Abstract
Background and aims
Ultramafic soils are characterized by relatively high concentrations of nickel (Ni), chromium (Cr), and cobalt (Co). Globally, some ultramafic outcrops are also rich in copper (Cu) and other metals. The occurrence of Cu-accumulating plants on such soils is a very rare phenomenon so far only described from Sri Lanka. The objective of this study was to evaluate the elemental profiles of plants growing in their natural habitat on polymetallic Cu-rich ultramafic soils, with particular focus on unusual uptake of Cu, and possible co-accumulation of other metals.
Methods
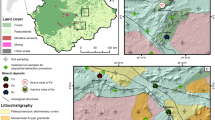
This study focused on Cu-rich ultramafic soils in the Bidu-Bidu Hills (Malaysia) and those in Macedo-Niquelândia and Americano do Brasil (Brazil) where chemical analyses of bedrock, soil and plant leaf samples was undertaken.
Results and conclusions
Although the elemental profile of plants growing on Cu-enriched ultramafic soils reflects that of their environment with elevated concentrations of Co, Cr, Cu and Zn, significant accumulation of these metals is rare. Accumulation of Cu by most plants follows an ‘Excluder’ response, with limited Cu uptake, even by Cu-tolerant plants on soils with high total and extractable Cu concentrations. Some plants show slightly higher uptake than normal, and might act as ‘Indicators’, but true hyperaccumulation of this metal is questionable.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anic V, Hinojosa LF, Díaz-Forester J, Bustamante E, Fuente L, De LM, Casale JF, de la Harpe JP, Montenegro G, Ginocchio R (2010) Influence of soil chemical variables and altitude on the distribution of high-alpine plants: the case of the Andes of central Chile. Arct Antarct Alp Res 42(2):152–163
Baillie I, Evangelista P, Inciong N (2000) Differentiation of upland soils on the Palawan ophiolitic complex, Philippines. Catena 39:283–299
Baker DE, Senef JP (1995) Copper. In: Alloway BJ (ed) Heavy metals in soils. Blackie Academic and Professional, London, pp 179–205
Berbert CO, Svisero DP, Sial AN, Meyer HOA (1981) Upper mantle material in the Brazilian shield. Earth Sci Rev 17:109–133
Beurlen H, Cassedanne JP (1981) The Brazilian mineral resources. Earth Sci Rev 17:177–206
Brooks RR (1977) Copper and cobalt uptake by Haumaniastrum species. Plant Soil 48:541–545
Brooks RR, Malaisse F (1985) The heavy metal-tolerant flora of southcentral africa – a multidisciplinary approach. Balkema, Rotterdam
Brooks RR, Wither ED, Westra LY (1978) Biogeochemical copper anomalies on Salajar Island, Indonesia. J Geochem Explor 10:181–188
Brooks RR, Reeves RD, Morrison RS, Malaisse F (1980) Hyperaccumulation of copper and cobalt: a review. Bull Soc Roy Bot Belg 13:166–172
Brooks RR, Trow JM, Veillon JM, Jaffré T (1981) Studies on manganese-accumulating Alyxia species from New Caledonia. Taxon 30(2):420–423
Brooks RR, Grégoire J, Madi L, Malaisse F (1982) Phytogéochimie de l’anticlinal de Kasonta (Shaba, Zaïre). Geo Eco Trop 6:219–228
Brooks RR, Naidu SD, Malaisse F, Lee J (1987) The elemental content of metallophytes from the copper/cobalt deposits of Central Africa. Bull Soc Roy Bot Belg 119:179–191
Brooks RR, Reeves RD, Baker AJM, Rizzo JA, Diaz Ferreira H (1990) The Brazilian serpentine plant expedition (BRASPEX), 1988. Natl Geogr Res 6:205–219
Brooks RR, Reeves RD, Baker AJM (1992) The serpentine vegetation of Goiás State, Brazil. In: Baker AJM, Proctor J, Reeves RD (eds) The vegetation of ultramafic (serpentine) soils, intercept. Andover, UK, pp 67–81
Chipeng FK, Hermans C, Colinet G, Faucon M-P, Ngongo M, Meerts P, Verbruggen N (2009) Copper tolerance in the cuprophyte Haumaniastrum katangense (S. Moore) P.A. Duvign. & Plancke. Plant Soil 328(1–2):235–244
Clarkson DT, Hanson JB (1980) The mineral nutrition of higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 31:239–298
Cole MM (1971) Biogeographical/geobotanical and biogeochemical investigations connected with exploration for nickel–copper ores in the hot wet summer/dry winter savanna woodland environment. J S Afr Inst Mines Metall 71:199–209
