Abstract
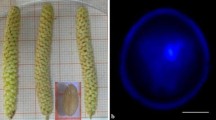
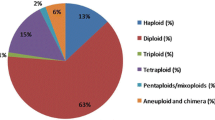
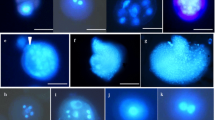
Jatropha curcas is an undomesticated crop and its plantations did not meet commercial expectation due to absence of high yielding commercial line with desired agronomic characters. Earlier, breeding efforts did not pay much attention on yield and disease improving traits due to lack of desired genetic variability. Isolated microspore culture is one of the most widely used in vitro techniques to induce gametic embryogenesis with wide degree of genetic variability for the development of haploids and doubled haploids. In this study, an efficient isolated microspore culture system was established for different genotypes with the optimization of various factors that affect microspore embryogenesis. After 15–20 days of culture at 25 °C, tetrads, mid, early un-vacuolated and vacuolated late stage uninucleate microspores, which were preincubated at 4 °C for 7 days under shaking conditions, induced the formation of embryo like structures (ELSs) in a modified MS medium with 2.0 mg/l, 2,4-d, 0.1 mg/l kinetin, 300 mg/l casein hydrolysate, 1 g/l glutamine, 0.5 mg/l folic acid, 0.05 mg/l biotin and 5% sucrose. It is observed that the shock at 4 °C for 7 days, subsequently incubation of microspore cultures at 25 °C for 15 days and then at 15 °C for 10 days played a significant role in induction and accelerated creation of ELSs in three different genotypes. Microscopic analyses confirmed the different developmental stages of microspore embryogenesis including cell division and multicellular embryo like structures. Additionally, flow cytometric analyses verified the calli and ELSs were haploids in nature and strengthened that the origin was from microspores. This study supports the evidence of gametic embryogenesis in Jatropha microspore culture.
Key message
Development of haploid and doubled haploids in Jatropha Microspore culture.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- DH:
-
Doubled haploids
- Kn:
-
Kinetin
- BAP:
-
6-Benzyl amino purine
- 2,4-d :
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscopy
- OM:
-
Optical microscopy
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- ELSs:
-
Embryo like structures
References
Blasco M, Badenes ML, Naval M (2015) Embryogenic response from anther culture of cultivars of loquat (Eriobotryajaponica (Thunb.) Lindl.) from different origins. Euphytica 205:337–348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1386-3
Brew-Appiah RA, Ankrah N, Liu W, Konzak CF, Von Wettstein D, Rustgi S (2013) Generation of doubled haploid transgenic wheat lines by microspore transformation. PLoS ONE 8(11):1–13
Britt AB, Kuppu S (2016) Cenh3: an emerging player in haploid induction technology. Front Plant Sci 7(357):1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00357
Bueno MA, Pintos B, Martin A (2006) Induction of embryogenesis via isolated microspore culture in Oleaeuropaea L. Olivebioteq 1:9–25
Bueno MA, Pintos B, Hofer M, Martin A (2005) Pro-embryos induction from Oleaeuropaea L. isolated microspore culture. Acta Physiol Plant 27:695–701
Chaubey P, Singh NP, Chetri SK, Heikrujam M, Agrawal V (2013) Effective micropropagation protocol in Jatropha curcas L. an important biodiesel plant and establishment of ISSR based genetic fidelity among the regenerants. Phytomorphology 63:33–44
Cheng Y, Ma R, Jiao Y, Qiao N, Li T (2013) Impact of genotype, plant growth regulators and activated charcoal on embryogenesis induction in microspore of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). S Afr J Bot 88:306–309
Chiancone B, Karasawa MM, Gianguzzi V (2015) Early embryo achievement through isolated microspore culture in Citrus clementina Hort. ex Tan., cvs. “Monreal Rosso” and “Nules.” Front Plant Sci 6:413
Currais LM, Canhoto JM, Linde PVD (2012) Microsporogenesis in Jatropha curcas L. Acta Hortic 935:113–120
Debnath M, Bisen PS (2008) Jatropha Curcas L., a multipurpose stress resistant plant with a potential for ethnomedicine and renewable energy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 9:288–306
