Abstract
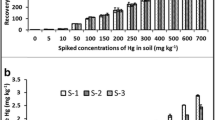
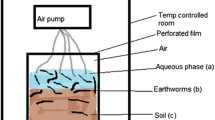
Bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) for inorganic mercury in earthworms are usually < 1; however, factors up to ∼10 have been reported. Little information is available concerning the bioaccumulation of organic mercury in earthworms from actual contaminated soils and thus there has been uncertainty in the risk characterization phase of ecological risk assessments of mercury-contaminated sites. This study was initiated to determine the rate of uptake and bioaccumulation of total mercury (T-Hg) and monomethylmercury (MMHg) in Eisenia fetida from soils which have been contaminated with mercury for approximately 30 years. The study consisted of a 28-day uptake phase in three mercury-contaminated soils and one soil with background concentrations of mercury followed by a 14-day depuration phase in background soil only. Total mercury concentrations in the study soils ranged from 85 to 11,542 μg kg−1 dry weight soil; MMHg concentrations ranged from 1.12 to 7.35 μg kg−1 dry weight soil. Time to 90% steady states for T-Hg ranged from 36 to 42 days. A steady state did not occur for any of the MMHg exposures during the 42-day study; estimated time to 90% steady state varied from 97 to 192 days. BAFs for T-Hg ranged from 0.6 to 3.3. BAFs for MMHg ranged from 175 to 249. The BAFs for T-Hg and MMHg were larger in earthworms exposed to the lower contaminated soils and smaller in the higher mercury-contaminated soils. The absolute concentrations of T-Hg and MMHg bioaccumulated in E. fetida, however, were higher in the earthworms exposed to the higher mercury soils and lower in the less mercury-contaminated soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials): 1998, ‘Standard Guide for Conducting Laboratory Soil Toxicity or Bioaccumulation Tests with the Lumbricid Earthworm Eisenia fetida’, ASTM Designation E 1676-97, in 1998 Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol. 11.05, American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, USA, pp. 1056–1074.
Beyer, W. N., Cromartie, E. and Moment, G. B.: 1985, ‘Accumulation of methylmercury in the earthworm, Eisenia foetida, and its Effect on Regeneration’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 157–162.
Blau, G. E. and Agin, G. L.: 1978, A Users Manual for BIOFAC: A Computer Program for Characterizing the Rates of Uptake and Clearance of Chemicals in Aquatic Organisms, Dow Chemical Co., Midland, MI, USA.
Boudou, A. and Ribeyre, F.: 1997, ‘Mercury in the food web: Accumulation and transfer mechanisms’, in A. Sigel and H. Sigel (eds), Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 34, Mercury and its Effects on Environment and Biology, Marcel Dekker, Inc., NY, USA, pp. 289–319.
Buckman, M. F.: 1999, ‘NOAA Screening Quick Reference Tables’, HAZMAT Rep. 99-1’, Coastal Protection and Restoration Division, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle, WA, USA, 11 pp.
Bull, K. R., Roberts, R. D., Inskip, M. J. and Goodman, G. T.: 1977, ‘Mercury concentrations in soil, grass, earthworms and small mammals near an industrial emission source’, Environ. Pollut. 12, 135–140.
Cocking, D., Hayes, R., King, M. L., Rohrer, M. J., Thomas, R. and Ward, D.: 1991, ‘Compartmentalization of mercury in biotic components of terrestrial flood plain ecosystems adjacent to the South River at Waynesboro, Va.’, Water Air Soil Pollut. 57–58, 159–170.
Cocking, D., King, M. L., Ritchie, L. and Hayes, R.: 1994, ‘Earthworm Bioaccumulation of Mercury from Contaminated Flood Plain Soils’, in C. J. Watras and J. W. Huckabee (eds), Mercury Pollution Integration and Synthesis, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp. 381–395.
