Abstract
Background and aims
The effects of tillage and N fertilization on CO2 and CH4 emissions are a cause for concern worldwide. This paper quantifies these effects in a Mediterranean dryland area.
Methods
CO2 and CH4 fluxes were measured in two field experiments. A long-term experiment compared two types of tillage (NT, no-tillage, and CT, conventional intensive tillage) and three N fertilization rates (0, 60 and 120 kg N ha−1). A short-term experiment compared NT and CT, three N fertilization doses (0, 75 and 150 kg N ha−1) and two types of fertilizer (mineral N and organic N with pig slurry). Aboveground and root biomass C inputs, soil organic carbon stocks and grain yield were also quantified.
Results
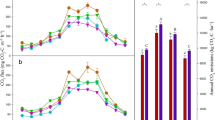
The NT treatment showed a greater mean CO2 flux than the CT treatment in both experiments. In the long-term experiment CH4 oxidation was greater under NT, whereas in the short-term experiment it was greater under CT. The fertilization treatments also affected CO2 emissions in the short-term experiment, with the greatest fluxes when 75 and 150 kg organic N ha−1 was applied. Overall, the amount of CO2 emitted ranged between 0.47 and 6.0 kg CO2−equivalent kg grain−1. NT lowered yield-scaled emissions in both experiments, but these treatment effects were largely driven by an increase in grain yield.
Conclusions
In dryland Mediterranean agroecosystems the combination of NT and medium rates of either mineral or organic N fertilization can be an appropriate strategy for optimizing CO2 and CH4 emissions and grain yield.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alluvione F, Halvorson AD, Del Grosso SJ (2009) Nitrogen, tillage, and crop rotation effects on carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from irrigated cropping systems. J Environ Qual 38:2023–2033
Almagro M, López J, Querejeta JI, Martínez-Mena M (2009) Temperature dependence of soil CO2 efflux is strongly modulated by seasonal patterns of moisture availability in a Mediterranean ecosystem. Soil Biol Biochem 41:594–605
Álvaro-Fuentes J, Arrúe JL, Gracia R, López MV (2008a) Tillage and cropping intensification effects on soil aggregation: Temporal dynamics and controlling factors under semiarid conditions. Geoderma 145:390–396
Álvaro-Fuentes J, López MV, Arrúe JL, Cantero-Martínez C (2008b) Management effects on soil carbon dioxide fluxes under semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Soil Sci Soc Am J 72:194–200
Álvaro-Fuentes J, Morell FJ, Madejón E, Lampurlanés J, Arrúe JL, Cantero-Martínez C (2013) Soil biochemical properties in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem as affected by long-term tillage and N fertilization. Soil Tillage Res 129:64–71
Balesdent J, Chenu C, Balabane M (2000) Relationship of soil organic matter dynamics to physical protection and tillage. Soil Tillage Res 53:215–230
Ball BC, Scott A, Parker JP (1999) Field N2O, CO2 and CH4 fluxes in relation to tillage, compaction and soil quality in Scotland. Soil Tillage Res 53:29–39
Beare MH, Cabrera ML, Hendrix PF, Coleman DC (1994) Aggregate-protected and unprotected organic matter pools in conventional- and no-tillage soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 58:787–795
Bender M, Conrad R (1995) Effect of CH4 concentrations and soil conditions on the induction of CH4 oxidation activity. Soil Biol Biochem 27:1517–1527
Böhm W (1979) Methods of studying root systems. Springer, Berlin, 188 pp
Cantero-Martínez C, Angás P, Lampurlanés J (2003) Growth, yield and water productivity of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) affected by tillage and N fertilization in Mediterranean semiarid, rainfed conditions of Spain. Field Crop Res 84:341–357
Cantero-Martínez C, Angás P, Lampurlanés J (2007) Long-term yield and water use efficiency under various tillage systems in Mediterranean rainfed conditions. Ann Appl Biol 150:293–305
Chadwick DR, Pain BF, Brookman SKE (2000) Nitrous oxide and methane emissions following application of animal manures to grassland. J Environ Qual 29:277–287
Conrad R (1995) Soil microbial processes involved in production and consumption of atmospheric trace gases. In: Gwynfryn J (ed) Advances in Microbial Ecology, vol 14. Plenum Press, New York, NY, USA, pp 207–250
Conrad R (1996) Soil microorganisms as controllers of atmospheric trace gases (H2, CO, CH4, OCS, N2O and NO). Microbiol Rev 60:609–640
Davidson EA, Janssens IA (2006) Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon decomposition and feedbacks to climate change. Nature 440:165–173
