Abstract
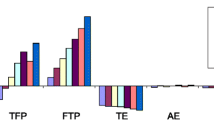
The purpose of this paper is to evaluate the variations in SOE efficiency and productivity from the perspectives of macroeconomic fluctuations and systematic reform in China during 1986–2003. We use Data Envelopment Analysis to measure SOE efficiency. Subsequently, we use the Malmquist Index of Productivity change to measure productivity growth. The empirical results show that SOE efficiency and productivity exhibited obvious improvements during periods of strong systematic reform and a prosperous economy. The systematic reform after 1998 had a clear-cut impact on SOE performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The research results of Jefferson and Rawski were published in (starting from 1987) the Journal of Comparative Economics, Economic Development and Cultural Change, China Quarterly, and some native Chinese journals. These articles were collected in Zheng and Rawski (1993), Jefferson and Rawski (1996), and Jefferson et al. (1996).
Nevertheless, some scholars suspected that these results were affected by measurement error in the data. For instance, intermediate input deflators over-deflated inputs, which resulted in an understatement of the quantity of intermediate inputs. At the same time, actual total output was overstated. Altogether these problems caused an over-statement of TFP. In addition, the deflator index of the industrial value added had a declining tendency in several years, which was also against the norm (Woo et al. 1993, 1994). In response to these criticisms, Jefferson et al. (1996) explained that the deflator index caused minor measurement error. The deflator index had a small impact on the SOE TFP even though its impact on township enterprises was relatively large. Thus the conclusion about the SOE’s TFP should be valid.
Most value-added data of 1986–1991 were taken from China Provincial Statistical Yearbook while the data of 1992–2003 were from China Statistical Yearbook.
The official term is state-owned and state-holding enterprises.
These reforms focused on enhancing SOEs’ independence in the process of deregulation, taking the responsibility of disposing the operating profit or loss, and distributing rewards according to productivity.
Note that the value in the supplementary model did not improve (see also Table 2).
Due to a minor revision in China Statistical Yearbook in 1993 and a substantial revision in 1998 that relate to firm coverage and classifications, we allow for breaks between 1992–1993 and 1997–1998.
References
Bai C, Li DD, Wang Y (1997) Enterprise productivity and efficiency: when is up really down. J Comp Econ 24(2):265–280
Bai CE, Li DD, Tao Z, Wang Y (2000) A multitask theory of state enterprise reform. J Comp Econ 28(4):716–738
Banker RD, Charnes A, Cooper WW (1984) Some models for estimating technical and scale efficiencies in data envelopment analysis. Manag Sci 30(9):1078–1092
Boisso D, Grosskopf S, Hayes K (2000) Productivity and efficiency in the US: effects of business cycles and public capital. Reg Sci Urban Econ 30:663–681
Charnes A, Cooper WW, Rhodes E (1978) Measuring the efficiency of decision making unit. Eur J Oper Res 2(6):429–444
Chen YS (1997) The relative productive efficiency of township-village—enterprises in Mainland China, Dissertation of University of Texas at Dallas
Cheng Y, Lo D (2002) Explaining the financial performance of China’s industrial enterprises: beyond the competition-ownership controversy. China Q 170:412–440
Chow G (1985) The Chinese economy. Harper and Row, NY
Dollar D (1990) Economic reform and allocative efficiency in China’s state-owned industry. Econ Dev Cult Change 39(1):89–105
Färe R, Grosskopf S, He Y, Horvath J (1996) Industrial productivity growth in China: 1980–84 vs. 1984–85. In: Färe R, Grosskopf S (eds) Intertemporal production frontiers: with dynamic DEA. Kluwer Academic Publishers
Färe R, Grosskopf S, Lindgren B, Roos P (1989) Productivity developments in Swedish hospitals: a Malmquist output index approach, Discussion Paper 89-3, Southern Illinois University at Carbondale
Jefferson GH, Rawski TG (1996) Industrial reform in China: innovation, competition and ownership induction policies. In: Lin CS (ed) Industrial reform and efficiency in China. People’s Publishing Company, Yunan, pp 52–98
Jefferson GH, Rawski TG, Zheng Y (1996) Chinese industrial productivity : trends, measurement issues, and recent development. J Comp Econ 23(2):146–180
Li DD, Wu C (2002) Reforming state-owned enterprises: diversifying ownership versus improving management. In: Tsui AS, Lau CM (eds) The management of enterprises in the People’s Republic of China. Kluwer Academic Publishers, pp 87–108
Lin Y, Cai F, Li Z (1997) On the relationship between the cooperation of modern enterprise system and the aim of the state-owned enterprises reform. Econ Res J (Jingji Yanjiu), March, 3–10
Liu F-C, Yang Y-M (1994) The operation loss of the SOEs and the loss-reduction polices. China Stat, October, 15–17
Lo D (1999) Reappraising the performance of China’s state-owned industrial enterprises, 1980–96. Camb J Econ 23(6):693–718
Parker E (1997) The effect of scale on the response to reform by Chinese state-owned construction units. J Dev Econ 52(2):331–353
Perkins D (1988) Reforming China’s economic system. J Econ Lit 26(2):601–645
Rawski TG (1993) On the relationship between economic benefit and economic efficiency. Econ Res J (Jingji Yanjiu), June, 38–40
Shiu A (2002) Efficiency of Chinese enterprise. J Prod Anal 17(3):255–267
Steinfeld ES (1999) Forging reform in China: the fate of state-owned industry. Cambridge University Press, NY
Tian G (1994) The state-owned enterprise reform of China and the mode, steps for transforming economic system smoothly. Econ Res J (Jingji Yanjiu) 11:3–9
Woo WT, Fan G, Hai W, Jin Y (1993) The efficiency and macroeconomic consequences of Chinese enterprises reform. China Econ Rev 4(2):153–168
Woo WT, Hai W, Jin Y, Fan G (1994) How successful has Chinese enterprise reform been? Fitfall in opposite biased and focus. J Comp Econ 18(3):410–437
World Bank (1985) China: long-term development issues and options. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Yu G, Wei Q, Brockett P (1996) A generalized data envelopment analysis model: a unification and extension of existing methods for efficiency analysis of decision making units. Ann Oper Res 66:47–89
Zhang W (1997) Decision rights, residual claim and performance: a theory of how the Chinese state enterprise reform works. China Econ Rev 8(1):67–82
Zhang A, Zhang Y, Zhao R (2001) Impact of ownership and competition on the productivity of Chinese enterprises. J Comp Econ 29(2):327–346
Zhang A, Zhang Y, Zhao R (2002) Profitability and productivity and productivity of Chinese industrial firms measurement and ownership implications. China Econ Rev 13(1):65–88
Zheng Y, Rawski TG (eds) (1993) Productivity and reform in China’s industry. Social Science Literature Publishing Company, Beijing
Zheng J, Liu X, Bigsten A (1998) Ownership structure and determinants of technical efficiency: an application of data envelopment analysis to Chinese enterprises (1986–1990). J Comp Econ 26(3):465–484
Zheng J, Liu X, Bigsten A (2003) Efficiency, technical progress, and best practice in Chinese state enterprises (1980–1994). J Comp Econ 31(1):134–152
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, FC., Vijverberg, CP.C. & Chen, YS. Productivity and efficiency of state-owned enterprises in China. J Prod Anal 29, 249–259 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-007-0078-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11123-007-0078-y