Abstract
Background and aims
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) have been widely studied for agricultural applications. One aim of this study was to isolate cadmium (Cd)-tolerant bacteria from nodules of Glycine max (L.) Merr. grown in heavy metal-contaminated soil in southwest of China. The plant growth-promoting (PGP) traits and the effects of the isolate on plant growth and Cd uptake by legume and non-legume plants in Cd-polluted soil were investigated.
Methods
Cd-tolerant bacteria were isolated by selective media. The isolates were identified by 16S rRNA gene and phylogenetic analysis. The PGR traits of the isolates were evaluated in vitro. Cd in soil and plant samples was determined by ICP-MS.
Results
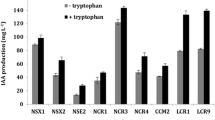
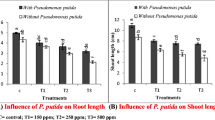
One of the most Cd-tolerant bacteria simultaneously exhibited several PGP traits. Inoculation with the PGPR strain had positive impacts on contents of photosynthesis pigments and mineral nutrients (Fe or Mg) in plant leaves. The shoot dry weights of Lolium multiflorum Lam. increased significantly compared to uninoculated control. Furthermore, inoculation with the PGPR strain increased the Cd concentrations in root of L. multiflorum Lam. and extractable Cd concentrations in the rhizosphere, while the Cd concentrations in root and shoot of G. max (L.) Merr. significantly decreased.
Conclusions
This study indicates that inoculation with Cd-tolerant PGPR can alleviate Cd toxicity to the plants, increase Cd accumulation in L. multiflorum Lam. by enhancing Cd availability in soils and plant biomass, but decrease Cd accumulation in G. max (L.) Merr. by increasing Fe availability, thus highlighting new insight into the exploration of PGPR on Cd-contaminated soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aleem A, Isar J, Malik A (2003) Impact of long-term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizosphere soil. Bioresour Technol 86(1):7–13
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSIBLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402
Arienzo M, Adamo P, Cozzolino V (2004) The potential of Lolium perenne for revegetation of contaminated soil from a metallurgical site. Sci Total Environ 319(1–3):13–25
Asada K, Endo T, Mano J, Miyake C (1998) Molecular mechanism for relaxation of and protection from light stress. In: Saton K, Murata N (eds) Stress responses of photosynthetic organisms. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 37–52
Barker AV (1979) Nutritional factors in photosynthesis of higher plants. J Plant Nutr 1(3):309–342
Balestrasse KB, Gallego SM, Tomaro ML (2004) Cadmium-induced senescence in nodules of soybean (Glycine max L.) plants. Plant Soil 262(1–2):373–381
Belimov AA, Dietz KJ (2000) Effect of associative bacteria on element composition of barley seedlings grown in solution culture at toxic cadmium concentrations. Microbiol Res 155(2):113–121
Belimov AA, Hontzeas N, Safronova VI, Demchinskaya SV, Piluzza G, Bullitta S, Glick BR (2005) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria associated with the roots of Indian mustard (Brassica juncea L. Czern.). Soil Biol Biochem 37(2):241–250
Chaoui A, El Ferjani E (2005) Effects of cadmium and copper on antioxidant capacities, lignification and auxin degradation in leaves of pea (Pisum sativum L.) seedlings. CR Biol 328(1):23–31
Chen YX, He YF, Yang Y, Yu YL, Zheng SJ, Tian GM, Luo YM, Wong MH (2003) Effect of cadmium on nodulation and N2-fixation of soybean in contaminated soils. Chemosphere 50(6):781–787
Chun J, Goodfellow M (1995) A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45(2):240–245
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clement C, Barka EA (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):4951–4959
Craciun AR, Courbot M, Bourgis F, Salis P, Saumitou-Laprade P, Verbruggen N (2006) Comparative cDNA-AFLP analysis of Cd-tolerant and sensitive genotypes derived from crosses between the Cd hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri and Arabidopsis lyrata ssp. petraea. J Exp Bot 57(12):2967–2983
Das P, Samantaray S, Rout GR (1997) Studies on cadmium toxicity in plants: a review. Environ Pollut 98(1):29–36
García-Fraile P, Carro L, Robledo M, Ramirez-Bahena MH, Flores-Felix JD, Fernandez MT, Mateos PF, Rivas R, Igual JM, Martinez-Molina E, Peix A, Velazquez E (2012) Rhizobium promotes non-legumes growth and quality in several production steps: towards a biofertilization of edible raw vegetables healthy for humans. Plos One 7(5):e38122
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28(3):367–374