Dolezel J, Greilhuber J, Suda J (2007) Estimation of nuclear DNA content in plants using flow cytometry. Nat Protoc 2:2233–2244
Dunwell JM (2010) Haploids in flowering plants: origins and exploitation. Plant Biotechnol J 8:377–424
Dunwell JM, Wilkinson MJ, Nelson S (2010) Production of haploids and doubled haploids in oil palm. BMC Plant Biol 10:218
Folling L, Olesen A (2002) Transformation of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) microspore derived callus and microspores by particle bombardment. Plant Cell Rep 20:629–636
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirement suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Germana MA (2006) Doubled haploid production in fruit crops. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 86:131–145
Germana MA (2007) Haploidy. In: Khan I (ed) Citrus, genetics, breeding and biotechnology. CABI, Wallingford, pp 167–196
Germana MA (2009) Haploid and doubled haploids in fruit trees. In: Touraev A, Forster B, Jain M (eds) Advances in haploid production in higher plants. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 241–263
Germana MA (2010) Anther culture for haploid and doubled haploid production. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 104:283–300
Germana MA (2011) Gametic embryogenic and haploid technology as valuable support to plant breeding. Plant Cell Rep 30:839–857
Gilbert N (2011) The seeds of an economy. Nature 474:S18–S19
Gu K, Mao H, Yin Z (2014) Production of marker-free transgenic Jatropha curcas expressing hybrid Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin Cry1 Ab/1Ac for resistance to larvae of tortrix moth (Archips micaceanus). Biotechnol Biofuels 7:68
Hassan AKMS, Begum N, Bari LS, Jahan MAA (2014) In vitro shoot multiplication of the biodiesel plant Jatropha curcas L. through direct organogenesis. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res 49(1):41–46
Hofer M (2004) In vitro androgenesis in apple-improvement of the induction phase. Plant Cell Rep 22:365–370
Hofer M, Touraev A, Heberle-Bors E (1999) Induction of embryogenesis from isolated apple microspores. Plant Cell Rep 18:1012–1017
Jalali S, Kancharla N, Yepuri V, Arockiasamy S (2020) Exploitation of Hi-C sequencing for improvement of genome assembly and in-vitro validation of differentially expressing genes in Jatropha curcas L. 3 Biotech 10(91):1–9
Kaewpoo M, Te-chato S (2010) Study on ploidy level of micropropagated Jatropha curcas L. via flow cytometry. J Agric Technol 6:391–400
Kancharla N, Jalali S, Narasimham JV, Nair V, Yepuri V, Thakkar B, Reddy V, Kuriakose B, Madan N, Arockiasamy S (2019) De novo sequencing and hybrid assembly of the biofuel crop Jatropha curcas L. identification of quantitative trait loci for geminivirus resistance. Genes 10:69
Kasha KJ, Maluszynski M (2003) Production of doubled haploids in crop plant. An introduction. Doubled haploid production in crop plants. Springer, New York, pp 1–4
Kelliher T, Starr D, Richbourg L, Chintamanani S, Delzer B, Michael L, Nuccio GJ, Chen Z, McCuiston J, Wang W, Liebler T, Bullock P, Martin B (2017) MATRILINEAL, a sperm-specific phospholipase, triggers maize haploid induction. Nature 542:105–109
Kelliher T, Starr D, Su X, Tang G, Chen Z, Carter J, Wittich PE, Dong S, Green J, Bruch E, McCuiston J, Gu W, Sun Y, Strebe T, Roberts J, Bate NJ, Que Q (2019) One step genome editing of elite crop germplasm during haploid induction. Nat Biotech 37:287–292
Kumar A, Sharma S (2008) An evaluation of multipurpose oil seed crop for industrial uses (Jatropha curcas L.). A review. Ind Crop Prod 28:1–10
Li C, Luo Li FuQ, Niu L, Xu FZ (2014) Isolation and functional characterization of JcFT, a FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT) homologous gene from the biofuel plant Jatropha curcas. Plant Biol 14:125
Lichter R (1982) Induction of haploid plants from isolated pollen of Brassica napus L. Z Pflanzenphysiol 105:427–434
Liu FH, Kirchoff BK, Wu GJ, Liao JP (2007) Microsporogenesis and male gametogenesis in Jatropha curcas (Euphorbiaceae). J Torrey Bot Soc 134:335–343