Cole MM (1973) Geobotanical and biogeochemical investigations in the sclerophyllous woodland and shrub associations of the Eastern Goldfields area of Western Australia with particular reference to the role of Hybanthus floribundus (Lindl.) F. Muell. as a nickel indicator and accumulator plant. J Appl Ecol 10:269–320
Cole MM (1991) The vegetation of the greenstone belts of Western Australia. In: Roberts BA, Proctor J (eds) The Ecology of Areas with Serpentinized Rocks: A World View. Academic Publishers, Kluwer, pp 343–373
Dohrmann R (2006) Cation exchange capacity methodology II: A modified silver–thiourea method. Appl Clay Sci 34:38–46
Duvigneaud P (1958) La végétation du Katanga et de ses sols métallifères. Bull Soc R Bot Belg 90(2):127–278
Faucon M-P, Shutcha MN, Meerts P (2007) Revisiting copper and cobalt concentrations in supposed hyperaccumulators from SC Africa: influence of washing and metal concentrations in soil. Plant Soil 301:29–36
Faucon M-P, Meersseman A, Shutcha MN, Mahy G, Luhembwe MN, Malaisse F, Meerts P (2010) Copper endemism in the Congolese flora: a database of copper affinity and conservational value of cuprophytes. Plant Ecol Evol 143:5–18
Fernandes JC, Henriques FS (1991) Biochemical, physiological, and structural effects of excess copper in plants. Bot Rev 57:246–27
Gonzalez I, Muena V, Cisternas M, Neaman A (2008) Acumulación de cobre en una comunidad vegetal afectada por contaminación minera en el valle de Puchuncaví. Chile central Rev Chil Hist Nat 81(2):279–291
Hall JL (2002) Cellular mechanisms for heavy metal detoxification and tolerance. J Exp Bot 53:1–11
Hochstetter F (1860) Dun Mountain Copper Mining Company. Nelson Examiner and New Zealand Chronicle, Volume XIX, Issue 34, 28 April 1860, pp 4
Jaffré T (1977) Accumulation du manganèse par des especes associées aux terrains ultrabasiques de Nouvelle-Calédonie. Comptes Rendus Academie des Science, Paris 284:1573–1575 Série D
Jiang LY, Yang XE, He ZL (2004) Growth response and phytoextraction of copper at different levels in soils by Elsholtzia splendens. Chemosphere 55:1179–1187
Kabata-Pendias A, Pendias H (2001) Trace elements in soils and plants, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Krämer U (2010) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 61:517–534
Krämer U, Clemens S (2006) Functions and homeostasis of zinc, copper, and nickel in plants. In: Tamás M, Martinoia E (eds) Molecular biology of metal homeostasis and detoxification from microbes to man. Springer, Berlin, pp 214–272
Küpper H, Gotz B, Mijovilovich A, Kupper FC, Meyer-Klaucke W (2009) Complexation and toxicity of copper in higher plants. I. Characterization of copper accumulation, speciation, and toxicity in Crassula helmsii as a new copper accumulator. Plant Physiol 151(2):702–714
Lee J (1977) Phytochemical and biogeochemical studies on nickel accumulation by some New Caledonian plants. PhD Thesis, Massey University, Palmerston North, NZ
Lee WG, Bannister P, Bastow Wilson J, Mark A (1997) Element uptake in an ultramafic flora, Red Mountain, New Zealand. In: Jaffré, T, Reeves, RD Becquer, T (ed) Écologie des milieu sur roches ultramafiques et sur sols métallifères, Documents Scientifiqueset Techniques No. III/2, ORSTOM, Nouméa, pp 179–186
Lindsay WL, Norvell WA (1978) Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese, and copper. Soil Sci Soc Amer J 42:421–428
Macnair M (2003) The hyperaccumulation of metals by plants. Adv Bot Res 40:63–105
Malaisse F, Grégoire J, Brooks RR, Morrison RS, Reeves RD (1978) Aeolanthus biformifolius: a hyperaccumulator of copper from Zaïre. Science 199:887–888
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic, London
Morrison RS (1980) Aspects of the accumulation of cobalt, copper and nickel by plants. PhD Thesis, Massey University, NZ
Morrison RS, Brooks RR, Reeves RD, Malaisse F (1979) Copper and cobalt uptake by metallophytes from Zaïre. Plant Soil 53:535–539
Newton-Smith J (1967) Bidu–Bidu Hills area, Sabah: explanation of sheet 5–117–2 and part of 5–117–1: Borneo Reg Malaysia Geol Surv Rept 4
