Abstract
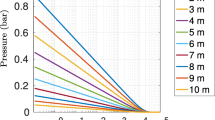
The injection of supercritical CO2 through wells into deep brine reservoirs is a topic of interest for geologic carbon sequestration. The injected CO2 is predominantly immiscible with the brine and its low density relative to brine leads to strong buoyancy effects. The displacement of brine by CO2 in general is a multidimensional, complex nonlinear problem that requires numerical methods to solve. The approximations of vertical equilibrium and complete gravity segregation (sharp interface) have been introduced to reduce the complexity and dimensionality of the problem. Furthermore, for the radial displacement process considered here, the problem can be formulated in terms of a similarity variable that reduces spatial and temporal dependencies to a single variable. However, the resulting ordinary differential equation is still nonlinear and exact solutions are not available. The existing analytical solutions are approximations limited to certain parameter ranges that become inaccurate over a large portion of the parameter space. Here, I use a matched boundary extrapolation method to provide much greater accuracy for analytical/semi-analytical approximations over the full parameter range.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bear J.: Dynamics of Fluids in Porous Media. American Elsevier Publishing Company Inc., New York (1972)
Dentz M., Tartakovsky D.: Abrupt-interface solution for carbon dioxide injection into porous media. Transp. Porous Med. 79, 15–27 (2009a)
Dentz M., Tartakovsky D.: Response to “Comments on Abrupt-Interface Solutionfor Carbon Dioxide Injection into Porous Media by Dentz and Tartakovsky (2008)” by Lu et al. Transp. Porous Med. 79, 39–41 (2009b)
IPCC: IPCC special report on Carbon dioxide capture and storage. Prepared by working group III of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Metz, B.O., Davidson, H.C., de Coninck, M.L., Meyer, L.A. (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge/New York (2005)
Juanes R., Spiteri E.J., Orr F.M. Jr, Blunt M.J.: Impact of relative permeability hysteresis on geological CO2 storage. Water Resour. Res. 42, W12418 (2006)
Liu Y., Wang L., Yu B.: Sharp front capturing method for Carbon dioxide plume propagation during injection into a deep confined aquifer. Energy Fuels 24, 1431–1440 (2010)
Nordbotten, J.M., Dahle, H.K.: Impact of capillary forces on large-scale migration of CO2. XVIII International Conference on Water Resources, CMWR, Barcelona (2010)
Nordbotten J.M., Celia M.A.: Similarity solutions for fluid injection into confined aquifers. J. Fluid Mech. 561, 307–327 (2006)
Nordbotten J.M., Celia M.A., Bachu S.: Injection and storage of CO2 in deep saline aquifers: analytical solution for CO2 plume evolution during injection. Trans. Porous Med. 58(3), 339–360 (2005)
Vilarrasa, V., Bolster, D., Dentz, M., Olivella, S., Carrera, J.: Effects of CO2 compressibility on CO2 storage in deep saline aquifers. Transp. Porous Med. (2010). doi:10.1007/s11242-010-9582-z
Yortsos Y.C.: A theoretical analysis of vertical flow equilibrium. Trans. Porous Med. 18, 107–129 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Houseworth, J.E. Matched Boundary Extrapolation Solutions for CO2 Well-Injection into a Saline Aquifer. Transp Porous Med 91, 813–831 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-011-9874-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-011-9874-y