Liu C, Li X, Meng D, Zhong Y, Chen C, Dong X, Xu X, Chen B, Li W, Li L, Tian X, Zhao H, Song W, Luo H, Zhang Q, Lai J, Jin W, Yan J, Chen S (2017) A 4-bp insertion at ZmPLA1 encoding a putative phospholipase A generates haploid induction in maize. Mol Plant 10(3):520–522
Mohammadi PP, Moieni A, Ebrahimi A, Javidfar F (2012) Doubled haploid plants following colchicine treatment of microspore-derived embryos of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 108:251–256
Mukherjee P, Varshney A, Johnson TS (2011) Jatropha curcas: a review on biotechnological status and challenges. Plant Biotechnol Rep 5:197–215
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Neeta SM, Arockiasamy S, Narasimham JV, Patil M, Yepuri V, Sarkar P (2019) Anther culture for the production of haploid and doubled haploids in Jatropha curcas L. and its hybrids. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 138(1):181–192
Ochatt SJ (2008) Flow cytometry in plant breeding. Cytometry A 73:581–598
Ochatt SJ, Zhang YX (1996) In vitro haploidization of fruit trees. In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In vitro haploid production in higher plants. Current plant science and biotechnology in agriculture, vol 25. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-017-1858-5_11
Otto F (1990) DAPI staining of fixed cells for high-resolution flow cytometry of nuclear DNA. Methods Cell Biol 33:105–110
Palmer CE, Keller WA, Arnison PG (1996) Utilization of Brassica haploids. In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In vitro haploid production in higher plants. Current plant science and biotechnology in agriculture, vol 25. Springer, Dordrecht
Perera PIP, Hocher V, Verdeil JL, Bandupriya HDD, Yakandawala DMD, Weerakoon LK (2008) Androgenic potential in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 92:293–302
Perera PIP, Ordonez CA, Lopez- Lavalle LAB, Dedicova B (2014) A milestone in the doubled haploid pathway of Cassava. Protoplasma 251:233–246
Perera PIP, Ordonez CA, Dedicova B, Ortega PE (2014) Reprogramming of cassava (Manihot esculenta) microspores towards sporophytic development. AoB Plants 6:1–19
Ravi M, Chan SW (2010) Haploid plants produced by centromere-mediated genome elimination. Nature 464:615–618
Ren J, Wu P, Tramp B, Tian X, Lubberstedt T, Chen S (2017) Novel technologies in doubled haploid line development. Plant Biotechnol 15:1361–1370
Reynolds TL (1997) Pollen embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 33:1–10
Saharan V, Shrimali D, Shah MA, Ranwah Brand Sharma R (2011) Factors influencing the establishment of haploid embryonic callus from anthers in Jatropha curcas (L.). Indian J Genet 71:283–285
Seguí-Simarro JM (2010) Androgenesis revisited. Bot Rev 76:377–404
Segui-Simarro JM (2015) Editorial: doubled haploidy in Model and Recalcitrant species. Front Plant Sci 6:1175
Segui-Simarro JM, Nuez F (2008) How microspores transform into haploid embryos: changes associated with embryogenesis induction and microspore-derived embryogenesis. Physiol Plant 134:1–12
Sen C, Singh RP, Singh MK, Singh HB (2011) Effect of cold pre-treatment on anther culture of boro rice hybrids. Int J Plant Reprod Biol 3:69–73
Shariatpanahi ME, Ahmadi B (2016) Isolated microspore culture and its applications in plant breeding and genetics. In: Anis M, Ahmad N (eds) Plant tissue culture: propagation, conservation and crop improvement. Springer, Singapore, pp 487–507
Shariatpanahi ME, Belogradova K, Hessamvaziri L, Heberle-Bors E, Touraev A (2006) Efficient embryogenesis and regeneration in freshly isolated and cultured wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) microspores without stress pretreatment. Plant Cell Rep 25:1294–1299
Singh K, Singh B, Verma SK, Patra DD (2014) Jatropha curcas: a ten-year story from hope to despair. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 35:356–360
Smykalova I, Vetrovcova M, Klima M, Machackova I, Griga M (2006) Efficiency of microspore culture for doubled haploid production in the breeding project “Czech Winter Rape.” Czech J Genet Plant Breed 42:58–71
Snape JW, Simpson E (1986) The utilization of doubled haploid lines in quantitative genetics. Bulletin de la Société Botanique de France. Actualités Botaniques 133(4):59–66
