Abstract
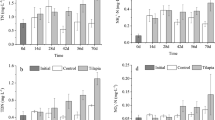
The introduction of omnivorous tilapia into a variety of aquatic systems worldwide has led to a number of serious ecological problems. One of the main issues is an increase in water turbidity, which affects not only light penetration but also primary production and the distribution of phytoplankton and benthic algae in shallow lakes. These changes cause deterioration of water quality in these lakes. A 12-week mesocosm experiment was set up to test the hypotheses that omnivorous Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) introduced to a shallow water system will increase turbidity and nutrient levels in the water column and thereby boost growth of phytoplankton and depress benthic algae. Relative to the control treatments, the presence of tilapia led to higher concentrations of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in the water column, greater biomass of phytoplankton as measured by chlorophyll a (Chl a), greater concentrations of total suspended solids and inorganic suspended solids, lower light intensity, and lower biomass of benthic algae at the sediment surface. A tube-microcosm experiment using 32P radio tracer indicated that the presence of tilapia accelerated the release of sediment phosphorus (P) into the water column. We conclude that these invasive omnivorous fish not only stimulate growth of phytoplankton in shallow lakes by increasing nutrients in water column, but also depress benthic algal growth by promoting sediment resuspension, leading to increased turbidity of the water. Thus the removal of tilapia could be a useful practice for managers of shallow aquatic ecosystems, promoting benthic primary production and improving water clarity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adámek Z, Maršálek B (2013) Bioturbation of sediments by benthic macroinvertebrates and fish and its implication for pond ecosystems: a review. Aquacult Int 21:1–17
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Barbour MT, Gerritsen J, Snyder BD, Stribling JB (1999) Rapid bioassessment protocols for use in streams and wadeable rivers. USEPA, Washington
Carpenter SR, Kitchell JF, Hodgson JR (1985) Cascading trophic interactions and lake productivity. Bioscience 35:634–639
Carpenter SR, Cottingham KL, Schindler DE (1992) Biotic feedbacks in lake phosphorus cycles. Trends Ecol Evol 7:332–336
Casal CMV (2006) Global documentation of fish introductions: the growing crisis and recommendations for action. Biol Invasions 8:3–11
Covich AP, Palmer MA, Crowl TA (1999) The role of benthic invertebrate species in freshwater ecosystems: zoobenthic species influence energy flows and nutrient cycling. Bioscience 49:119–127
Datta S, Jana BB (1998) Control of bloom in a tropical lake: grazing efficiency of some herbivorous fishes. J Fish Biol 53:12–24
Diana JS, Dettweiler DJ, Lin CK (1991) Effect of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on the ecosystem of aquaculture ponds, and its significance to the trophic cascade hypothesis. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:183–190
Dodds WK (2003) The role of periphyton in phosphorus retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. J Phycol 39:840–849
Elser JJ, Urabe J (1999) The stoichiometry of consumer-driven nutrient recycling: theory, observations, and consequences. Ecology 80:735–751
Figueredo CC, Giani A (2005) Ecological interactions between Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus, L.) and phytoplanktonic community of the Furnas Reservoir (Brazil). Freshw Biol 50:1391–1403
Genkai-Kato M, Vadeboncoeur Y, Liboriussen L, Jeppesen E (2012) Benthic-planktonic coupling, regime shifts, and whole-lake primary production in shallow lakes. Ecology 93:619–631
GISD (2012) Global invasive species database—Oreochromis niloticus. Available from: http://www.issg.org/database/species/ecology.asp?si=1322&fr=1&sts=sss&lang=EN
Gulati RD, Van Donk E (2002) Lakes in the Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: state-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia 478:73–106
Hansson LA (1988) Effects of competitive interactions on the biomass development of planktonic and periphytic algae in lakes. Limnol Oceanogr 33:121–128
Hansson LA (1989) The influence of a periphytic biolayer on phosphorus exchange between substrate and water. Arch Hydrobiol 115:21–26
Hansson LA (1992) Factors regulating periphytic algal biomass. Limnol Oceanogr 37:322–328
Havens KE (1991) Fish-induced sediment resuspension: effects on phytoplankton biomass and community structure in a shallow hypereutrophic lake. J Plankton Res 13:1163–1176
Havens KE, Hauxwell J, Tyler AC, Thomas S, McGlathery KJ, Cebrian J, Valiela I, Steinman AD, Hwang SJ (2001) Complex interactions between autotrophs in shallow marine and freshwater ecosystems: implications for community responses to nutrient stress. Environ Pollut 113:95–107
Jeppesen E, Søndergaard M, Lauridsen TL, Davidson TA, Liu ZW, Mazzeo N, Trochine C, Özkan K, Jensen HS, Trolle D, Starling F, Lazzaro X, Johansson LS, Bjerring R, Liboriussen L, Larsen SE, Landkildehus F, Egemose S, Meerhoff M (2012) Biomanipulation as a restoration tool to combat eutrophication: recent advances and future challenges. Adv Ecol Res 47:411–488
Jespersen AM, Christoffersen K (1987) Measurements of chlorophyll a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Arch Hydrobiol 109:445–454
Lammens EHRR (1991) Diets and feeding behaviour. In: Winfield IJ, Nelson JS (eds) Cyprinid fishes: systematics, biology, and exploitation. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 127–155
Leung B, Lodge DM, Finnoff D, Shogren JF, Lewis MA, Lamberti G (2002) An ounce of prevention or a pound of cure: bioeconomic risk analysis of invasive species. Proc R Soc Lond B 269:2407–2413
