Abstract
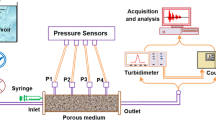
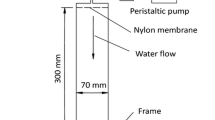
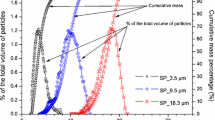
A laboratory study was undertaken on the transport and the deposition of suspended particles (silt of modal diametre 6 µm) in three columns of different length, filled with glass beads or gravel. Tracer tests were carried out at various flow velocities by short pulses of a mixture of suspended particles/dissolved tracer. The breakthrough curves were competently described with the analytical solution of a convection dispersion equation with a first-order deposition rate and the hydro-dispersive parameters were deduced. For the same experimental conditions, the results showed a difference in the behaviour of the suspended particles transport and deposition rates within the two porous media tested. The internal structure of both media governs the particle-grain collision frequency as well as the particles trapping. The scale effect was highlighted and affects the dispersivity, the size exclusion effect, the recovery rates and the deposition rates. Longitudinal dispersion increases with mean pore velocity and is described with a nonlinear relationship. The dispersivity increases with the column length. The size exclusion effect is more important in the short column. The recovery rate increases with flow velocity and decreases while increasing column length. The deposition rates increases until a critical flow velocity then decreases. This critical velocity is also sensitive to the scale effect, and increases with the column length.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C :
-
Dissolved tracer/suspended particle concentration in solution
- C 0 :
-
Initial concentration
- C R :
-
Relative concentration, equals CV P/m
- C u :
-
Uniformity coefficient
- d 50 :
-
Median grain size
- D :
-
Column inner diametre
- D 0 :
-
Molecular diffusion coefficient
- D L :
-
Longitudinal dispersion coefficient
- K :
-
Hydraulic conductivity
- K dep :
-
The deposition rate coefficient
- L :
-
Column length
- m :
-
Masse of particle injected
- Pe :
-
Péclet number
- Q :
-
Flow rate
- R :
-
Recovery rate
- t :
-
Time
- t c :
-
Convection time
- U :
-
Darcy’s velocity
- U cr :
-
Critical Darcy’s velocity
- u :
-
The average travel velocity of particles/dissolved tracer
- u r :
-
Relative velocity factor, equals (u SP − u T)/u T
- u SP :
-
The average travel velocity of suspended particles
- u T :
-
The average travel velocity of dissolved tracer
- V inj :
-
Solute injected volume
- V P :
-
Pore volume of the porous medium
- x :
-
Travel distance (column length)
- α L :
-
Longitudinal dispersivity
- δ(t):
-
Dirac function
- β :
-
A coefficient (in \({\alpha_{\rm L}=\kappa d_{50}^\beta}\))
- κ :
-
A constant (in \({\alpha_{\rm L}=\kappa d_{50}^\beta}\))
- τ :
-
tortuosity
References
Ahfir N.-D., Wang H.Q., Benamar A., Alem A., Massei N., Dupont J.-P.: Transport and deposition of suspended particles in saturated porous media: hydrodynamic effect. Hydrogeol. J. 15, 659–668 (2007)
Bear J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. Elsevier, New York (1972)
Benamar A., Wang H.Q., Ahfir N.-D., Alem A., Massei N., Dupont J.P.: Inertial effects on the transport and the rate deposition of fine particles in a soil. C. R. Geosci. 337, 497–504 (2005)
Bonelli S., Brivois O., Borghi R., Benahmed N.: On the modelling of piping erosion. C. R. Mecanique 334, 555–559 (2006)
Bouwer H.: Artificial recharge of groundwater: hydrogeology and engineering. Hydrogeol. J. 10, 121–142 (2002)
Brusseau M.L.: The influence of solute size, pore water velocity, and intraparticle porosity on solute dispersion and transport in soil. Water Resour. Res. 29(04), 1071–1080 (1993)
de Marsily G.: Quantitative Hydrogeology. Groundwater hydrology for engineers. Academic Press INC, New York (1986)
Detay M.: Le forage d’eau: Réalisation, entretien, réhabilitation. Masson, Paris (1993)
Dieulin, A.: Propagation de pollution dans un aquifère alluvial: l’effet de parcours. PhD Thesis, Université Paris-6, France (1980)
Dodds J.: La chromatographie hydrodynamique [Hydrodynamic chromatography]. Analusis 10, 109–119 (1982)
Ebach E.A., Whate R.R.: Mixing of fluids flowing through beds of packed solids. J. Am. Inst. Chem. Eng. 4, 161–164 (1958)
Elimelech M., Gregory J., Jia X., Williams R.A.: Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modeling, and Simulation. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (1995)
Frey J.M., Schmitz P., Dufreche I., Gohr Pinheiro I.: Particle deposition in porous media: analysis of hydrodynamic and weak inertial effects. Transp. Porous Media 37, 25–54 (1999)
Gohr Pinheiro I., Schmitz P., Houi D.: Particle capture in porous media when physico-chemical effects dominate. Chem. Eng. Sci. 54, 3801–3813 (1999)
