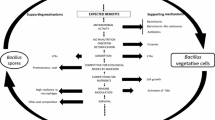
Abstract
An investigation was carried out into the recovery from calf faeces of Bacillus coagulans spores added to the feed as probiotic. For this purpose, Bacillus coagulans spores (9 log10 CFU g−1) were given daily to 10 calves during the whole farming periods; another 10 calves acted as controls. Throughout the trial the faecal spore counts were significantly (P < 0.01) higher in the treated group than in the controls (averaging 2.1 × 105 vs 3.7 × 104 CFU g−1). Bacterial cells were recovered from faecal samples and ribotyping matched the strain isolated from faecal sample to the clone administered to the animals. In addition, the recovered cells were found to maintain their functionality aspects of acid production, survival in artificial gastric juice and in the presence of bile, and attachment to human intestinal epithelial cells. The results further elucidate the fate of spore formers administered to calves, and this will help in the development of new species-specific nutritional strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abada EAE (2008) Isolation and characterization of an antimicrobial compound from Bacillus coagulans. Anim Cells Syst 12:41–46
Adami A, Cavazzoni V (1993) Biomass production, preservation and characteristics of a strain of Bacillus coagulans usable as probiotic. Microbiologie Aliments Nutrition 11:93–100
Adami A, Cavazzoni V (1999) Occurrence of selected bacterial groups in the faeces of piglets fed with Bacillus coagulans as probiotic. J Basic Microbiol 39:3–9. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-4028(199903)39:1<3::AID-JOBM3>3.0.CO;2-O
Adami A, Sandrucci A, Cavazzoni V (1997) Piglets fed from birth with the probiotic Bacillus coagulans as additive: zootechnical and microbiological aspects. Ann Microbiol Enzimol 47:139–149
Annuk H, Shchepetova J, Kullisaar T, Songisepp E, Zilmer M, Mikelsaar M (2003) Characterization of intestinal lactobacilli as putative probiotic candidates. J Appl Microbiol 94:403–412. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.2003.01847.x
Atlas RM (2004) Handbook of microbiological media. 3rd edn. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton
Bondi M, Messi P, Danila I, Marchioretto DI (2000) Biological characteristics of LABLYS98, a Lactobacillus sporogenes for use as a probiotic compound. Industrie Alimentari 39:704–710
Bruce J (1996) Automated system rapidly identifies and characterizes microorganisms in food. Food Technol 50:77–81
Casula G, Cutting SM (2002) Bacillus probiotics: spore germination in the gastrointestinal tract. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:2344-2352. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.5.2344-2352.2002
Cavazzoni V, Adami A (1998) Caecal microflora in chickens fed with Bacillus coagulans as probiotic. Ann Microbiol Enzimol 48:13–18
Cavazzoni V, Adami A, Castrovilli C (1998) Performance of broiler chickens supplemented with Bacillus coagulans as probiotic. Brit Poult Sci 39:526–529 doi:10.1080/00071669888719
Ciffo F, Dacarro C, Giovanetti M, Mazza PG (1987) Gastric resistance of Bacillus subtilis spores used in oral bacteriotherapy: in vitro studies. Farmacia Terapia 4:163–169
De Clerk E, Rodriguez-Diaz M, Forsyth G, Lebbe L, Logan NA, DeVos P (2004) Polyphasic characterization of Bacillus coagulans strains, illustrating heterogeneity within the species, and emended description of the species. System Appl Microbiol 27:50–60. doi:10.1078/0723-2020-00250
De Vecchi E, Drago L (2006) Lactobacillus sporogenes or Bacillus coagulans: misidentification or mislabelling? Int J Prob Preb 1:3–10
Donskey CJ, Hoyen CK, Das SM, Farmer S, Dery M, Bonomo RA (2001) Effect of oral Bacillus coagulans administration on the density of vancomycin-resistant enterococci in the stool of colonized mice. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:84–88. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2001.00948.x