European Commission: 1999, ‘European Union Risk Assessment Report benzene, C10−13 alkyl derives, Volume 3’, EUR 19011, in B. G. Hansen, S. J. Munn, G. Schoening, M. Luotamo, A. van Haelst, C. J. A. Heidorn, Pellegrini, R. Allanou and H. Loonen (eds), Office for Official Publications of the European Communities, Luxembourg.
Fischer, E. and Koszorus, L.: 1992, ‘Sublethal effects, accumulation capacities and elimination rates of As, Hg and Se in the Manure Worm, Eisenia fetida (Oligochaeta, Lumbricidae)’, Pedobiologia 36, 172–178.
Fleckenstein, J. and Graff, O.: 1982, ‘Schwermetallaufnahme aus Mullkompost Durch den Regenwurm Eisenia foetida (Savigny 1826)’, Landbauforschung Volkenrode 32, 198–202.
Gibbs, M. H., Wicker, L. F. and Stewart, A. J.: 1996, ‘A method for assessing sublethal effects of contaminants in soils to the earthworm, Eisenia fetida’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 15, 360–368.
Helmke, P. A., Robarge, W. P., Korotev, R. L. and Schomberg, P. J.: 1979, ‘Effects of soil-applied sludge on concentrations of elements in earthworms’, J. Environ. Qual. 8, 322–327.
Ireland, M. P.: 1979, ‘Metal accumulation by the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus, Dendrobaena veneta and Eiseniella tetraedra living in heavy metal polluted sites’, Environ. Pollut. 19, 201–206.
Jager, T.: 1998, ‘Mechanistic approach for estimating bioconcentration of organic chemicals in earthworms (Oligochaeta)’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 2080–2090.
Janssen, R. P. T., Posthuma, L., Baerselman, R., Den Hollander, H. A., Van Veen, R. P. M. and Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M.: 1997, ‘Equilibrium partitioning of heavy metals in Dutch field soils. II. Prediction of metal accumulation in earthworms’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 12, 2479–2488.
Jeffries, J. R. and Audsley, E.: 1988, ‘A Population Model for the Earthworm Eisenia foetida’, in C. A. Edwards and E. F. Neuhauser (eds), Earthworms in Waste and Environmental Management, SPB Acad Publ bv The Hague, The Netherlands, pp. 119–134.
Keating, M. H., Mahaffey, K. R., Shoeny, R., Rice, G. E., Bulluck, O. R., Ambrose, R. B., Jr., Swartout, J. and Nichols, J. W.: 1997, ‘Mercury Study Report to Congress, Vol. 1: Executive Summary’, EPA-452/H-97-003, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, DC, USA.
Lanno, R., Wells, J., Conder, J., Bradham, K. and Basta, N.: 2004, ‘The bioavailability of chemicals in soil for earthworms’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 57, 39–47.
Lock, K. and Janssen, C. R.: 2001a, ‘Zinc and cadmium body burdens in terrestrial oligochates: use and significance in environmental risk assessment’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 20, 2067–2072.
Lock, K. and Janssen, C. R.: 2001b, ‘Cadmium toxicity for terrestrial invertebrates: Taking soil parameters affecting bioavailability into account’, Ecotoxicology 10, 315–322.
Lock, K. and Janssen, C. R.: 2003, ‘Influence of aging on metal availability in soils’, Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 178, 1–21.
Loux, N. T.: 1998, ‘An Assessment of mercury-species-dependent binding with natural organic carbon’, Chem. Speciation Bioavailability 10, 127–136.
Ma, W.-C.: 2004, ‘Estimating heavy metal accumulation in oligochaete earthworms: A meta-analysis of field data’, Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 72, 663–670.
Ma, W.-C., Edelman, T., Van Beersum, I. and Jans, T.: 1983, ‘Uptake of cadmium, zinc, lead, and copper by earthworms near a zinc-smelting complex. Influence of soil pH and organic matter’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 30, 424–427.
Major, M. A. and Rosenblatt, D. H.: 1991, ‘The octanol/water partition coefficient of methylmercuric chloride and methylmercuric hydroxide in pure water and salt solutions’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 10, 5–8.
