jose A R Gillespie (1998) ArticleTitleAllelopathy in black walnut (Juglans nigra L.) alley cropping. I. Spatio-temporal variation in soil juglone in a black walnut-corn (Zea mays L.) alley cropping system in the midwestera USA Plant Soil 203 191–197 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnvFemt7o%3D
R Kaminsky (1981) ArticleTitleThe microbial origin of the allelopathic potential of Adenostoma fasiculatum H & A EcoL Monogr. 51 365–382 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXls1emsLo%3D
H Kaur Inderjit K I Keating (2002) Do allelochemicals operate independent of substratum factors? Inderjit A U Mallik (Eds) Chemical Ecology of Plants: Allelopathy in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems Birkhauser-Verlag AG Basal 99–107
P Kumar R W Gagliardo W S Chilton (1993) ArticleTitleSoil transformation of wheat and corn metabolites MBOA and DIM2BOA into aminophenoxazinoes J. Chem. Ecol 19 2453–2561 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00980682 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhsFKmsb0%3D
F Kunc (1971) ArticleTitleDecomposition of vanillin by soil microorganisms Folia Mcrobiol. 16 41–50 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3MXht1Wltbw%3D
H Lambers F S Chapin SuffixIII T L Pons (1998) Plant Physiological Ecology Springer-Verlag Berlin 540
R G Lehmann H H Cheng J B Harsh (1987) ArticleTitleOxidation of phenolic acids by iron and manganese oxides Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51 352–356 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXktVKgt7w%3D Occurrence Handle10.2136/sssaj1987.03615995005100020017x
E Levy S Carmeli (1995) Biological control of plant pathogen by antibiotic-producing bacteria Inderjit K M M Dakshini F A Einhellig (Eds) Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications American Chemical Society Washington, DC 300–309
J A Lewis R L Starkey (1968) ArticleTitleVegetable tannins, their decomposition and effects on decomposition of some organic compounds Soil Sci. 106 241–247 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1MXhvFagtg%3D%3D
D A Lipson C W Schadt S K Schmidt (2002) ArticleTitleChanges in soil microbial community structure and function in an alpine dry meadow following spring snow melt Microb. Ecol. 43 307–314 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00248-001-1057-x Occurrence Handle12037609 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XkvFSnsrw%3D
A Michelsen I K Schmidt S Jonasson J Dighton H E Jones T V Callaghan (1995) ArticleTitleInhibition of growth, and effects on nutrient uptake of arctic graminoids by leaf extracts – allelopathy or resource competition between plants and microbes Oecologia 103 407–418 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00328678 Occurrence HandleA1995RV95300002
M G Nair C J Whiteneck A R Putnam (1990) ArticleTitle2, 2′-oxo-l, 1′-azobenzene, a microbially transformed allelochemical from 2, 3-benzoxazorinone:I J. Chem. Ecol. 16 353–364 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01021770 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXhvFeks7Y%3D
H Nishimura S Hiramoto J Mizutani Y Noma A Furusaki T Matsumoto (1983) ArticleTitleStructure and biological activity of bottrospicatol, a novel monoterpene produced by microbial transformation of (-)-cis-carveol Agric. Biol. Chem. 47 2697–2699 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2cXmtleruw%3D%3D
H Nishimura Y Noma J Mizutani (1982) ArticleTitleEucalyptus as biomass. novel compounds from microbial conversion of 1, 8-cineole Agric. Biol. Chem. 46 2601–2604 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXisFyl
Y Noma S Yamasachi Y Asakawa (1992a) ArticleTitleBiotransformation of limonene and related compounds by Aspergillus cellulosae Phytochemistry 31 2725–2727 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlvVyjsrc%3D Occurrence HandleA1992JG58800030
F Ponder SuffixJr S H Tadros (1985) ArticleTitleJuglone concentration hi soil beneath black walnut interplanted with nitrogen-fixing sp J. Chem. Ecol 11 937–942 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01012079 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlt1agsL4%3D
K J Pue U Blum T M Gerig S R Shafer (1995) ArticleTitleMechanism by which noninhibitory concentrations of glucose increase inhibitory activity of p-coumaric acid on morning-glory seedling biomass accumulation J. Chem. Ecol. 21 833–847 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02033464 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmsFChs7c%3D
H Rettenmaier U Kupas F Lingens (1983) ArticleTitleDegradation of juglone by Pseudomonas putida Jl FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 19 193–197 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0378-1097(83)90058-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXltlKlsr4%3D
E L Rice (1984) Allelopathy Academic Press Orlando, FL. 422
D R Richardson G B Williamson (1988) ArticleTitleAllelopathic effects of shrubs of the sand pine scurb on pines and grasses of the sandhills For. Sci. 34 592–605
W J Rietveld (1983) ArticleTitleAllelopathic effects of juglone on germination and growth of several herbaceous and woody species J. Chem. Ecol 9 295–308 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhslCksL8%3D
J T Romeo (2000) ArticleTitleRaising the baem: moving beyond phytotoxicity J. Chem. Ecol. 26 2011–2014 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFaisbs%3D
J T Romeo J D Weidenhamer (1998) Bioassays for allelopathy in terrestrial plants K F Haynes J G Millar (Eds) Methods in Chemical Ecology. Bioas-say Methods Kluwer Academic Publishing Norvell, MA 179–211
S K Schmidt R E Ley (1999) Microbial competition and soil structure limit the expression of phytochemicals in nature Inderjit K M M Dakshini C L Foy (Eds) Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology: Allelochemical Interactions CRC Press Boca Raton, FL 339–351
S K Schmidt (1988) ArticleTitleDegradation of juglone by soil bacteria J. Chem. Ecol. 14 1561–1571 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01012522 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXlsVGqurg%3D
S K Schmidt (1990) ArticleTitleEcological implications of the destruction of juglone (5-hydroxy-l,4-naphthoquinone) by soil bacteria J. Chem. Ecol 16 3547–3549
S K Schmidt D A Lipson T A Raab (2000) ArticleTitleEffects of willows (Salix brachyearpa) on populations of salicylate-maineralizing microorganisms in alpine soils J. Chem. Ecol. 26 2049–2057 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005508230152 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFaisbc%3D
Schmidt S K and Lipson D A 2004 Microbial growth under the snow: implications for nutrient and allelochemical availability in temperate soils. Plant Soil 259: 1--7.