Srivastava P, Chaturvedi R (2008) In vitro androgenesis in tree species: an update and prospect for further research. Biotechnol Adv 26:482–491
Stoehr MU, Zsuffa L (1990) Induction of haploids in Populus maximowiczii via embryogenic calli. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 23:49–58
Sujatha M, Mukta N (1996) Morphogenesis and plant regeneration from tissue cultures of Jatropha curcas. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 44:135–141
Van Eijck J, Romijn H, Balkema A, Faaij A (2014) Global experience with Jatropha cultivation for bioenergy: an assessment of socio-economic and environmental aspects. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 32:869–889
Wang H, Dong B, Jiang J, Fang W, Guan Z, Liao Y, Chen S, Chen F (2014) Characterization of in vitro haploid and doubled haploid Chrysanthemum morifolium plants via unfertilized ovule culture for phenotypical traits and DNA methylation pattern. Front Plant Sci 5:738
Wedzony M, Forster BP, Zur I, Golemiec E, Szechynska-Hebda M, Dubas GG (2009) Progress in doubled haploid technology in higher plants. In: Touraev A, Forster BP, Jain SM (eds) Advances in haploid production in higher plants. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–34
Yan G, Liu H, Wang H, Lu Z, Wang Y, Mullan D, Hamblin J, Liu C (2017) Accelerated generation of selfed pure line plants for gene identification and crop breeding. Front Plant Sci 8:1786
Yao L, Zhang Y, Liu C, Liu Y, Wang Y, Liang D, Liu J, Sahoo G, Kelliher T (2018) OsMATL mutation induces haploid seed formation in indica rice. Nat Plants 4:530–533
Yepuri V, Narasimham JV, Sai Shankar P, Kancharla N, Jalali S, Arockiasamy S (2018) Influence of genetic and morphological markers in evaluation of Jatropha diversity. Int J Pure App Biosci 6:114–123
Yepuri V, Jalali S, Kancharla N, Reddy VB, Arockiasamy S (2020) Development of genome wide transposable elements based repeat junction markers in Jatropha (Jatropha curcas L.). Mol Biol Rep 47:5091–5099
Zhang H, Tan E, Suzuki Y, Hirose Y, Kinoshita S, Okano H, Kudoh J, Shimizu A, Saito K, Watabe S, Asakawa S (2014) Dramatic improvement in genome assembly achieved using doubled-haploid genomes. Sci Rep 4:6780
Zhang C, Zhang L, Zhang S, Zhu S, Wu P, Chen Y, Li M, Jiang H, Wu G (2015) Global analysis of gene expression profiles in physic nut (Jatropha curcas L.) seedlings exposed to drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 15:17
Zhao X, Meng Z, Wang Y, Chen W, Sun C, Cui B, Cui J, Yu M, Zeng Z, Guo S, Luo D, Cheng JQ, Zhang R, Cui H (2017) Pollen magnetofection for genetic modification with magnetic nanoparticles as gene carriers. Nat Plants 3:956–964
Zheng MY (2003) Microspore culture in wheat (Triticum aestivum)-doubled haploid production via induced embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 73:213–230
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Ajit Sapre, R&D Group President at the Reliance Industries Ltd, for the encouragement and support for this work and Mr. Janyavula V. Narasimham and Dr Makarand Phadke for their guidance all through this study. We thank Reliance Industries Limited for funding this research. We thank Dr. Jose M. Seguí Simarro (Spain) & Dr. Raja Krishna Kumar for critically evaluating the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SA conceptualized the Idea, designed the experiments, wrote and edited the manuscript. VS, MP and SA conducted microspore culture experiments. PS did optical, SEM and TEM study. SH provided germplasm and hybrids. VS, MP and PS reviewed and edited the manuscript. SD provided guidance, support, reviewed and edited the paper. SA supervised the entire study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they don’t have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Maria Antonietta Germanà.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shrivastava, V., Savarimuthu, A., Patil, M. et al. Gametic embryogenesis and callogenesis in Isolated microspore culture of Jatropha curcas L. a recalcitrant bioenergy crop. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 144, 359–370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01959-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-020-01959-3