Abstract
Aims
We assessed the effects of native and exotic tree leaf litter on soil properties in two contrasting scenarios. The native Quercus robur and Pinus pinaster tree species coexist with the aliens Eucalyptus globulus and Acacia dealbata in acid soils of NW Spain. The native trees Fraxinus angustifolia and Ulmus minor coexist with the aliens Ailanthus altissima, Robinia pseudoacacia and Ulmus pumila in eutrophic basic riparian soils in Central Spain.
Methods
Four plastic trays per species were filled with homogenized top-soil of the site and covered with leaf litter. Before and after 9 months of incubation, litter mass, soil pH, organic matter, mineral and total N were measured. Available mineral N (NO −3 -N and NH +4 -N) was assessed every 2 months.
Results
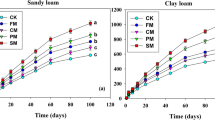
Soil biological activity was higher in the basic than in the acid soil. Litter of the exotic trees tended to decompose less than litter of native species, probably due to the presence of secondary metabolites in the former. Soil pH, mineral and total N responded differently to different litter types, irrespective of their exotic or native origin (acid soil), or was similar across litter treatments (basic riparian soil). The similar response of the basic soil to the addition of different litter types may be due to the low contrast of litter quality between the species. E. globulus litter inhibitied soil microbial activity much more than the rest of the studied litter types, leading to a drastic impoverishment of N in soils.
Conclusion
Litter of exotic N-fixing trees (A. dealbata and R. pseudoacacia) did not increase soil N pools because of the inhibition of microbial activity by secondary compounds. Therefore, secondary metabolites of the litter played a major role explaining exotic litter impact on soil properties.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams MM, Jarrell WM (1992) Bioavailability index for phosphorus using ion exchange resin impregnated membranes. Soil Sci Am J 56:1532–1537
Aerts R, Chapin FS (2000) The mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evalutation of processes and patterns. Adv Ecol Res 30:1–67
Allen SE, Grimshaw HM, Rowland AP (1986) Chemical analysis. In: Moore PD, Chapman SB (eds) Methods in plant ecology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Sci. Pub, Oxford, pp 285–344
Alonso A, González-Muñoz N, Castro-Díez P (2010) Comparison of leaf decomposition and macroinvertebrate colonization between exotic and native trees in a freshwater ecosystem. Ecol Res 25:647–653
Ashton IW, Hyatt LA, Howe KM, Gurevitch J, Lerdau MT (2005) Invasive species accelerate decomposition and litter nitrogen loss in a mixed deciduous forest. Ecol Appl 15(4):1263–1272
Bai YF, Wu JG, Pan QM, Huang JH, Wang QB, Li FS, Buyantuyev A, Han XG (2007) Positive linear relationship between productivity and diversity: evidence from the Eurasian Steppe. J Appl Ecol 44(5):1023–1034
Baruch Z, Bilbao B (1999) Effects of fire and defoliation on the life history of native and invader C-4 grasses in a Neotropical savanna. Oecologia 119(4):510–520
Bowman WD, Theodose TA, Schardt JC, Conant RT (1993) Constraints of nutrient availability on primary production in two alpine tundra communities. Ecology 74(7):2085–2097
Castro-Díez P, González-Muñoz N, Alonso A, Gallardo A, Poorter L (2009) Effects of exotic invasive trees on nitrogen cycling: a case study in Central Spain. Biol Invasion 11:1973–1986
Chamier AC (1987) Effect of pH on microbial-degradation of leaf litter in seven streams of the English-Lake-District. Oecologia 71(4):491–500
Corbeels M, O’Connell AM, Grove TS, Mendham DS, Rance SJ (2003) Nitrogen release from eucalypt leaves and legume residues as influenced by their biochemical quality and degree of contact with soil. Plant Soil 250(1):15–28
Cornelissen JHC, Thompson K (1997) Functional leaf attributes predict litter decomposition rate in herbaceous plants. New Phytol 135:109–114
Ehrenfeld JG (2003) Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cyling processes. Ecosystems 6:503–523
Ehrenfeld JG, Kourtev P, Huang W (2001) Changes in soil functions following invasions of exotic understory plants in deciduous forests. Ecol Appl 11:1287–1300
Eiland F, Klamer M, Lind AM, Leth M, Baath E (2001) Influence of initial C/N ratio on chemical and microbial composition during long term composting of straw. Microb Ecol 41(3):272–280
Field A (2005) Discovering statistics using SPSS. Sage Publications, London
Finzi AC, Canham CD, Van Breemen N (1998) Canopy tree-soil interactions within temperate forests: species effects on pH and cations. Ecol Appl 8(2):447–454