Duc LH, Hong HA, Barbosa TM, Henriques O, Cutting S (2004) Characterization of Bacillus probiotics available for human use. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2161–2171. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.4.2161-2171.2004
Fuller R (1992) Probiotics: The scientific basis. Chapman and Hall, London
FAO/WHO (2002) Joint FAO/WHO (Food and Agriculture Organization/Word Health Organization) working group report on drafting guidelines for the evaluation of probiotics in food. London, Ontario, Canada
Hammer BW (1915) Bacteriological studies on the coagulation of evaporated milk. Iowa Agric Exp Stn Res Bull 19:119–131
Hoa TT, Duc LH, Isticato R, Baccigalupi L, Ricca E, Van PH, Cutting SM (2001) The fate and dissemination of Bacillus subtilis spores in a murine model. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3819–3823. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.9.3819-3823.2001
Hong HA, Duc LH, Cutting SM (2005) The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:813–835. doi:10.1016/j.femsre.2004.12.001
Huang JM, La Ragione RM, Nunez A, Cutting SM (2008) Immunostimolatory activity of Bacillus spores. FEMS Immunol Med Mic 53:195–203. doi:10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00415.x
Hyronimus B, Le Marrec C, Hadj Sassi A, Deschamps A (2000) Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 61:193–197. doi:10.1016/S0168-1605(00)00366-4
Hyronimus B, Le Marrec C, Urdaci MC (1998) Coagulin, a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance produced by Bacillus coagulans I4. J Appl Microbiol 85:42–50. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2672.1998.00466.x
Jadamus A, Vahjen W, Simon O (2001) Growth behaviour of a spore forming probiotic strain in the gastrointestinal tract of broiler chicken and piglets. Arch Anim Nutr 54:1–17 doi:10.1080/17450390109381962
Joy AD, Samuel JJ (1997) Effect of probiotic supplementation on the performance of broilers. J Vet Anim Sci 28:10–14
Khan HM, Bhat AS, Mir MS (2003) Effect of probiotic supplementation on the performance of Corriedale lambs. Indian J Small Rumin 9:60–61
La Rosa M, Bottaro G, Gulino N, Gambuzza F, di Forti F, Ini G, Tornambe E (2003) Prevention of antibiotic-associated diarrhea with Lactobacillus sporogenes and fructo-oligosaccharides in children. A multicentric doubleblind vs placebo study. Minerva Pediatrica 55:447–452
Le Marrec C, Hyronimus B, Bressollier P, Verneuil B, Urdaci MC (2000) Biochemical and genetic characterization of coagulin, a new antilisterial bacteriocin in the pediocin family of bacteriocins, produced by Bacillus coagulans I4. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5213-5220 doi:10.1128/AEM.66.12.5213-5220.2000
Leser TD, Knarreborg A, Worm J (2008) Germination and outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis spores in the gastrointwsstinal tract of pigs. J Appl Microb 104:1025–1033. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2007.03633.x
Lonkar P, Harne SD, Kalorey D, Kurkure NV (2005) Isolation, in vitro antibacterial activity, bacterial sensitivity and plasmid profile of Lactobacilli. Asian-Australas J Anim Sci 18:1336–1342
Mangin I, Bouhnik Y, Bisetti N, Decaris B (1999) Molecular monitoring of human intestinal Bifidobacterium strain diversity. Res Microbiol 150:343–350 doi:10.1016/S0923-2508(99)80060-6
Manickam R, Viswanathan K, Mohan M (1994) Effect of probiotics in broiler performance. Indian Vet J 71:737–739
Mazza P (1994) The use of Bacillus subtilis as an antidiarrhoeal microorganism. Boll Chim Farm 133:3–18
Muscettola M, Grasso G, Blach-Olszewska Z, Migliaccio P, Borghesi-Nicoletti C, Giarratana M, Gallo VC (1992) Effects of Bacillus subtilis spores on interferon production. Pharmacol Res 26 (suppl 2):176–177. doi:10.1016/1043-6618(92)90652-R
