Abstract
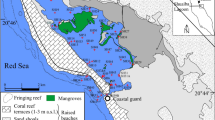
The concentrations and distribution of selected heavy metals in epipelic and benthic sediments of Cross River Estuary mangrove swamp were studied to determine the extent of anthropogenic inputs from industrial activities and to estimate the effects of seasonal variations on geochemical processes in this tropical estuarine ecosystem. The analysis shows that the mean concentrations (mg/kg, dw) of Cu, Cr, Fe, Ni, Pb, V and Zn vary from 24.1–32.4, 19.9–27.4, 666.7–943.5, 15.2–30.3, 8.8–24.7, 2.2–6.9 and 140.1–188.9, respectively. An important observation is that, in general, lowest metal concentrations are found during the dry season, compared to wet season. Pollution load index (PLI) and index of geoaccumulation (I geo) revealed overall low values but the enrichment factors (EFs) for Cr, Zn, and V were high, and this reflects the intensity of anthropogenic inputs related to industrial discharge into the estuary. The mean concentrations of Zn, Cu and to some extent Ni exceeded the Effects Range—Low (ERL) and Threshold Effect Level (TEL) values in majority of the samples studied, indicating that there may be some ecotoxicological risk to organisms living in these sediments. The inter-element relationship revealed the identical source of elements in the sediments of the studied area. The concentration of heavy metals reported in this work will be useful as baselines for comparison in future sediment quality studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo, P., Arienzo, M., Imperato, M., Naimo, D., Nardi, G., & Stanzione, D. (2005). Distribution and partition of heavy metals in surface and sub-surface sediments of Naples city port. Chemosphere, 61, 800–809. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.04.001.
Alagarsamy, R. (2006). Distribution and seasonal variation of trace metals in surface sediments of the Mandovi estuary west coast of India. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 67, 333–339. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2005.11.023.
Aloupi, M., & Angelidis, M. O. (2001). Geochemistry of natural and anthropogenic metals in the coastal sediments of the island of Lesvos, Aegean Sea. Environmental Pollution, 113, 211–219. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(00)00173-1.
Angulo, E. (1996). The Tomllinson pollution load index applied to heavy metals ‘Mussel-Watch’ data: a useful index to assess coastal pollution. The Science of the Total Environment, 187, 19–56. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(96)05128-5.
AOAC (1975). Methods for soil analysis (12th ed.). Washington, DC: Association of Official Analytical Chemist.
Apte, S. C., Gardner, M. J., Gunn, A. M., Ravenscroft, J. E., & Vale, J. (1989). Trace metals in the Severn estuary—a reappraisal pp. 1–9. Marlow: Water Research Centre.
Berner, R. A. (1980). Early diagenesis. A theoretical approach. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Binning, K., & Baird, D. (2001). Survey of heavy metals in the sediments of the Swatkop River Estuary, Port Elizabeth South Africa. Water S.A, 24(4), 461–466.
Birth, G. A. (2003). A scheme for assessing human impacts on coastal aquatic environments using sediments. In: Woodcoffe, C.D; Furness, R.A (eds.), Coastal GIS 2003. Wollongong University Papers in Centre for Maritime Policy, 14, Australia.
Black, C. A., Evans, D. D., White, J. L., Esminger, L. B., & Clark, F. E. (1961). Methods of soil analysis 2. Chemical and microbiological properties. Madison: American Society of Agronomy.
Breit, G. N., & Wanty, R. B. (1991). Vanadium accumulation in carbonaceous rocks: a review of geochemical controls during deposition and diagenesis. Chemical Geology, 91, 83–97. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(91)90083-4.
Chapman, P. M., & Wang, F. (2001). Assessing sediment contamination in estuaries. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 20, 3–22. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2001)020<0003:ASCIE>2.0.CO;2.
Che, Y., He, Q., & Lin, W. Q. (2003). The distribution of particulate heavy metals and its indications to the transfer of sediments in the Changjiang estuary and Hangzhons bay, China. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 46, 123–131. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(02)00355-7.