Follstad Shah JJ, Harner MJ, Tibbets TM (2010) Elaeagnus angustifolia elevates soil inorganic nitrogen pools in riparian ecosystems. Ecosystems 13:46–61
Gallardo A, Merino J (1992) Nitrogen inmobilization in leaf litter at two Mediterranean ecosystems of SW Spain. Biogeochem 15:213–228
Gallardo A, Merino J (1993) Leaf decomposition in two Mediterranean ecosystems of southwest Spain: influence of substrate quality. Ecology 74(1):152–161
Gallardo A, Parama R (2007) Spatial variability of soil elements in two plant communities of NW Spain. Geoderma 139:199–208
Gilliam FS, Dick DA (2010) Spatial heterogeneity of soil nutrients and plant species in herb-dominated communities of contrasting land use. Plant Ecol 209(1):83–94
Godoy O, Castro-Díez P, Van Logtestijn RSP, Cornelissen JHC, Valladares F (2010) Leaf litter traits of invasive species slow down decomposition compared to Spanish natives: a broad phylogenetic comparison. Oecologia 162:781–790
Gomez-Aparicio L, Canham CD (2008) Neighborhood models of the effects of invasive tree species on ecosystem processes. Ecol Monogr 78(1):69–86
Grigulis K, Lavorel S, Davies ID, Dossantos A, Lloret F, Vila M (2005) Landscape-scale positive feedbacks between fire and expansion of the large tussock grass, Ampelodesmos mauritanica in Catalan shrublands. Glob Chang Biol 11(7):1042–1053
Grotkopp E, Rejmánek M (2007) High seedling relative growth rate and specific leaf area are traits of invasive species: Phylogenetically independent contrasts of woody angiosperms. Am J Bot 94(4):526–532
Hattenschwiler S, Vitousek PM (2000) The role of polyphenols in terrestrial ecosystem nutrient cycling. Trends Ecol Evol 15(6):238–243
Hawkes CV, Wren IF, Herman DJ, Firestone MK (2005) Plant invasion alters nitrogen cycling by modifying the soil nitrifying community. Ecol Lett 8(9):976–985
Heisey RM, Heisey TK (2003) Herbicidal effects under field conditions of Ailanthus altissima bark extract, which contains ailanthone. Plant Soil 256(1):85–99
Hobbie SE, Reich PB, Oleksyn J, Ogdahl M, Zytkowiak R, Hale C, Karolewski P (2006) Tree species effects on decomposition and forest floor dynamics in a common garden. Ecology 87(9):2288–2297
Hobbie SE, Oleksyn J, Eissenstat DM, Reich PB (2010) Fine root decomposition rates do not mirror those of leaf litter among temperate tree species. Oecologia 162(2):505–513
Kittle DL, McGraw JB, Garbutt K (1995) Plant litter decomposition in wetlands receiving acid-mine drainage. J Environ Qual 24(2):301–306
Kowarik I, Saumel I (2007) Biological flora of Central Europe: Ailanthus altissima (Mill.) Swingle. Perspect Plant Ecol 8(4):207–237
Lake JC, Leishman MR (2004) Invasion success of exotic plants in natural ecosystems: the role of disturbance, plant attributes and freedom from herbivores. Biol Conserv 117:215–226
Le Maitre DC, van Wilgen BW, Chapman RA, McKelly DH (1996) Invasive plants and water resources in the Western Cape Province, South Africa: modelling the consequences of a lack of management. J Appl Ecol 33:161–172
Levine JM, Vila M, D’Antonio CM, Dukes JS, Grigulis K, Lavorel S (2003) Mechanisms underlying the impacts of exotic plant invasions. Proc R Soc Lond [Biol] 270(1517):775–781
Ley RE, D’Antonio CM (1998) Exotic grass invasion alters potential rates of N fixation in Hawaiian woodlands. Oecologia 113:179–187
Liao CZ, Peng RH, Luo YQ, Zhou XH, Wu XW, Fang CM, Chen JK, Li B (2008) Altered ecosystem carbon and nitrogen cycles by plant invasion: a meta-analysis. New Phytol 177(3):706–714
Mack MC, D’Antonio CM (1999) Impacts of biological invasions on disturbance regimes. Trends Ecol Evol 13:195–198
Mack MC, D’Antonio CM, Ley RE (2001) Alteration of ecosystem nitrogen dynamics by exotic plants: a case study of C4 grasses in Hawaii. Ecol Appl 11:1323–1335
Mayer PM, Tunnell SJ, Engle DM, Jorgensen EE, Nunn P (2005) Invasive grass alters litter decomposition by influencing macrodetritivores. Ecosystems 8(2):200–209
Mendham DS, Heagney EC, Corbeels M, O’Connell AM, Grove TS, McMurtrie RE (2004) Soil particulate organic matter effects on nitrogen availability after afforestation with Eucalyptus globulus. Soil Biol Biochem 36(7):1067–1074
Motavalli PP, Palm CA, Parton WJ, Elliott ET, Frey SD (1995) Soil pH and organic C dynamics in tropical forest soils: Evidence from laboratory and simulation studies. Soil Biol Biochem 27(12):1589–1599
Noe GB, Hupp CR (2005) Carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus accumulation in floodplains of Atlantic coastal plain rivers, USA. Ecol Appl 15(4):1178–1190
Ohte N, Koba K, Yoshikawa K, Sugimoto A, Matsuo N, Kabeya N, Wang LH (2003) Water utilization of natural and planted trees in the semiarid desert of Inner Mongolia, China. Ecol Appl 13(2):337–351