Ding WX, Meng L, Yin YF, Cai ZC, Zheng XH (2007) CO2 emission in an intensively cultivated loam as affected by long-term application of organic manure and nitrogen fertilizer. Soil Biol Biochem 39:669–679
Dörr H, Katruff L, Levin I (1993) Soil texture parameterization of the methane uptake in aerated soils. Chemosphere 26:697–713
Dunfield PF, Knowles R (1995) Kinetics of inhibition of methane oxidation by nitrate, nitrite, and ammonium in a humisol. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3129–3135
Ellert BH, Bettany JR (1995) Calculation of organic matter and nutrients stored in soils under contrasting management regimes. Can J Soil Sci 75:529–538
Forster P, Ramaswamy V, Artaxo P, Berntsen T, Betts T, Fahey DW, Haywood J, Lean J, Lowe DC, Myhre G, Nganga J, Prinn R, Raga G, Schulz M, Van Dorland R (2007) Changes in Atmospheric Constituents and in Radiative Forcing. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H, Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller H (eds) Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, United Kingdom
Grossman RB, Reinsch TG (2002) Bulk density and linear extensibility. In: Dane JH, Topp GC (eds) Methods of soil analysis. Part 4. Physical methods. American Society of Agronomy, Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI, pp 201–228
Hutchinson GL, Mosier AR (1981) Improved soil cover method for field measurement of nitrous oxide fluxes. Soil Sci Soc Am J 45:311–316
Hütsch BW (1998) Tillage and land use effects on methane oxidation rates and their vertical profiles in soil. Biol Fertil Soils 27:284–292
Hütsch BW (2001) Methane oxidation in non-flooded soils as affected by crop production – invited paper. Eur J Agron 14:237–260
Hütsch BW, Webster CP, Powlson DS (1993) Long-term effects of nitrogen fertilization on methane oxidation in soil of the Broadbalk wheat experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1307–1315
IPCC (1995) In: Houghton JT, Meria Filho LG, Bruce J, Lee H, Callander BA, Haites E, Harris N, Maskell K (eds) Climate change 1994: Radiative forcing of climate change and an evaluation of the IPCC IS92 emission scenarios. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, p 339
Kessavalou A, Mosier AR, Doran JW, Drijber RA, Lyon DJ, Heinemeyer O (1998) Fluxes of carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide, and methane in grass sod and winter wheat-fallow tillage management. J Environ Qual 27:1094–1104
Le Mer J, Roger P (2001) Production, oxidation and consumption of methane by soils: A review. Eur J Soil Biol 37:25–50
Madejón E, Murillo JM, Moreno F, López MV, Arrúe JL, Álvaro-Fuentes J, Cantero-Martínez C (2009) Effect of long-term conservation tillage on soil biochemical properties in Mediterranean Spanish areas. Soil Tillage Res 105:55–62
Mebius LJ (1960) A rapid method for the determination of organic carbon in soil. Anal Chim Acta 22:120–124
Meijide A, Cárdenas LM, Sánchez-Martín L, Vallejo A (2010) Carbon dioxide and methane fluxes from a barley field amended with organic fertilizers under Mediterranean climatic conditions. Plant Soil 328:353–367
Morell FJ, Cantero-Martínez C, Lampurlanés J, Plaza-Bonilla D, Álvaro-Fuentes J (2011) Soil carbon dioxide flux and organic carbon content: effects of tillage and nitrogen fertilization. Soil Sci Soc Am J 75:1874–1884
Morell FJ, Whitmore AP, Álvaro-Fuentes J, Lampurlanés J, Cantero-Martínez C (2012) Root respiration of barley in a semiarid Mediterranean agroecosystem: Field and modelling approaches. Plant Soil 351:135–147
Mosier AR, Halvorson AD, Reule CA, Liu XJJ (2006) Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in irrigated cropping systems in northeastern Colorado. J Environ Qual 35:1584–1598
Nelson DW, Sommers LE (1996) Total carbon, organic carbon and organic matter. In: Methods of soil analysis. Part 3. Chemical methods. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, pp 961–1010
Paustian K, Collins HP, Paul EA (1997) Management controls on soil carbon. In: Soil organic matter in temperate agroecosystems. Long-term experiments in North America. Paul EA, Paustian K, Elliott ET, Cole CV (Eds.). CRC Press, Boca Raton FL., USA, pp. 15–49
Piva JT, Dieckow J, Bayer C, Zanatta JA, de Moraes A, Pauletti V, Tomazi M, Pergher M (2012) No-till reduces global warming potential in a subtropical Ferralsol. Plant Soil 361:359–373
Plaza C, Hernández D, García-Gil JC, Polo A (2004) Microbial activity in pig-slurry-amended soils under semiarid conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1577–1585