Cho, Y.-G., Lee, C. B., & Choi, M.-S. (1999). Geochemistry of surface sediments off the southern and western coast of Korea. Marine Geology, 159, 111–129. doi:10.1016/S0025-3227(98)00194-7.
Dickinson, W. W., Dunbar, G. B., & Mclead, H. (1996). Heavy metal history from cores in Wellington Harbour, New Zealand. Environmental Geology, 27, 59–69. doi:10.1007/BF00770603.
Duxbury, D. S. (2000). Introduction to the world’s ocean (6th ed.). UK: McGraw Hill.
Essien, J. P. (2007). Ecology and Physiological diversity of heterotrophic and hydrocarbon utilizing microorganisms in sediments of the Niger Delta Mangrove Swamp ecosystem. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Calabar, Calabar, Nigeria, p 500.
Fatoki, O. S., & Mathabatha, S. (2001). An assessment of heavy metal pollution in the East London and Port Elizabeth harbours. Water S.A., 27, 233–240.
Feng, H., Han, X., Zhang, W., & Yu, L. (2004). A preliminary study of heavy metal contamination in Yangtze River intertidal zone due to urbanization. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 910–915. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.06.014.
Forstner, U., & Wittman, G. T. W. (1979). Metal pollution in the aquatic environment p. 486. Berlin: Springer.
Guerra-Garcia, J. M., & Garcia-Gomez, J. C. (2005). Assessing pollution levels in sediments of a harbour with two opposing entrances: environmental implications. Journal of Environmental Management, 77, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2005.01.023.
Hatch, J. R., & Leventhal, J. S. (1992). Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian (Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, KS, USA. Chemical Geology, 99, 65–82. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(92)90031-Y.
Hem, J. D. (1985). Study and interpretation of the chemical characteristics of natural waters (3rd ed., pp. 2254–2263). US Geological Surveys Water Supply Paper.
Ho, S. T., Tsai, I. J., & Yu, K. C. (2003). Correlation among aqua-regia extractable heavy metals in vertical river sediments. Diffuse Pollution Conference, Dublin, 14, 12–18.
Huang, K. M., & Lin, S. (2003). Consequences and implication of heavy metal spatial variations in sediments of the Keelung River drainage basin, Taiwan. Chemosphere, 53, 1113–1121. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(03)00592-7.
Hung, J. J., & Hsu, C. L. (2004). Present state and historical changes of trace metal pollution in Kaoping coastal sediments, southwestern Taiwan. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 986–998. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2004.06.028.
Jacobsen, S. T. (1992). Chemical reaction and air change during the decomposition of organic matter. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 6, 529–539.
Juo, A. S. R. (1979). Selected methods for soil and plant analysis: manual series p. 70. Ibadan: International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA).
Kawamura, K., & Ishiwatari, R. (1981). Polyunsaturated fatty acids in a lacustrine sediment as a possible indicator of paleoclimate. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45, 149–155. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90158-7.
Lewan, M. D. (1984). Factor controlling the proportionality of vanadium to nickel in crude oils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48, 2231–2238. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(84)90219-9.
Lewan, M. D., & Maynard, J. B. (1982). Factors controlling enrichment of vanadium and nickel in the bitumen of organic sedimentary rocks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 46, 2547–2560. doi:10.1016/0016-7037(82)90377-5.
Liao, J. F. (1990). The chemical properties of the mangrove Solonchak in the northeast part of Hainan Island. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 9(4), 67–72 Supp.
Long, E. R., Field, L. J., & MacDonald, D. D. (1998). Predicting toxicity in marine sediments with numerical sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 17, 714–727. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(1998)017<0714:PTIMSW>2.3.CO;2.
