Abstract
Background and aims
Soluble boron (B) sources pose a risk of B toxicity to seedlings just after planting and leaching losses after application and before plant uptake. Boron phosphate (BPO4) has low water solubility and slowly releases B, and hence could be safe for seedlings. Therefore, we investigated the toxicity of several B sources co-granulated with mono-ammonium phosphate (MAP) or co-compacted with potassium chloride referred to as muriate of potash (MOP) on canola seedlings.
Methods
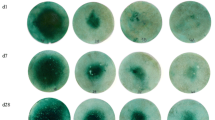
Ulexite, borax, colemanite and BPO4 compounds synthesized at 500 or 800 °C for 1 h were co-granulated with MAP or co-compacted with MOP at inclusion rates of 0.5, 1.0 and 2.0 % B. The seedling toxicity of these products was evaluated by placing a fertilizer granule in the centre of a soil-filled Petri dish in which canola was seeded. The area of the non-vegetated zone around the granule application site was evaluated after 7 and 12 days of growth.
Results
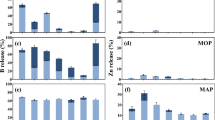
Application of ulexite, borax and colemanite co-granulated with MAP resulted in toxicity symptoms at the lowest concentration of 0.5 % B, and the area of the affected zone increased with increasing concentrations of B in the granule, whereas no toxicity symptoms were observed with the application of co-granulated BPO4 products even at 2.0 % B content. Similar results were observed for the MOP fertilizers, except for colemanite which showed no toxicity when combined with MOP. Hot water-soluble B concentrations were measured in concentric sections around the granule application site and were in agreement with the toxicity results, with concentration in the toxic range close to the granule for the most soluble B sources.
Conclusions
BPO4 is potentially a seedling-safe B fertilizer source.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abat M, Degryse F, Baird R, McLaughlin MJ (2014a) Formulation, synthesis and characterization of boron phosphate (BPO4) compounds as raw materials to develop slow-release boron fertilizers. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 177:860–868
Abat M, Degryse F, Baird R, McLaughlin MJ (2014b) Responses of canola to the application of slow-release boron fertilizers and their residual effect. doi:10.2136/sssaj2014.07.0280
Bingham FT (1982) Boron. In: Page AL, Miller RH, Keeney DR (eds) In methods of soil analysis part 2 - chemical and microbiological properties, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, pp 431–448
Broschat TK (2008) Release rates of soluble and controlled-release boron fertilizers. Hort Techn 18:471–474
Byers DE, Mikkelsen RL, Cox FR (2001) Greenhouse evaluation of four boron fertilizer materials. J Plant Nutr 24:717–725
Camacho-Cristobal JJ, Rexach J, Gonzalez-Fontes A (2008) Boron in plant: deficiency and toxicity. J Integ Plant Biol 50:1247–1255
Cayton MTC (1985) Boron toxicity in rice. pp 1–11. International Rice Research Institute
Gupta UC (1979) Boron nutrition of crops. Adv Agron 31:273–307
Gupta UC (1983) Boron deficiency and toxicity symptoms for several crops as related to tissue boron levels. J Plant Nutr 6:387–395
Hughes-Games G (1991) Boron for field crops. Soil factsheet order no. 631.021-1. Ministry of Agriculture and Food British Columbia, Abbotsford, pp 1–3
Keren R, Bingham FT (1985) Boron in water, soil and plants. Adv Soil Sci 1:229–276
Magda A, Pode R, Muntean C, Medeleanu M, Popa A (2010) Synthesis and characterization of ammonium phosphate fertilizers with boron. J Serbian Chem Soc 75:951–963
Marschner H (1986) Mineral nutrition in higher plants. Academic, London
Miller MH, Bates TE, Singh D, Baweja AS (1971) Response of corn to small amounts of fertilizer placed with the seed: 1. Greenhouse studies. Agron J 63:365–368
Mortvedt JJ (1994) Needs for controlled-availability micronutrient fertilizers. Fertil Res 38:213–221
Mortvedt JJ, Osborn G (1965) Boron concentration adjacent to fertilizer granules in soil, and its effect on root growth. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 29:187
Nable RO, Banuelos GS, Paull JG (1997) Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 193:181–198
Ozturk O, Soylu S, Ada R, Gezgin S, Babaoglu M (2010) Studies on differential response of spring canola cultivars to boron toxicity. J Plant Nutr 33:1141–1154
Qian P, Schoenau J (2010) Effects of conventional and controlled release phosphorus fertilizer on crop emergence and growth response under controlled environment conditions. J Plant Nutr 33:1253–1263
Ray LF (1972) Boron phosphate as boron source for plant life. Ed. U S Patent. pp 1–4, United States
Shorrocks V (1997) The occurrence and correction of boron deficiency. Plant Soil 193:121–148
Sims JT, Johnson GV (1991) Micronutrient soil tests. In: Mortvedt JJ, Cox FR, Shuman LM, Welch RM (eds) Micronutrients in agriculture, 2nd edn. Soil Science Society of America, Madison
Wear JI, Wilson CM (1954) Boron materials of low solubility and their use for plant growth. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 18:425–428
Winsor HW (1950) Boron sources of moderate solubility as supplements for sandy soils. Soil Sci 69:321–332
Acknowledgments
The first author thanks the University of Adelaide for the scholarship to enable her to pursue her PhD and the Sarawak State Government for a study leave. The authors also thank Bogumila Tomczak, Deepika Setia, Colin Rivers, Ashleigh Broadbent and the staff of CSIRO Land and Water for their advice and technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ismail Cakmak.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abat, M., Degryse, F., Baird, R. et al. Boron phosphates (BPO4) as a seedling-safe boron fertilizer source. Plant Soil 391, 153–160 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2424-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2424-6