Abstract
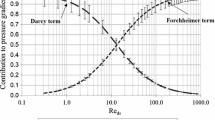
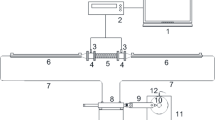
The aim of our experimental work was to establish a simple relation between the flow parameters and the morphological parameters of metallic foam. We used foam samples made from different metals or alloys (Cu, Ni, Ni-Cr, etc) and of various thicknesses. Pore size ranged between 500 and 5000 μm. We measured the pressure profiles in foam samples using a specific experimental set-up of 12 pressure sensors distributed 1 cm apart along the main flow axis. The experimental loop made it possible to use indifferently water or air as working fluid. For the study of the gas (air) flow, velocities ranged roughly from 0 up to 20 m/s and for the liquid (water) flow, velocities ranged between 0 and 0.1 m/s. The measurements of the pressure gradients were performed systematically. We validated the Forchheimer flow model. The influence of the compressibility effects on permeability and inertia coefficient was emphasized. We demonstrated that the pore size Dp in itself is sufficient to describe flow laws in such high porosity material: K and β are respectively proportional to Dp2 and Dp−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashby M.F. and Evans A.G. et al. (2000). Metal Foams: A Design Guide. Butterworth – Heinemann, Boston, MA
Banhart J. (2001). Manufacture, Characterization and application of cellular metals and metal foams. Prog. Mater. Sci. 46: 559–632
Bhattacharya A. and Calmidi V. et al. (2002). Thermophysical properties of high porosity metal foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45(5): 1017–1031
Boomsma K. and Poulikakos D. (2001). On the effective thermal conductivity of a threedimensionally structured fluid-saturated metal foam. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 44: 827–836
Calmidi, V.V.: Transport phenomena in high porosity metal foam. Boulder, CO, University of Colorado. Ph. D. thesis (1998)
Calmidi V.V. and Mahajan R.L. (2000). Forced convection in high porosity metal foams. J. Heat Transf. 122: 557–565
Catillon, S., Louis, C. et al.: Influence of cellular structure in catalytic reactors for H2 production: Application to improvement of methanol steam reformer by the addition of a copper foam. J. Hydrogen Energy sous presse (2005)
Chauveteau, G.: Essai sur la loi de Darcy. Université de Toulouse, Ph.D. thesis (1965)
Darcy H.P.G. (1856). Exposition et application des principes à suivre et des formules à employer dans les questions de distribution d’eau. Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon. Victor Delmont, Paris
Despois J.-F. and Mortensen A. (2005). Permeability of open-pore microcellular materials. Acta Materialia 53: 1381–1388
Du Plessis P. and Montillet A. et al. (1994). Pressure Drop Prediction for Flow through High Porosity Metallic Foams. Chem. Eng. Sci. 49: 3545–3553
Dukhan N. (2006). Correlations for the pressure drop for flow through metal foam.. Exp. Fluids 41(4): 665–672
Dukhan P.-F.R. and Alvarez-Hernandez A.R. (2006). Air flow through compressed and uncompressed aluminum foam: Measurements and correlations. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 128(5): 1004–1012
Dullien, F.A.L.: Porous Media. Fluid Transport and Pore Structure, Academic Press (1992)
Ergun S. (1952). Fluid flow through packed columns. Chem. Eng. Prog 48: 89–94
Firdaous M. and Guermond J.L. et al. (1997). Nonlinear corrections to Darcy’s law at low Reynolds numbers. J. Fluid Mech. 343: 331–50
Fourar M. and Lenormand R. et al. (2005). Inertia effects in high-rate flow through heterogeneous porous media. Trans. Porous Media 60: 353–370
Fourar M. and Radilla G. et al. (2004). On the non-linear behavior of a laminar single-phase flow through two and three-dimensional porous media. Adv. Water Res. 27: 669–677
Fourie J.G. and Du Plessis J.P. (2002). Pressure drop modelling in cellular metallic foams. Chemical Engineering Science 57(14): 2781–2789
Hernández, Á. R. Á.: Combined flow and heat transfer characterization of open cell aluminum foams, University of puerto rico. Master Sci. 93 (2005)
Hunt M.L. and Tien C.L. (1988). Effects of thermal dispersion on forced convection in fibrous media. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 31: 301–309
JIMIC-4: METFOAM2005, Kyoto, Japan (2005)
Kaviany, M.: Principles of Heat Transfer in Porous Media. Springer-Verlag (1992)
Khayargoli P. and Loya V. et al. (2004). The impact of microstructure on the permeability of metal foams. CSME 2004 Forum, Ontario, London
Langlois S. and Coeuret F. (1989). Flow-through and flow-by porous electrodes of nickel foam. I. Material characterisation. J. Appl. Electrochem. 19: 43–50
Liu J.F. and Wu W.T. et al. (2006). Measurement and correlation of friction characteristic of flow through foam matrixes. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 30(4): 329–336
Madani, B., Topin, et al. F.: Flow laws in metallic foams: experimental determination of inertial and viscous contribution. J. Porous Media 10(1) (2006)
Mei C. and Auriault J.L. (1993). The effect of weak inertia on flow through a porous medium. J. Fluid Mech. 222: 647–663
Moreira E.A. and Innocentini M.D.M. et al. (2004). Permeability of ceramic foams to compressible and incompressible flow. J. Eur. Ceramic Soc. 24: 3209–3218
Phanikumar M.S. and Mahajan R.L. (2002). Non-Darcy natural convection in high porosity metal foams. Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 45: 3781–3793
Renard P. and Genty A. et al. (2001). Laboratory détermination of the full permeability tensor. J. Geophys. Res. 106(B11): 26443–26452
Richardson J.T. and Peng Y. et al. (2000). Properties of ceramic foam catalyst supports: pressure drop. Appl. Catal. A: General 204: 19–32
Schatan, B.: Développement d’échangeur à haute température type IHX-Concept à base de mousses métalliques. france, école polytechnique universitaire de Marseille. Département Mécanique-Energétique 68 (2006)
Tadrist L. and Miscevic M. et al. (2004). About the Use of Fibrous Materials in Compact Heat Exchangers. Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 28: 193–199
Vicente, J., Daurelle, J.V., et al.: Structural properties measurement: A Morphological tool for transport properties determination 4th International Conference on Porous Metals and Metal Foaming Technology, Kyoto, Japan (2005)
Vicente J. and Topin F. et al. (2006). Open celled material structural properties measurement: from morphology to transport properties. Mater. Trans 47(9): 2195–2202
Wallis G. (1969). One-Dimensional Two-Phase Flow. Mc graw Hill, New-York, NY
Whitaker S. (1986). Flow in porous media I: a théoritical dérivation of Darcy’s law. Trans. Porous Media 1(1): 3–25
Whitaker, S.: The Forchheimer Equation: A Theoretical Development. Transport in Porous Media 25(27–61) (1996)
Wodie J.C. and Levy T. (1991). Correction non linéaire de la loi de Darcy. C. R. Acad. Sci. 312(II): 157–161
Zhao, C.Y., et al.: Thermal Transport Phenomena in Porvair. Metal Foams and Sintered Beds, in Technical report. Micromechanics Centre & Whittle Lab, Department of Engineering, University of Cambridge, Cambridge (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonnet, JP., Topin, F. & Tadrist, L. Flow Laws in Metal Foams: Compressibility and Pore Size Effects. Transp Porous Med 73, 233–254 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-007-9169-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-007-9169-5