Long, E. R., & MacDonald, D. D. (1998). Recommended uses of empirically derived, sediment quality guidelines for marine and estuarine ecosystems. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment, 4(5), 1019–1039. doi:10.1080/10807039891284956.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Smith, S. L., & Calder, F. O. (1995). Incidence of adverse biological effects within ranges of chemical concentrations in marine and estuarine sediments. Environmental Management, 19, 81–97. doi:10.1007/BF02472006.
Long, E. R., MacDonald, D. D., Severn, C. G., & Hong, C. B. (2000). Classifying probabilities of acute toxicity in marine sediments with empirically derived sediment quality guidelines. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 19, 2598–2601. doi:10.1897/1551-5028(2000)019<2598:CPOATI>2.3.CO;2.
Loring, H. D., & Rantala, R. (1992). Manual for the geochemical analyses of marine sediments and suspended particulate matter. Earth-Science Reviews, 32, 235–283. doi:10.1016/0012-8252(92)90001-A.
MacDonald, D. D., Ingerosoll, C. G., & Berger, T. A. (2000). Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 39, 20–31. doi:10.1007/s002440010075.
Matagi, S. V., swai, D., & mugabe, R. (1998). heavy metal removal mechanisms in wetlands. African J. Tropical Hydrobiol. Fisher., 8, 23–35.
McCready, S., Birch, G. F., & Long, E. R. (2006). Metallic and organic contaminants in sediments of Sydney harbour, Australia and vicinity—a chemical dataset for evaluating sediment quality guidelines. Environment International, 32, 455–465. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2005.10.006.
Meyers, P. A. (1994). Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic matter. Chemical Geology, 144, 289–302. doi:10.1016/0009-2541(94)90059-0.
Meyers, P. A. (1997). Organic geochemical proxies of paleoceanographic, paleolimnologic and paleoclimatic processes. Organic Geochemistry, 27, 213–250. doi:10.1016/S0146-6380(97)00049-1.
Miroslav, R., & Vladimir, N. B. (1999). Practical environmental analysis p. 466. Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Morillo, J., Usero, J., & Gracia, I. (2004). Heavy metal distribution in marine sediments from the southwest coast of Spain. Chemosphere, 55, 431–442. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.10.047.
Muller, G. (1979). Schwermetalle in den sediments des Rheins-Veran-derngren seitt. 1971. Umschan, 79, 778–783.
Muniz, P., Danula, E., Yannicelli, B., Garcia-Alonso, J., Medina, G., & Bicego, M. C. (2004). Assessment of contamination by heavy metals and petroleum hydrocarbons in sediments of Monterideo harbour (Uruguay). Environment International, 29, 1019–1028. doi:10.1016/S0160-4120(03)00096-5.
Niencheskil, L. F. H., Windom, L. H., & Smith, R. (1994). Distribution of particulate trace metal in Patos lagoon estuary (Brazil). Marine Pollution Bulletin, 28(2), 96–102. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(94)90545-2.
Olajire, A. A., & Oderinde, R. A. (1993). Trace metals in Nigerian crude oils and their heavy-end distillates. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 66(2), 630–632. doi:10.1246/bcsj.66.630.
Owens, M. (1984). Severn estuary—an appraisal of water quality. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 15, 41–47. doi:10.1016/0025-326X(84)90460-0.
Paetzel, M., Nes, G., Leifsen, L. O., & Schrader, H. (2003). Sediment pollution in the Vagen, Bergen harbour, Norway. Environmental Geology, 43, 476–483.
Page, A. L., Miller, R. H., & Keeney, D. R. (1982). Methods of soil analysis. Part 2. Chemical and microbiological properties (2nd ed., p. 1159). American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, pp. 538–580.
Pedersen, F., Bjornestad, E., Andersen, H. V., Kjolholt, J., & Poll, C. (1998). Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen harbour by use of biotests. Water Science and Technology, 37(6–7), 233–240. doi:10.1016/S0273-1223(98)00203-0.