Nes IF, Johnsborg O (2004) Exploration of antimicrobial potential in LAB by genomics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 15:100–104. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2004.02.001
Nicholson WL (2002) Roles of Bacillus endospores in the environment. Cell Mol Life Sci 59:410–416 doi:10.1007/s00018-002-8433-7
Ouwehand AC, Kirjavainen PV, Shortt C, Salminen S (1999) Probiotics: mechanisms and established effects. Int Dairy J 9:43–52 doi:10.1016/S0958-6946(99)00043-6
Panda AK, Rao SVR, Raju MVLN, Sharma SR (2006) Dietary supplementation of Lactobacillus sporogenes on performance and serum biochemico-lipid profile of broiler chickens. J Poult Sci 43:235–240. doi:10.2141/jpsa.43.235
Rebucci R, Sangalli L, Fava M, Bersani C, Cantoni C, Baldi A (2007) Evaluation of functional aspects in Lactobacillus strains isolated from dry fermented sausages. J Food Quality 30:187–201. doi:10.1111/j.1745-4557.2007.00114.x
Mohan Kumar OR, Christopher KJ (1988) The role of Lactobacillus sporogenes (probiotic) as feed additive. Poult Guide 25:37–40
Ripamonti B, Rebucci R, Stella S, Baldi A, Savoini G, Bersani C, Bertasi B, Panteghini C, Cantoni C (2007) Screening and selection of lactic acid bacteria from calves for designing a species-specific probiotic supplement. Ital J Anim Sci 6(suppl 1):350–352
Rowan NJ, Deans K, Anderson JG, Gemmell CG, Hunter IS, Chaithong T (2001) Putative virulence factor expression by clinical and food isolates of Bacillus spp. after growth in reconstituted infant milk formulae. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3873–3881. doi:10.1128/AEM.67.9.3873-3881.2001
Sanders ME, Morelli L, Tompkins TA (2003) Sporeformers as human probiotics: Bacillus, Sporolactobacillus and Brevibacillus. CRFSFS 2:101–110. doi:10.1111/j.1541-4337.2003.tb00017.x
SCAN (2001) Report of Scientific Committee on Animal Nutrition on product Toyocerin® for use as feed additive. European Commission, Health & Consumer Protection Directorate-General. Available from: http://europa.eu.int/commm/food/fs/sc/scan/out72_en.pdf. Accessed 3 march 2009
Singh S, Sharma VP, Panwar VS (1999a) Effect of different levels of probiotic and energy on microbial population in broiler chicks. Indian Vet J 76:1026–1028
Singh S, Sharma VP, Panwar VS (1999b) Influence of the levels of probiotic and energy on mortality and economics of broilers in summer. Indian J Anim Sci 69:830–831
Spinosa MR, Braccini T, Ricca E, De Felice M, Morelli L, Pozzi G, Oggioni MR (2000) On the fate of ingested Bacillus spores. Res Microbiol 151:361–368 doi:10.1016/S0923-2508(00)00159-5
Succi G, Sandrucci A, Tamburini A, Adami A, Cavazzoni V (1995) Effects of a new strain of Bacillus coagulans as probiotic on piglet performance. Rivista di Suinicoltura 36:59–63
Tam NKM, Uyen NQ, Hong HA, Duc LH, Hoa TT, Serra CR, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (2006) The intestinal life cycle of Bacillus subtilis and close relatives. J Bacteriol 188:2692–2700. doi:10.1128/JB.188.7.2692-2700.2006
Tuomola E, Crittenden R, Playne M, Isolauri E, Salminen S (2001) Quality assurance criteria for probiotic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr 73(suppl):393S–398S
Wu XY, Walker M, Vanselow B, Chao RL, Chin J (2007) Characterization of mesophilic bacilli in faeces of feedlot cattle. J Appl Microbiol 102:872–879. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03106.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ripamonti, B., Agazzi, A., Baldi, A. et al. Administration of Bacillus coagulans in calves: recovery from faecal samples and evaluation of functional aspects of spores. Vet Res Commun 33, 991–1001 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-009-9318-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11259-009-9318-0