Plaza-Bonilla D, Cantero-Martínez C, Álvaro-Fuentes J (2013) Soil aggregation and organic carbon protection in a no-tillage chronosequence under Mediterranean conditions. Geoderma 193–194:76–82
Porta J (1998) Methodologies for the analysis and characterization of gypsum in soils: A review. Geoderma 87:31–46
Reicosky DC, Dugas WA, Torbert HA (1997) Tillage-induced soil carbon dioxide loss from different cropping systems. Soil Tillage Res 41:105–118
Rochette P, Chadwick DR, de Klein CAM, Cameron K (2012) Deployment protocol. Ch. 3. In: de Klein CAM, Harvey MJ (Eds.) Nitrous oxide chamber methodology guidelines. Global Research Alliance on Agricultural Greenhouse Gases (available at: http://www.globalresearchalliance.org/app/uploads/2013/05/Chamber_Methodology_Guidelines_Chapter3.pdf)
Rochette P, Gregorich EG (1998) Dynamics of soil microbial biomass C, soluble organic C and CO2 evolution after three years of manure application. Can J Soil Sci 78:283–290
Ryan J, Ibrikci H, Sommer R, McNeill A (2009) Nitrogen in rainfed and irrigated cropping systems in the Mediterranean region. Adv Agron 104:53–136
Sainju UM, Stevens WB, Caesar-TonThat T, Liebig MA (2012) Soil greenhouse gas emissions affected by irrigation, tillage, crop rotation, and nitrogen fertilization. J Environ Qual 41:1774–1786
SAS Institute (1990) SAS user’s guide: statistics. 6th edn. Vol. 2. SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
SAS Institute Inc (2012) Using JMP 10. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Smith P (2004) Carbon sequestration in croplands: the potential in Europe and the global context. Eur J Agron 20:229–236
Smith P, Martino D, Cai Z, Gwary D, Janzen H, Kumar P, McCarl B, Ogle S, O‘Mara F, Rice C, Scholes B, Sirotenko O (2007) Agriculture. In: Metz B, Davidson OR, Bosch PR, Dave R, Meyer LA (eds) Climate Change 2007: Mitigation. Contribution of working group III to the fourth assessment report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press. Cambridge, United Kingdom/New York, NY, USA
Soil Survey Staff (1975) Soil Taxonomy: a basic system of soil classification for making and interpreting soil surveys. US Department of Agriculture, Soil Conservation Service, Washington, DC
United Nations (1998) Adoption of the Kyoto Protocol to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. Report of the Conference of the Parties on its third session held at Kyoto from 1 to 11 December 1997. Decision 1/CP.3, FCCC/CP/1997/7/Add. 1 (available at: http://unfccc.int/resource/docs/cop3/07a01.pdf).
Van Groenigen JW, Velthof GL, Oenema O, Van Groenigen KJ, Van Kessel C (2010) Towards an agronomic assessment of N2O emissions: a case study for arable crops. Eur J Soil Sci 61:903–913
Venterea RT, Burger M, Spokas KA (2005) Nitrogen oxide and methane emissions under varying tillage and fertilizer management. J Environ Qual 34:1467–1477
Whittenbury R, Phillips KC, Wilkinson JK (1970) Enrichment, isolation and some properties of methane utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 61:205–218
Yagüe MR, Quílez D (2013) Residual effects of fertilization with pig slurry: Double cropping and soil. Agron J 105:70–78
Acknowledgments
The priceless involvement of Montse Llovera in setting-up and maintaining the gas chromatography equipment facilitated this work. We also acknowledge the field and laboratory assistance of Silvia Martí, Carlos Cortés, Miquèl Segalàs, Josan Palacio, Héctor Martínez, Ana Bielsa, Jonatan Ovejero, Douglas Winter, Soni Hueftle and Dr. Jorge Lampurlanés. Dr. Carmen Castañeda and Dr. Juan Herrero characterized the soil of the short-term experiment. D. Plaza-Bonilla was awarded an FPU fellowship by the Spanish Ministry of Education. This research was supported by the Comisión Interministerial de Ciencia y Tecnología of Spain (grants AGL 2007-66320-C02-01 and AGL 2010-22050-C03-01/02), the Aragon Government and La Caixa (grant GA-LC-050/2011), the Department of Agriculture of the Government of Catalonia (grant 2012 AGEC 00012) and the European Union (FEDER funds).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Kees Jan van Groenigen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plaza-Bonilla, D., Cantero-Martínez, C., Bareche, J. et al. Soil carbon dioxide and methane fluxes as affected by tillage and N fertilization in dryland conditions. Plant Soil 381, 111–130 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2115-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2115-8