Perin, G., Bonardi, M., Fabris, R., Simoncini, B., Manente, S., Tosi, L., et al. (1997). Heavy metal pollution in central Venice Lagoon bottom sediments: evaluation of the metal bioavailability by geochemical speciation procedure. Environmental Technology, 18, 593–604.
Popek, E. P. (2003). Sampling and analysis of environmental pollutants: a complete guide p. 356. USA: Academic.
Poulton, D. J., Morris, W. A., & Coakley, J. P. (1996). Zonation of contaminated bottom sediments in Hamilton harbour as defined by statistical classification techniques. Water Quality Research Journal of Canada, 31, 505–528.
Radojevic, M., & Bashkin, V. N. (1999). Practical environmental analysis (p. 465). Royal Society of Chemistry, Thomas Graham House, Cambridge CB4 OWF, UK.
Reddy, M. S., Basha, S., Sravan Kumar, V. G., Joshi, H. V., & Ramachandraiah, G. (2004). Distribution, enrichment and accumulation of heavy metals in coastal sediments of Alang–Sosiya ship scrapping yard, India. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 48, 1055–1059. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.12.011.
Rhykered, R. I., Weaver, R. W., & Mclnnes, K. J. (1995). Influence of salinity on bioremediation of oil in soil. Environmental Pollution, 90, 127–130. doi:10.1016/0269-7491(94)00087-T.
Rubio, B., Nombela, M. A., & Vilas, F. (2000). Geochemistry of major and trace elements in sediments of the Ria de Vigo (N W Spain): an assessment of metal pollution. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 40, 968–980. doi:10.1016/S0025-326X(00)00039-4.
Salomons, W., & Forstner, U. (1984). Metal in the hydrocycle p. 349. Berlin: Springer.
Selvaraj, K., Ram Mohan, V., & Szefer, P. (2004). Evaluation of metal contamination in coastal sediments of the Bay of Bengal, India: geochemical and statistical approaches. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 49, 174–185.
Tahal Consultants (1979). (Nigeria) Ltd. Qua Iboe River Basin Pre-feasibility study. Cross River Basin Development Authority, Nigeria, vol. 2, Annex II: A 1–14.
Teugels, G. C., Reid, F. M., & King, R. P. (1992). Fishes of the Cross River Basin (Cameroon–Nigeria): taxonomy, zoogeography, ecology and conservation. Annals Science Zoologiques, 1, 216–248.
Tomllinson, D. C., Wilson, J. G., Harris, C. R., & Jeffrey, D. W. (1980). Problems in the assessment of heavy metals levels in estuaries and the formation of pollution index. Helgoländer Wissenschaftliche Meeresuntersuchungen, 33, 566–569.
Vald’es, J., Vargas, G., Sifeddine, A., Ortlieb, L., & Guinez, M. (2005). Distribution and enrichment of heavy metals in Mejillones Bay (23°S), Northern Chile: geochemical and statistical approach. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 50, 1558–1568.
Ward, D. M., Atlas, R. M., Boehm, P. D., & Calder, J. A. (1980). Microbial biodegradation and the chemical evolution of Amoco Cadiz oil pollutants. Ambio, 9, 277–283.
Woitke, P., Wellmitz, J., Helm, D., Kube, P., Lepom, P., & Litheraty, P. (2003). Analysis and assessment of heavy metal pollution in suspended solids and sediments of the river Danube. Chemosphere, 51, 633–642.
Zhang, J., & Liu, C. L. (2002). Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 54, 1051–1070.
Zwolsman, I. G. J., Berger, W. G., & Vaneck, M. T. G. (1993). Sediment accumulation rates, historical input, post depositional mobility and retention of major elements and trace metals in salt marsh sediments of the Scheldt estuary, SW Netherlands. Marine Chemistry, 44, 73–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Essien, J.P., Antai, S.P. & Olajire, A.A. Distribution, Seasonal Variations and Ecotoxicological Significance of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Cross River Estuary Mangrove Swamp. Water Air Soil Pollut 197, 91–105 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9793-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-008-9793-x