Glick BR, Cheng Z, Czarny J, Duan J (2007) Promotion of plant growth by ACC deaminase-producing soil bacteria. Eur J Plant Pathol 119(3):329–339
Gomez-Sagasti MT, Alkorta I, Becerril JM, Epelde L, Anza M, Garbisu C (2012) Microbial monitoring of the recovery of soil quality during heavy metal phytoremediation. Water Air Soil Pollut 223(6):3249–3262
Gordon SA, Weber RP (1951) Colorimetric estimation of indoleacetic acid. Plant Physiol 26(1):192–195
Guo JK, Tang SR, Ju XH, Ding YZ, Liao SQ, Song NN (2011) Effects of inoculation of a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. D54 on plant growth and metal uptake by a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance grown on multiple metal contaminated soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(12):2835–2844
Hansch R, Mendel RR (2009) Physiological functions of mineral micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Mn, Fe, Ni, Mo, B, Cl). Curr Opin Plant Biol 12(3):259–266
Hao XL, Xie P, Johnstone L, Miller SJ, Rensing C, Wei GH (2012) Genome sequence and mutational analysis of plant-growth-promoting bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens CCNWGS0286 isolated from a zinc-lead mine tailing. Appl Environ Microbiol 78(15):5384–5394
Hattab S, Dridi B, Chouba L, Kheder MB, Bousetta H (2009) Photosynthesis and growth responses of pea Pisum sativum L. under heavy metals stress. J Environ Sci-China 21(11):1552–1556
He CQ, Tan GE, Liang X, Du W, Chen YL, Zhi GY, Zhu Y (2010) Effect of Zn-tolerant bacterial strains on growth and Zn accumulation in Orychophragmus violaceus. Appl Soil Ecol 44(1):1–5
Heggo A, Angle A, Chaney RL (1990) Effects of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on heavy metal uptake by soybeans. Soil Bio Biochem 22(6):865–869
Jiang CY, Sheng XF, Qian M, Wang QY (2008) Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant Burkholderia sp. from heavy metal-contaminated paddy field soil and its potential in promoting plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in metal-polluted soil. Chemosphere 72(2):157–164
Kitajima K, Hogan KP (2003) Increases of chlorophyll a/b ratios during acclimation of tropical woody seedlings to nitrogen limitation and high light. Plant Cell Environ 26(6):857–865
Kloepper JW, Schoth MN, Miller TD (1980) Effects of rhizosphere colonization by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on potato plant development and yield. Phytopathol 70(11):1078–1082
Kuffner M, De Maria S, Puschenreiter M, Fallmann K, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Strauss J, Rivelli AR, Sessitsch A (2010) Culturable bacteria from Zn- and Cd-accumulating Salix caprea with differential effects on plant growth and heavy metal availability. J Appl Microbiol 108(4):1471–1484
Lauber CL, Strickland MS, Bradford MA, Fierer N (2008) The influence of soil properties on the structure of bacterial and fungal communities across land-use types. Soil Biol Biochem 40(9):2407–2415
Li ZY, Tang SR, Deng XF, Wang RG, Song ZG (2010) Contrasting effects of elevated CO2 on Cu and Cd uptake by different rice varieties grown on contaminated soils with two levels of metals: implication for phytoextraction and food safety. J Hazard Mater 177(1–3):352–361
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Isolation and characterization of Ni mobilizing PGPB from serpentine soils and their potential in promoting plant growth and Ni accumulation by Brassica spp. Chemosphere 75(6):719–725
Martinez-Viveros O, Jorquera MA, Crowley DE, Gajardo G, Mora ML (2010) Mechanisms and practical considerations involved in plant growth promotion by rhizobacteria. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 10(3):293–319
McGrath SP, Brooks PC, Giller KE (1988) Effects of potentially toxic metals in soil derived from past applications of sewage sludge on nitrogen fixation by Trifolium repens L. Soil Biol Biochem 20(4):415–424
McLaughlin MJ, Parker DR, Clarke JM (1999) Metals and micronutrients—food safety issues. Field Crop Res 60(1–2):143–163
Middleton EM, Teramura AH (1993) The role of flavonol glycosides and carotenoids in protecting soybean from UV-B damage. Plant Physiol 103(3):741–752
Noriega GO, Balestrasse KB, Batlle A, Tomaro ML (2007) Cadmium induced oxidative stress in soybean plants also by the accumulation of δ-aminolevulinic acid. Biometals 20(6):841–851
Pal A, Dutta S, Mukherjee PK, Paul AK (2005) Occurrence of heavy metal resistance in microflora from serpentine soil of Andaman. J Basic Microbiol 45(3):207–218
Quartacci MF, Argilla A, Baker AJM, Navari-Izzo F (2006) Phytoextraction of metals from a multiply contaminated soil by Indian mustard. Chemosphere 63(6):918–925
