Abstract
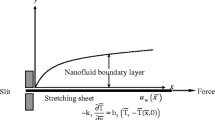
In this article, a similarity solution of the steady boundary layer flow near the stagnation-point flow on a permeable stretching sheet in a porous medium saturated with a nanofluid and in the presence of internal heat generation/absorption is theoretically studied. The governing partial differential equations with the corresponding boundary conditions are reduced to a set of ordinary differential equations with the appropriate boundary conditions via Lie-group analysis. Copper (Cu) with water as its base fluid has been considered and representative results have been obtained for the nanoparticle volume fraction parameter \({\phi}\) in the range \({0\leq \phi \leq 0.2}\) with the Prandtl number of Pr = 6.8 for the water working fluid. Velocity and temperature profiles as well as the skin friction coefficient and the local Nusselt number are determined numerically. The influence of pertinent parameters such as nanofluid volume fraction parameter, the ratio of free stream velocity and stretching velocity parameter, the permeability parameter, suction/blowing parameter, and heat source/sink parameter on the flow and heat transfer characteristics is discussed. Comparisons with published results are also presented. It is shown that the inclusion of a nanoparticle into the base fluid of this problem is capable to change the flow pattern.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, c:
-
Constants
- C f :
-
Skin friction coefficient
- C p :
-
Specific heat at constant pressure
- G :
-
Invariant group of transformations
- k nf :
-
Effective thermal conductivity of the nanofluid
- k f :
-
Thermal conductivity of the fluid
- K :
-
Permeability of the porous medium
- K 1 :
-
Permeability parameter
- Nu :
-
Local Nusselt number
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- q w :
-
Wall heat flux
- Q 0 :
-
Heat generation/absorption coefficient
- Re x :
-
Local Reynolds number
- S :
-
Suction/injection parameter
- T :
-
Temperature of the nanofluid
- T w :
-
Surface temperature
- T ∞ :
-
Temperature of the ambient nanofluid fluid
- \({\bar{{u}}, \bar{{v}}}\) :
-
Velocity components along \({\bar{{x}}}\) and \({\bar{{y}}}\) directions
- u, v:
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- \({\bar{{u}}_w (\bar{{x}})}\) :
-
Stretching velocity
- \({\bar{{U}}}\) :
-
Free stream velocity of the nanofluid
- U :
-
Dimensionless free stream velocity of the nanofluid
- \({\bar{{v}}_w}\) :
-
Mass flux velocity
- \({\bar{{x}}, \bar{{y}}}\) :
-
Cartesian coordinates along the surface and normal to it
- x, y:
-
Dimensionless coordinates
- α nf :
-
Effective thermal diffusivity of the nanofluid
- α f :
-
Thermal diffusivity of the fluid
- α i :
-
Constants in (14)
- \({\phi}\) :
-
Solid volume fraction of the nanoparticles
- η :
-
Similarity variable
- λ:
-
Heat generation/absorption parameter
- μ nf :
-
Effective dynamic viscosity of the nanofluid
- μ f :
-
Dynamic viscosity of the fluid
- ν f :
-
Kinematic viscosity of the fluid
- θ :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- ρ nf :
-
Effective density of the nanofluid
- ψ :
-
Stream function
- nf:
-
Nanofluid
- f:
-
Fluid
- s:
-
Solid
- *:
-
G Group variables
References
Abel M.S., Sanjayanand E., Nandeppanavar M.M.: Viscoelastic MHD flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet with viscous and ohmic dissipations. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13, 1808–1821 (2008)
Abu-Nada E.: Application of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement of separated flows encountered in a backward facing step. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29, 242–249 (2008)
Abu-Nada E., Oztop H.F.: Effects of inclination angle on natural convection in enclosures filled with Cu-water nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 30, 669–678 (2009)
Ahmad S., Pop I.: Mixed convection boundary layer flow from a vertical flat plate embedded in a porous medium filled with nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 37, 987–991 (2010)
Aminossadati S.M., Ghasemi B.: Natural convection cooling of a localized heat source at the bottom of a nanofluid-filled enclosure. Eur. J. Mech. B/Fluids 28, 630–640 (2009)
Buongiorno J.: Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 128, 240–250 (2006)
Cheng P., Minkowycz W.J.: Free convection about a vertical flat plate embedded in a porous medium with application to heat transfer from a dike. J. Geophys. Res. 82, 2040–2044 (1977)
Congedo, P.M., Collura, S., Congedo, P.M.: Modeling and analysis of natural convection heat transfer in nanofluids. In: Proceedings of ASME Summer Heat Transfer Conference, vol. 3, pp. 569–579 (2009)
Cortell R.: Flow and heat transfer of a fluid through a porous medium over a stretching surface with internal heat generation/absorption and suction/blowing. Fluid Dyn. Res. 37, 231–245 (2005)
Das S.K., Choi S.U.S., Yu W., Pradeep T.: Nanofluids: Science and Technology. Wiley, New Jersey (2007)
Elbashbeshy E.M.A., Basid M.A.A.: Heat transfer in a porous medium over a stretching surface with internal heat generation and suction or injection. Appl. Math. Comput. 158, 799–807 (2004)
Ghasemi B., Aminossadati S.M.: Natural convection heat transfer in an inclined enclosure filled with a water-CuO nanofluid. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 55, 807–823 (2009)
Ghasemi B., Aminossadati S.M.: Periodic natural convection in a nanofluid-filled enclosure with oscillating heat flux. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 1–9 (2010)