Olde Venterink H, Vermaat JE, Pronk M, Wiegman F, van der Lee GEM, van den Hoorn MW, Higler L, Verhoeven JTA (2006) Importance of sediment deposition and denitrification for nutrient retention in floodplain wetlands. Appl Veg Sci 9(2):163–174
Pattison RR, Goldstein G, Ares A (1998) Growth, biomass allocation and photosynthesis of invasive and native Hawaiian rainforest species. Oecologia 117:449–459
Porta Casanellas J, López-Acevedo Reguerín M, Rodríguez Ochoa R (1982) Técnicas y Experimentos en Edafología. Universitat de Lleida
Rothstein DE, Vitousek PM, Simmons BL (2004) An exotic tree alters decomposition and nutrient cycling in a Hawaiian montane forest. Ecosystems 7:805–814
Rovira P, Vallejo VR (1997) Organic carbon and nitrogen mineralization under Mediterranean climatic conditions: the effects of incubation depth. Soil Biol Biochem 29(9–10):1509–1520
Sanz Elorza M, Dana Sánchez ED, Sobrino Vesperinas E (2004) Atlas de las plantas alóctonas invasoras en España. Dirección General para la Biodiversidad. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid
Schlesinger WC (1991) Biogeochemistry. Academic, New York
Soudzilovskaia NA, Onipchenko VG (2005) Experimental investigation of fertilization and irrigation effects on an alpine heath, northwestern Caucasus, Russia. Arct Antarct Alp Res 37(4):602–610
Stevens CJ, Dupre C, Dorland E, Gaudnik C, Gowing DJG, Bleeker A, Diekmann M, Alard D, Bobbink R, Fowler D, Corcket E, Mountford JO, Vandvik V, Aarrestad PA, Muller S, Dise NB (2010) Nitrogen deposition threatens species richness of grasslands across Europe. Environ Pollut 158(9):2940–2945
Stock WD, Wienand KT, Baker AC (1995) Impacts of Invading N2-Fixing Acacia species on patterns of nutrient cycling in two Cape ecosystems - Evidence from soil incubation studies and N-15 natural-abundance values. Oecologia 101(3):375–382
Subler S, Blair JM, Edwards CA (1995) Using anion-exchange membranes to measure soil nitrate availability and net nitrification. Soil Biol Biochem 27 (7):911–917
Tateno R, Tokuchi N, Yamanaka N, Du S, Otsuki K, Shimamura T, Xue ZD, Wang SQ, Hou QC (2007) Comparison of litterfall production and leaf litter decomposition between an exotic black locust plantation and an indigenous oak forest near Yan’an on the Loess Plateau, China. For Ecol Manag 241(1–3):84–90
Taylor BR, Parkinson D, Parsons WFJ (1989) Nitrogen and lignin content as predictors of litter decay-rates - a microcosm test. Ecology 70(1):97–104
Tennesen M (2008) When Juniper and woody plants invade, water may retreat. Science 322:1630–1361
Vanderhoeven S, Dassonville N, Meerts P (2005) Increased topsoil mineral nutrient concentrations under exotic invasive plants. Plant Soil 275:169–179
Vilà M, Tessier M, Suehs CM, Brundu G, Carta L, Galanidis A, Lambdon P, Manca M, Médails F, Moragues E, Traveset A, Roumbis AY, Hulme PE (2006) Local and regional assessment of the impacts of plant invaders on vegetation structure and soil properties of Mediterranean islands. J Biogeogr 33(5):853–861
Vitousek PM, Walker LR (1989) Biological invasion by Myrica faya in Hawai’i: plant demography, nutrient fixation, ecosystem effects. Ecol Monogr 59:247–265
Whalen JK, Sampedro L (2009) Soil ecology and management. CAB International,
Xiong YM, Xia HX, Li ZA, Cai XA, Fu SL (2008) Impacts of litter and understory removal on soil properties in a subtropical Acacia mangium plantation in China. Plant Soil 304(1–2):179–188
Yelenik SG, Stock WD, Richardson DM (2007) Functional group identity does not predict invader impacts: differential effects of nitrogen-fixing exotic plants on ecosystem function. Biol Invasion 9:117–125
Yoshitake S, Sasaki A, Uchida M, Funatsu Y, Nakatsubo T (2007) Carbon and nitrogen limitation to microbial respiration and biomass in an acidic solfatara field. Eur J Soil Biol 43(1):1–13
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge Dr. Esther Pérez-Corona for her revision of this manuscript. This study was supported by the grants CGL2007-61873/BOS, CGL2010-16388/BOS of the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, POII10-0179-4700 of Junta de Comunidades de Castilla-La Mancha and the REMEDINAL network S2009/AMB-1783 (Comunidad de Madrid). NGM was supported by a grant of the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (FPI fellowship. BES-2008-002457).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alfonso Escudero.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro-Díez, P., Fierro-Brunnenmeister, N., González-Muñoz, N. et al. Effects of exotic and native tree leaf litter on soil properties of two contrasting sites in the Iberian Peninsula. Plant Soil 350, 179–191 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0893-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-0893-9