Munthre, J.: 1994, ‘The Atmospheric Chemistry of Mercury: Kinetic Studies of Redox Reactions’, in Watras, C. J. and Huckabee, J. W. (eds), Mercury Pollution Integration and Synthesis, Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp. 273–279.
Napier, B. A., Kennedy, W. E., Ikenberry, T. A., Hunacek, M. M. and Kennedy, A. M.: 2004, ‘Technical Basis for the Derivation of Authorized Limits for Units of the Hanford Reach National Monument’, PNNL-14531, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA, USA.
Neuhauser, E. F., Cukic, Z. V., Malecki, M. R., Loehr, R. C. and Durkin, P. A.: 1995, ‘Bioconcentration and biokinetics of heavy metals in the earthworm’, Environ. Pollut. 89, 293–301.
Neuhauser, E. F., Hartenstein, R. and Kaplan, D. L.: 1980, ‘Growth of the earthworm Eisenia foetida in relation to population density and food rationing’, Oikos 35, 93–98.
Newman, M. C. and Unger, M. A.: 2003, Fundamentals of Ecotoxicology (2nd ed.), Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA.
Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M., Baerselman, R., de Groot, A. C., Jager, T., Posthuma, L. and Van Veen, R. P. M.: 1999a, ‘Relating environmental availability to bioavailability: soil-type-dependent metal accumulation in the oligochaete Eisenia andrei’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 44, 294–310.
Peijnenburg, W. J. G. M., Posthuma, L., Zweers, P. G. P. C., Baerselman, R., de Groot, A. C., Van Veen, R. P. M. and Jager, T.: 1999b, ‘Prediction of metal bioavailability in Dutch field soils for the oligochaete Enchytraeus crypticus’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 43, 170–186.
PMRA: 2004, ‘Regulatory Note, Methoxyfenozide’, REG2004-08, Pest Management Regulatory Agency, Health Canada, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada.
Sample, B. E., Suter, G. W., II, Beauchamp, J. J. and Efroymson, R. A.: 1999, ‘Literature-derived bioaccumulation models for earthworms: Development and validation’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 18, 2110–2120.
Seigneur, C., Lohman, K., Pai, P., Heim, K., Mitchell, D. and Levin, L.: 1999, ‘Uncertainty analysis of regional mercury exposure’, Water Air Soil Pollut. 112, 151–162.
Sijm, D., Kraaij, R. and Belfroid, A.: 2000, ‘Bioavailability in soil or sediment: Exposure of different organisms and approaches to study it’, Environ. Pollut. 108, 113–119.
Stein, E. D., Cohen, Y. and Winer, A. M.: 1996, ‘Environmental distribution and transformation of mercury compounds’, Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 1–43.
Svendsen, C. and Weeks, J. M.: 1997, ‘Relevance and applicability of a simple earthworm biomarker of copper exposure. II. Validation and applicability under field conditions in a mesocosm experiment with Lumbricus rubellus’, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 36, 80–88.
Talmage, S. S. and Walton, B. T.: 1993, ‘Food chain transfer and potential renal toxicity of mercury to small mammals at a contaminated terrestrial field site’, Ecotoxicology 2, 243–256.
U.S. Congress: 1972, ‘Federal Water Pollution Control Act’, 33 U.S.C. pp. 1251–1376, Pub. L. No 95-500, Sect. 307, 86 Stat. 816, U.S. Congress, Washington, DC, USA.
van Gestel, C. A. M., Dirven-van Breemen, E. M. and Baerselman, R.: 1992, ‘Influence of environmental conditions on the growth and reproduction of the earthworm Eisenia andrei in an artificial soil substrate’, Hydrobiologia 36, 109–120.
Wolfe, M. F., Schwarzbach, S. and Sulaiman, R. A.: 1998, ‘Effect of mercury on wildlife: A comprehensive review’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 17, 146–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burton, D.T., Turley, S.D., Fisher, D.J. et al. Bioaccumulation of Total Mercury and Monomethylmercury in the Earthworm Eisenia Fetida . Water Air Soil Pollut 170, 37–54 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-3113-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-006-3113-0