J S Singh A S Raghubanshi R S Singh S C Srivastava (1989) ArticleTitleMicrobial biomass acts as a source of plant nutrients in dry tropical forest and savana Nature 338 499–500 Occurrence Handle10.1038/338499a0 Occurrence HandleA1989U008400053
J M Stark S C Hart (1997) ArticleTitleHigh rates of nitrification and nitrate turnover in undisturbed coniferous forests Nature 385 61–64 Occurrence Handle10.1038/385061a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXisl2qsg%3D%3D Occurrence HandleA1997WA73100048
J B Sutherland D L Crawford A L Pometto SuffixIII (1983) ArticleTitleMetabolism of cinnamic, p-coumaric and ferulic acids by Streptomyces setonii Can. J Microbiol. 29 1253–1257 Occurrence Handle6661696 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXlvFWgtro%3D Occurrence Handle10.1139/m83-195
B F Tack P J Chapman S Dagley (1972) ArticleTitleMetabolism of gallic and syringic acids by Pseudomonas putida J. Biol. Chem. 247 6438–6443 Occurrence Handle4342601 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXht1yitQ%3D%3D
C S Tang W F Cai K Kohl R K Nishimoto (1995) Plant stress and allelopathy Inderjit K M M Dakshini F A Einhellig (Eds) Allelopathy: Organisms, Processes and Applications American Chemical Society Washington, DC 142–157
N Tanrisever F R Fronczek N H Fischer G B Williamson (1987) ArticleTitleCeratiolin and other flavonoids from Ceratiola ericoides Phytochemistry 26 175–179 Occurrence HandleA1987F436700034
J A Turner E L Rice (1975) ArticleTitleMicrobiological decomposition of ferulic acids in soil J. Chem. Ecol. 1 41–58 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00987719 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXkt1Crurk%3D
D A Wardle A Ghani (1995) ArticleTitleA crtique of the microbial metabolic quotient (qCO2) as a bioindicator of disturbance of ecosystem development Soil Biol. Biochem. 27 1601–1610 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXhtVSntrfM
D A Wardle M-C Nilsson (1997) ArticleTitleMicrobe-plant competition, allelopathy and artic plants Oecologia 109 291–293 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050086 Occurrence HandleA1997WE99300015
J D Weidenhamer (1996) ArticleTitleDistinguishing resource competition and chemical interference: overcoming the methodological impasse Agron. J. 88 866–875 Occurrence Handle10.2134/agronj1996.00021962003600060005x
D W S Westlake G Talbot E R Blackley F J Simpson (1959) ArticleTitlemicrobial decomposition of rutin Can. J Microbiol. 5 621–629 Occurrence Handle13844170 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3cXjsVOhsg%3D%3D
G B Williamson J D Weidenhamer (1990) ArticleTitleBacterial degradation of juglone: Evidence against allelopathy? J. Chem. Ecol. 16 1739–1742 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01014105 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3cXkt1Smtbs%3D
G B Williamson E M Obee J D Weidenhamer (1992) ArticleTitleInhibition of Sckizachyrium scoparium (poaceae) by the allelochemical hydrocinnamic acid J. Chem. Ecol 18 2095–2105 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00981930 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3sXit1Cn
R J Willis (2000) ArticleTitleJuglans spp., juglone and allelopathy Allelo. J. 7 1–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inderjit Soil Microorganisms: An Important Determinant of Allelopathic Activity. Plant Soil 274, 227–236 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0159-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0159-x