Ho, C.J., Chen, M.W., Li, Z.W.: Effect of natural convection heat transfer of nanofluid in an enclosure due to uncertainties of viscosity and thermal conductivity. In: Proceedings of ASME/JSME Thermal Engineering. Summer Heat Transfer Conference—HT, vol. 1, pp. 833–841 (2007)
Ho C.J., Chen M.W., Li Z.W.: Numerical simulation of natural convenction of nanofluid in a square enclosure: Effects due to uncertainties of viscosity and thermal conductivity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 51, 4506–4516 (2008)
Ibrahim F.S., Mansour M.A., Hamad M.A.A.: Lie-group analysis of radiation and magnetic field effects on free convection and mass transfer flow past a semi-infinite vertical flat plate. Elect. J. Diff. Equ. 2005, 1–17 (2005)
Ingham, D.B., Pop, I. (eds): Transport Phenomena in Porous Media III. Elsevier, Oxford (2005)
Ishak A., Nazar R., Pop I.: Magnaetohydrodynamic stagnation point flow towards a stretching vertical sheet. Magnetohydrodynamics 42, 17–30 (2006)
Kakaç S., Pramuanjaroenkij A.: Review of convective heat transfer enhancement with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 3187–3196 (2009)
Kandasamy R., Muhaimin I.: Scaling transformation for the effect of temperature-dependent fluid viscosity with thermophoresis particle deposition on MHD-free convection heat and mass transfer over a porous stretching surface. Transp. Porous Media 84, 549–568 (2010)
Khan W.A., Pop I.: Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 53, 2477–2483 (2010)
Lakshmisha K.N., Venkateswaran S., Nath G.: Three-dimensional unsteady flow with heat and mass transfer over a continuous stretching surface. ASME J. Heat Transf. 110, 590–595 (1988)
Layek G.C., Mukhopadhyay S., Samad S.A.: Heat and mass transfer analysis for boundary layer stagnation-point flow towards a heated porous stretching sheet with heat absorption/generation and suction/blowing. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 34, 347–356 (2007)
Mahapatra T.R., Gupta A.S.: Heat transfer in stagnation-point flow towards a stretching sheet. Heat Mass Transf. 38, 517–521 (2002)
Muhaimin I., Kandasamy R., Hashim I.: Scalimg transformation for the effect of chemical reaction on free convection heat and mass transfer in the presence of variable stream conditions. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 88, 1320–1328 (2010)
Mukhopadhyay S., Layek G.C., Samad S.A.: Study of MHD boundary layer flow over a heated stretching sheet with variable viscosity. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 48, 4460–4466 (2005)
Muthtamilselvan M., Kandaswamy P., Lee J.: Heat transfer enhancement of copper-water nanofluids in a lid-driven enclosure. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 1501–1510 (2010)
Nazar R., Amin N., Filip D., Pop I.: Unsteady boundary layer flow in the region of the stagnation-point on a stretching sheet. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 42, 1241–1253 (2004)
Nield D.A., Bejan A.: Convection in Porous Media, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2006)
Nield D.A., Kuznetsov A.V.: The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 52, 5792–5795 (2009)
Oztop H.F., Abu-Nada E.: Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 29, 1326–1336 (2008)
Pal D.: Heat and mass transfer in stagnation-point flow towards a stretching surface in the presence of buoyancy force and thermal radiation. Meccanica 44, 145–158 (2009)
Prasad K.V., Vajravelu K., Datti P.S.: The effects of variable fluid properties on the hydro-magnetic flow and heat transfer over a non-linearly stretching sheet. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 49, 603–610 (2010a)
Prasad K.V., Pal D., Umesh V., Rao N.S.P.: The effect of variable viscosity on MHD viscoelastic fluid flow and heat transfer over a stretching sheet. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 15, 331–344 (2010b)
Raptis A., Perdikis C.: Viscous flow over a non-linearly stretching sheet in the presence of chemical reaction and magnetic field. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 41, 527–529 (2006)
Tiwari R.K., Das M.K.: Heat transfer augmentation in a two-sided lid-driven differentially heated square cavity utilizing nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 50, 2002–2018 (2007)
Vadasz, P. (ed.): Emerging Topics in Heat and Mass Transfer in Porous Media. Springer, New York (2008)
Vafai, K. (ed.): Handbook of Porous Media, 2nd edn. Taylor & Francis, New York (2005)
Wang C.Y.: Free convection on a vertical stretching surface. J. Appl. Math. Mech. (ZAMM) 69, 418–420 (1989)
Wang X.-Q., Mujumdar A.S.: Heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids: a review. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 46, 1–19 (2007)
Wang X.-Q., Mujumdar A.S.: A review on nanofluids—Part I: theoretical and numerical investigations. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 25, 613–630 (2008a)
Wang X.-Q., Mujumdar A.S.: A review on nanofluids—Part II: experiments and applications. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 25, 631–648 (2008b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamad, M.A.A., Pop, I. Scaling Transformations for Boundary Layer Flow near the Stagnation-Point on a Heated Permeable Stretching Surface in a Porous Medium Saturated with a Nanofluid and Heat Generation/Absorption Effects. Transp Porous Med 87, 25–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9683-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-010-9683-8