Abstract
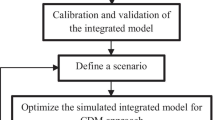
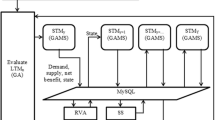
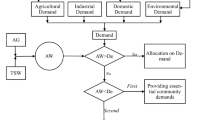
This paper presents a model for the optimal allocation of water resources in saltwater intrusion areas. The model is comprised of four modules: a joint operation of river and reservoirs module (JORRM), a saltwater intrusion analysis module (SIAM), an economic analysis and in-stream ecology demand module (EAIEDM) and a water allocation module (WAM). Considering the social, economic and environmental aspects, the model has three objectives: the maximization of economic interest (OF 1), maximization of social satisfaction (OF 2) and the minimization of the amounts of polluted water (OF 3). A genetic algorithm is also employed to optimize the module. The model has then been applied to a case study of optimization of water resources for the Pearl River Delta in China. The results indicate that there is water shortage in Pearl River Delta and engineering projects are needed to satisfy water demand during the dry season when saltwater intrusion happens. The model provides a useful tool for the operation of reservoirs and freshwater allocation in saltwater intrusion area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang FI, Chen L (1998) Real-coded genetic algorithm for rule-based flood control reservoir management. Water Resour Manage 12(3):185–198. doi:10.1023/A:1007900110595
Cohon JL, Marks DM (1975) A review and evaluation of multi-objective programming techniques. Water Resour Res 11(2):208–220. doi:10.1029/WR011i002p00208
Doorenbos J, Pruitt WO (1977) Crop water requirements. Irrigation and Drainage Paper. No. 24 (rev.) FAO, Rome, Italy. 144 p
Goetz RU, Martinez Y, Jofre R (2008) Water allocation by social choice rules: the case of sequential rules. Ecol Econ 65(2):304–314. doi:10.1016/j.ecolecon.2007.06.018
Goldberg DE (1989) Genetic algorithms in search, optimization and machine learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading
Gwo JP (2001) In search of preferential flow paths in structured porous media using a simple genetic algorithm. Water Resour Res 37(6):1589–1601. doi:10.1029/2000WR900384
Holland J (1975) Adaptation in neural and artificial systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor
Holland JH (1992) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems, 2nd edn. MIT, Cambridge
Janejira T, Ichiro K, Masayuki I, and Kitamura Y (2005) Optimization of a multiple reservoir system operation using a combination of genetic algorithm and discrete differential dynamic programming: a case study in Mae Klong system, Thailand. Paddy Water Environ 3(1):29–38. doi:10.1007/s10333-005-0070-y
Madan KJ, Nanada G, Samuel MP (2004) Determining hydraulic characteristics of production wells using genetic algorithm. Water Resour Manage 18(4):353–377. doi:10.1023/B:WARM.0000048485.62254.1c
McKinney DC, Lin MD (1994) Genetic algorithm solution of groundwater management models. Water Resour Res 30(6):1897–1906. doi:10.1029/94WR00554
Meier RW, Barkdoll BD (2000) Sampling design for network model calibration using genetic algorithms. J Water Resour Plan Manage 126(4):245–250. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9496(2000)126:4(245)
Mohammed M, Mac Kirby M, Qureshi E (2007) Integrated hydrologic-economic modeling for analyzing water acquisition strategies in the Murray River Basin. Agric Water Manage 93(1):123–135. doi:10.1016/j.agwat.2007.06.011
Morshed J, Kaluarachchi JJ (2000) Enhancements to genetic algorithm for optimal groundwater management. J Hydraul Engineer ASCE 5(1):67–73. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)1084-0699(2000)5:1(67)
Ochiewo J (2001) Socio-economic aspects of water management along the coast of Kenya. Hydrobiologia 458:267–273. doi:10.1023/A:1013182901790
Rauch W, Harremoes P (1999) Genetic algorithms in real time control applied to minimize transient pollution from urban wastewater systems. Water Res 33(5):1265–1277. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00304-2
Reca J, Roldan J, Alcaide M, Camacho E (2001) Optimization model for water allocation in deficit irrigation system: I. Description of the model. Agric Water Manage 48(2):103–116. doi:10.1016/S0378-3774(00)00126-8
Reed P, Minisker BS, Goldberg DE (2000) Designing a competent simple genetic algorithm for search and optimization. Water Resour Res 36(12):3757–3761. doi:10.1029/2000WR900231
Salman AZ, Al-Karablieh EK, Fisher FM (2001) An inter-seasonal agricultural water allocation system (SAWAS). Agric Syst 68(3):233–252. doi:10.1016/S0308-521X(01)00010-5
Sarkar D, Modak MM (2003) Optimization of fed-batch bioreactors using genetic algorithms. Chem Eng Sci 58(11):2283–2296. doi:10.1016/S0009-2509(03)00095-2
Shangguan ZP, Shao MA, Horton R et al (2002) A model for regional optimal allocation of irrigation water resources under deficit irrigation and its applications. Agric Water Manage 52(2):139–154. doi:10.1016/S0378-3774(01)00116-0
Smalley JB, Minsker BS, Goldberg DE (2000) Risk-based in situ bioremediation design using a noisy genetic algorithm. Water Resour Res 36(10):3043–3052. doi:10.1029/2000WR900191
Sohn SH, Oh SC, Yeo YK et al (1999) Prediction of Air Pollutants by Using an Artificial Neural Network. Korean J Chem Eng 16(3):382–387. doi:10.1007/BF02707129
Tennant DL (1976) Instream flow regimens for fish, wildlife, recreation and related environmental resources. Fisheries 1(4):6–10. doi:10.1577/1548-8446(1976)001<0006:IFRFFW>2.0.CO;2
Van Dijk S, Thierens D, de Berg M (2002) Using genetic algorithms for solving hard problems in GIS. GeoInformatica 6(4):381–413. doi:10.1023/A:1020809627892
Vink K, Schot P (2002) Multiple-objective optimization of drinking water production strategies using a genetic algorithm. Water Resour Res 38(9):1181–1181. doi:10.1029/2000WR000034
Wang QJ (1991) The genetic algorithm and its application to calibrating conceptual rainfall-runoff models. Water Resour Res 27(9):2467–2471. doi:10.1029/91WR01305
Wardlaw R, Bhaktikul K (2001) Application of generic algorithm for water allocation in an irrigation system. Irrig Drain 50(2):159–170. doi:10.1002/ird.9
Yeh WW-G, Becker L (1982) Multiobjective analysis of multireservoir operations. Water Resour Res 18(5):1326–1336. doi:10.1029/WR018i005p01326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Chen, X. & Lou, Z. A Model for the Optimal Allocation of Water Resources in a Saltwater Intrusion Area: A Case Study in Pearl River Delta in China. Water Resour Manage 24, 63–81 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9437-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9437-y