Lèveque C (2002) Out of Africa: the success story of tilapias. Environ Biol Fish 64:461–464
Liboriussen L, Jeppesen E (2003) Temporal dynamics in epipelic, pelagic and epiphytic algal production in a clear and a turbid shallow lake. Freshw Biol 48:418–431
Liu Z, Zhong P, Zhang X, Ning J, Larsen SE, Jeppesen E (2014) Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded (submitted)
Loeb SL, Reuter JE, Goldman CR (1983) Littoral zone production of oligotrophic lakes. Periphyton of freshwater ecosystems. Springer, Netherlands, pp 161–167
Lu K, Jin C, Dong S, Gu B, Bowen SH (2006) Feeding and control of blue-green algal blooms by tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Hydrobiologia 56:111–120
Lubarsky HV, Hubas C, Chocholek M, Larson F, Manz W, Paterson DM, Gerbersdorf SU (2010) The stabilization potential of individual and mixed assemblages of natural bacteria and microalgae. PLoS ONE 5:e13794
Menezes RF, Attayde JL, Vasconcelos RF (2010) Effects of omnivorous filter-feeding fish and nutrient enrichment on the plankton community and water transparency of a tropical reservoir. Freshw Biol 55:767–779
Milstein A, Ahmed AF, Masud OA, Kadir A, Wahab MA (2006) Effects of the filter feeder silver carp and the bottom feeders mrigal and common carp on small indigenous fish species (SIS) and pond ecology. Aquaculture 258:439–451
Panek FM (1987) Biology and ecology of carp. In: Cooper EL (ed) Carp in North America. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, pp 1–15
Parker IM, Simberloff D, Lonsdale WM et al (1999) Impact: toward a framework for understanding the ecological effects of invaders. Biol Invasions 1:3–19
Persson A (1997) Phosphorus release by fish in relation to external and internal load in a eutrophic lake. Limnol Oceanogr 42:577–583
Scheffer M, Hosper SH, Meijer M-L, Moss B, Jeppesen E (1993) Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends Ecol Evol 8:275–279
Schindler DE, Scheuerell MD (2002) Habitat coupling in lake ecosystems. Oikos 98:177–189
Spears BM, Carvalho L, Perkins R, Paterson DM (2008) Effects of light on sediment nutrient flux and water column nutrient stoichiometry in a shallow lake. Water Res 42:977–986
Suresh AV, Lin CK (1992) Tilapia culture in saline waters: a review. Aquaculture 106:201–226
Tolhurst TJ, Consalvey M, Paterson DM (2008) Changes in cohesive sediment properties associated with the growth of a diatom biofilm. Hydrobiologia 596:225–239
Torres GS, Silva LS, Rangel LM, Attayde JL, Huszar VLM (2016) Cyanobacteria are controlled by omnivorous filter-feeding fish (Nile tilapia) in a tropical eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 765:115–129
Turker H, Eversole AG, Brune DE (2003) Filtration of green algae and cyanobacteria by Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, in the Partitioned Aquaculture System. Aquaculture 215:93–101
van Dam AA, Beveridge MC, Azim ME, Verdegem MC (2002) The potential of fish production based on periphyton. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 12:1–31
Vanni MJ (1996) Nutrient transport and recycling by consumers in lake food webs: implications for algal communities. In: Polis GA, Winemiller KO (eds) Food webs: Integration of patterns and dynamics. Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 81–95
Vanni MJ (2002) Nutrient cycling by animals in freshwater ecosystems. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 33:341–370
Yi C, Guo L, Ni L, Luo C (2016) Silver carp exhibited an enhanced ability of biomanipulation tocontrol cyanobacteria bloom compared to bighead carp inhypereutrophic Lake Taihu mesocosms. Ecol Eng 89:7–13
Zambrano L, Martinez-Meyer E, Menezes N, Peterson AT (2006) Invasive potential of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in American freshwater systems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63:1903–1910
Zhang XF, Liu ZW, Gulati RD, Jeppesen E (2013) The effect of benthic algae on phosphorus exchange between sediment and overlying water in shallow lakes: a microcosm study using 32P as tracer. Hydrobiologia 710:109–116
Zhang XF, Liu ZW, Jeppesen E, Taylor WD (2014) Effects of deposit-feeding tubificid worms and filter-feeding bivalves on benthic–pelagic coupling: implications for the restoration of eutrophic shallow lakes. Water Res 50:135–146
Zhang XF, Mei XY, Gulati RD, Liu ZW (2015) Effects of N and P enrichment on competition between phytoplankton and benthic algae in shallow lakes: a mesocosm study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:4418–4424
Zhang XF, Liu ZW, Jeppesen E, Taylor WD, Rudstam LG (2016) Effects of benthic-feeding common carp and filter-feeding silver carp on benthic-pelagic coupling: implications for shallow lake management. Ecol Eng 88:256–264
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Lars G. Rudstam in Cornell University for his comments and the comments of editor and anonymous reviewers substantially improved the paper. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Ken Chan for improving the English of this manuscript. This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No: 31570456) and Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Anhui (No. 1608085MD85) and Guangdong (No. 2016A030313103). It was completed while the senior author was a visiting scientist at Cornell University, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Mei, X. & Gulati, R.D. Effects of omnivorous tilapia on water turbidity and primary production dynamics in shallow lakes: implications for ecosystem management. Rev Fish Biol Fisheries 27, 245–254 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-016-9458-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11160-016-9458-6