Grolimund D., Borkovec M., Barmettler K., Sticher H.: Colloid-facilitated transport of strongly sorbing contaminants in natural porous media: a laboratory column study. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 3118–3123 (1996)
Grolimund D., Elimelich M., Borcovec M., Barmettler K., Kretzschmar R., Sticher H.: Transport of in situ mobilized colloidal particles in packed soil columns. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 3562–3569 (1998)
Herzig J.P., Leclerc D.M., Le Goff P.: Flow of suspension through porous media: application to deep bed filtration. Indian Eng. Chem. 62, 8–35 (1970)
Hu Q., Brusseau M.L.: The effect of solute size on diffusive-dispersion transport in porous media. J. Hydrol. 158, 305–317 (1994)
Kanti Sen T., Khilar K.C.: Review on subsurface colloids and colloid-associated contaminant transport in saturated porous media. Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci. 119, 71–96 (2006)
Koltz D., Seiler K.P., Moser H., Neumaier F.: Dispersivity and velocity relationship from laboratory and field experiments. J. Hydrol. 45, 169–184 (1980)
Kretzschmar R., Barmettler K., Grolimund D., Yan Y.D., Borkovec M., Sticher H.: Experimental determination of colloid deposition rates and collision efficiencies in natural porous media. Water Resour. Res. 33, 1129–1137 (1997)
Kretzschmar R., Borkovec M., Grolimund D., Elimelech M.: Mobile subsurface colloids and their role in contaminant transport. Adv. Agron. 66, 121–194 (1999)
Massei N., Lacroix M., Wang H.Q., Dupont J.P.: Transport of particulate material and dissolved tracer in a highly permeable porous medium: comparison of the transfer parameters. J. Contamin. Hydrol. 57, 21–39 (2002)
McDowell-Boyer L.M., Hunt J.R., Sitar N.: Particle transport through porous media. Water Resour. Res. 22(13), 1901–1921 (1986)
Moghadasi J., Müller-Steinhagen H., Jamialahmadi M., Sharif A.: Theoretical and experimental study of particle movement and deposition in porous media during water injection. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 43, 163–181 (2004a)
Moghadasi J., Müller-Steinhagen H., Jamialahmadi M., Sharif A.: Model study on the kinetics of oil field formation damage due to salt precipitation from injection. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 43, 201–217 (2004b)
Pfannkuch H.O.: Contribution à l’étude des déplacements de fluides miscibles dans un milieu poreux [Contribution to the study of miscible fluids displacements in a porous medium]. Rev. Inst. Fr. Pétrol. 18, 215–270 (1963)
Porel, G.: Transfert de soluté en aquifère crayeux: causes de modifications des résultats de traçages. PhD Thesis, Lille University, France (1988)
Roychoudhury A.N.: Dispersion in unconsolidated aquatic sediments. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 53, 745–757 (2001)
Ryan J.N., Elimelech M.: Colloid mobilization and transport in groundwater. Colloids Surf. A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 107, 1–56 (1996)
Santos A., Bedrikovetsky P.: A stochastic model for particulate suspension flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 62, 23–53 (2006)
Shapiro A.A., Bedrikovetsky P.G., Santos A., Medvedev O.O.: A stochastic model for filtration of particulate suspensions with incomplete pore plugging. Transp. Porous Media 67, 135–164 (2007)
Vigneswaran S., Suazo Ronillo B.: A detailed investigation of physical and biological clogging during artificial recharge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 35, 119–140 (1987)
Vigneswaran S., Jeyaseelan S., Das Gupta A.: A pilot-scale investigation of particle retention during artificial recharge. Water Air Soil Pollut. 25, 1–13 (1985)
Wang H.Q.: Transferts de matières en milieu saturé: outils mathématiques et modélisation numérique Mémoire HDR. Université de Rouen, France (2001)
Wang H.Q., Crampon N., Huberson S., Garnier J.M.: Linear graphical method for determining hydrodispersive characteristics in tracer experiments with instantaneous injection. J. Hydrol. 95, 143–154 (1987)
Wang H.Q., Lacroix M., Massei N., Dupont J.P.: Particle transport in porous medium: determination of hydrodispersive characteristics and deposition rates. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris Sci. Terre Planèt. 331, 97–104 (2000)
Weronski P., Walz J.Y., Elimelech M.: Effect of depletion interactions on transport of colloidal particles in porous media. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 262, 372–383 (2003)
Xu M., Eckstein Y.: Statistical analysis of the relationships between dispersivity and other physical properties of porous media. Hydrogeol. J. 5, 4–20 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahfir, ND., Benamar, A., Alem, A. et al. Influence of Internal Structure and Medium Length on Transport and Deposition of Suspended Particles: A Laboratory Study. Transp Porous Med 76, 289–307 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-008-9247-3