Nilson AA (1981) The nature of the Americano do Brasil mafic–ultramafic complex and associated sulfide mineralization, Goiás, Brazil. PhD Thesis, Department of Geology, University of Western Ontario, London, Ont
Paton A, Brooks RR (1996) A re-evaluation of Haumaniastrum species as geobotanical indicators of copper and cobalt. J Geochem Explor 56(1):37–45
Peng H, Wang-Müller Q, Witt T, Malaisse F, Küpper H (2012) Differences in copper accumulation and copper stress between eight populations of Haumaniastrum katangense. Environ Exp Bot 79:58–65
Pollard AJ, Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2014) Facultative hyperaccumulation of heavy metals and metalloids. Plant Sci 217–218:8–17
Proctor J (2003) Vegetation and soil and plant chemistry on ultramafic rocks in the tropical Far East. Perspect Plant Ecol 6:105–124
Proctor J, Cole MM (1991) The ecology of ultramafic areas in Zimbabwe. In: Roberts BA, Proctor J (ed), The Ecology of Areas with Serpentinized Rocks: A World View, Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 313–331
Rajakaruna N, Baker AJM (2004) Serpentine: a model habitat for botanical research in Sri Lanka. Cey J Sci (Bio Sci) 32:1–19
Rajakaruna N, Bohm BA (2002) Serpentine and its vegetation: a preliminary study from Sri Lanka. J Appl Botany 76:20–28
Reeves RD (2003) Tropical hyperaccumulators of metals and their potential for phytoextraction. Plant Soil 249:57–65
Reeves RD (2006) Hyperaccumulation of trace elements by plants. In: Morel JL, Echevarria G, Goncharova N (eds) Phytoremediation of metal–contaminated soils, Proceedings of the NATO Advanced Study Institute, Třešt’ Castle, Czech Republic, 18–30 August 2002, NATO Science Series: IV: Earth and Environmental Sciences 68. Springer, Berlin, pp 25–52
Reeves RD, Baker AJM (2000) Metal-accumulating plants. In: Raskin I, Ensley BD (eds) Phytoremediation of toxic metals: using plants to clean up the environment. Wiley, New York, pp 193–229
Reeves RD, Brooks RR (1978) Trace element analysis of geological materials. Wiley, New York
Reeves RD, Baker AJM, Becquer T, Echevarria G, Miranda ZJG (2007) The flora and biogeochemistry of the ultramafic soils of Goiás state, Brazil. Plant Soil 293:107–119
Reuther W (1957) Copper and soil fertility. In: Soil, the yearbook of agriculture. U.S. Gov. Printing Office, Washington, D.C. pp 128–135
Shepherd PR (1983) Biogeochemical and geobotanical studies of the ultramafic areas of North Cape. BSc (Hons.) Report, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand
Stevenson FJ (1986) Cycles of soil– carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, micronutrients. Wiley, NewYork
Tang S, Wilke B, Huang C (1999) The uptake of copper by plants dominantly growing on copper mining spoils along the Yangtze River, the People’s Republic of China. Plant Soil 209(2):225–232
Trescases JJ, Melfi AJ, Barros de Oliveira SM (1981) Nickeliferous laterites of Brazil. In: Laterization Processes. Proceedings of the international seminar on laterization processes. Trivandrum, India 1979:170–184
Van der Ent A, Baker AJM, Reeves RD, Pollard AJ, Schat H (2013) Hyperaccumulators of metal and metalloid trace elements: facts and fiction. Plant Soil 362(1–2):319–33
Wang H, Shan X-Q, Wen B, Zhang S, Wang ZJ (2004) Responses of antioxidative enzymes to accumulation of copper in a copper hyperaccumulator of Commelina communis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 47:1–9
Weng G, Wu L, Wang Z, Luo Y, Christie P (2005) Copper uptake by four Elsholtzia ecotypes supplied with varying levels of copper in solution culture. Environ Int 31(6):880–884
Wernick B (1981) The archaean of Brazil. Earth Sci Rev 17:31–48
Yruela I (2009) Copper in plants: acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct Plant Biol 36(5):409–430
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Henk Schat.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Ent, A., Reeves, R.D. Foliar metal accumulation in plants from copper-rich ultramafic outcrops: case studies from Malaysia and Brazil. Plant Soil 389, 401–418 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2385-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2385-9