Rother JA, Millbank JW, Thornton I (1983) Nitrogen fixation by white clover (Trifolium repens) in grasslands on soils contaminated with cadmium, lead and zinc. J Soil Sci 34(1):127–136
Sabreen S, Sugiyama SI (2008) Cadmium phytoextraction capacity in eight C3 herbage grass species. Grassl Sci 54(1):27–32
Saleh SS, Glick BR (2001) Involvement of gas S and pro s in enhancement of the plant growth-promoting capabilities of Enterobacter cloacae CAL2 and UW4. Can J Microbiol 47(8):698–705
Salt DE, Blaylock M, Kumar NPBA, Dushenkov V, Ensley BD, Chet I, Raskin I (1995) Phytoremediation: a novel strategy for the removal of toxic metals from the environment using plants. Biotechnol 13(5):468–474
Sárvári E, Solti A, Basa B, Meszaros I, Levai L, Fodor F (2011) Impact of moderate Fe excess under Cd stress on the photosynthetic performance of poplar (Populus jacquemontiana var. glauca cv. Kopeczkii). Plant Physiol Biochem 49(5):499–505
Sarwar N, Saifullah, Malhi SS, Zia MH, Naeem A, Bibi S, Farid G (2010) Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J Sci Food Agric 90(6):925–937
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160(1):47–56
Smeets K, Cuypers A, Lambrechts A, Semane B, Hoet P, Van Laere A, Vangronsveld J (2005) Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidative mechanisms in Phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol Biochem 43(5):437–444
Sriprang R, Hayashi M, Yamashita M, Ono H, Saeki K, Murooka Y (2002) A novel bioremediation system for heavy metals using the symbiosis between leguminous plant and genetically engineered rhizobia. J Biotechnol 99(3):279–293
Star L, Matan O, Dardanelli MS, Kapulnik Y, Burdman S, Okon Y (2012) The Vicia sativa spp. nigra–Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae symbiotic interaction is improved by Azospirillum brasilense. Plant Soil 356(1–2):165–174
Vivas A, Voros A, Biro B, Barea JM, Ruiz-Lozano JM, Azcon R (2003) Beneficial effects of indigenous Cd-tolerant and Cd-sensitive Glomus mosseae associated with a Cd-adapted strain of Brevibacillus sp. in improving plant tolerance to Cd contamination. Appl Soil Ecol 24(2):177–186
Wan Y, Luo SL, Chen JL, Xiao X, Chen L, Zeng GM, Liu CB, He YJ (2012) Effect of endophyte-infection on growth parameters and Cd-induced phytotoxicity of Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Chemosphere 89(6):743–750
Wani PA, Khan MS, Zaidi A (2007) Effect of metal tolerant plant growth promoting Bradyrhizobium sp. (Vigna) on growth, symbiosis, seed yield and metal uptake by greengram plants. Chemosphere 70(1):36–45
Watanabe FS, Olsen SR (1965) Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorous in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 29(6):677–678
Wei GH, Chen WM, Zhu WF, Chen C, Young JPW, Bontemps C (2009) Invasive Robinia pseudoacacia in China is nodulated by Mesorhizobium and Sinorhizobium species that share similar nodulation genes with native American symbionts. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 68(3):320–328
Wellburn AR (1994) The spectral determination of chlorophylls a and b, as well as total carotenoids, using various solvents with spectrophotometers of different resolution. J Plant Physiol 144(3):307–313
Whitten MG, Ritchie GSP (1991) Calcium chloride extractable cadmium as an estimate of cadmium uptake by subterranean clover. Aust J Soil Res 29(2):215–221
Xie H, Pasternak JJ, Glick BR (1996) Isolation and characterization of mutants of the plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium Pseudomonas putida GR12–2 that overproduce indole acetic acid. Curr Microbiol 32(2):67–71
Yeh TY, Pan CT (2012) Effect of chelating agents on copper, zinc uptake by sunflower, Chinese cabbage, cattail, and reed for different organic contents of soils. J Bioanal Biomed 4(1):006–010
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64(6):991–997
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (41001191) and the Central Public Research Institutes Basic Funds for Research and Development (Agro-Environmental Protection Institute, Ministry of Agriculture).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Euan K. James.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 49 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J., Chi, J. Effect of Cd-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobium on plant growth and Cd uptake by Lolium multiflorum Lam. and Glycine max (L.) Merr. in Cd-contaminated soil. Plant Soil 375, 205–214 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1952-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1952-1