Abstract
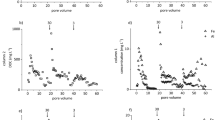
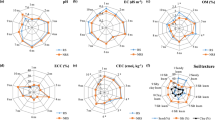
As floodplain soils are often contaminated, we studied the release of trace metals from three topsoil horizons in column experiments with variable flow interruptions and flow velocities, compared it with that in batch leaching tests and evaluated the column data by inverse simulations. Only small proportions (<1%) of trace metals present in the neutral and humic soils were mobilised by the batch leaching tests and the column experiments. Release of Cr, Cu, Ni and Zn in the column experiments was rate-limited, as detected by increased concentrations after flow interruptions. A combination of linear equilibrium and non-equilibrium isotherms reflected the Ni and Zn elution data, with Zn release being slower. Simulated values for initially bound metals available for release are in the same order of magnitude as those determined by the batch leaching tests. However, the consistency of both experimental approaches decreases with increasing rate limitation, as detected here for Zn.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ad hoc, Boden, A. G. (2005). Bodenkundliche Kartieranleitung (KA 5). Stuttgart: E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung.
Ajiboye, B., Akinremi, O. O., Hu, Y., & Jürgensen, A. (2008). XANES speciation of phosphorus in organically amended and fertilized Vertisol and Mollisol. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 72, 1256–1262. doi:10.2136/sssaj2007.0078.
BBodSchV (1999). Verordnung zur Durchführung des Bundes-Bodenschutzgesetzes (Bundes-Bodenschutz- und Altlastenverordnung, BBodSchV vom 16.7.1999). BGBl, I, 1554–1582.
Berger, W., Scheuering, I., & Peiffer, S. (2006). Emissionsabschätzung aus kontaminierten Materialien—was können Labormethoden hierzu leisten? altlasten spektrum, 15, 154–161.
Brümmer, G. W., Gerth, J., & Tiller, K. G. (1988). Reaction kinetics of the adsorption and desorption of nickel, zinc and cadmium by goethite. I. Adsorption and diffusion of metals. Journal of Soil Science, 39, 37–52. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2389.1988.tb01192.x.
Brusseau, M. L. (1992). Nonequilibrium transport of organic chemicals: The impact of pore-water velocity. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 9, 353–368. doi:10.1016/0169-7722(92)90003-W.
Buczko, U., Hopp, L., Berger, W., Durner, W., Peiffer, S., & Scheithauer, M. (2004). Simulation of chromium transport in the unsaturated zone for predicting contaminant entries into groundwater. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 167, 284–292. doi:10.1002/jpln.200421371.
Delay, M., Lager, T., Schulz, H. D., & Frimmel, F. H. (2007). Comparison of leaching tests to determine and quantify the release of inorganic contaminants in demolition waste. Waste Management, 27, 248–255. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2006.01.013.
Devai, I., Patrick, W. H., Jr., Neue, H.-U., DeLaune, R. D., Kongchum, M., & Rinklebe, J. (2005). Methyl mercury and heavy metal content in soils of rivers Saale and Elbe (Germany). Analytical Letters, 38, 1037–1048.
Du Laing, G., Rinklebe, J., Vandecasteele, B., & Tack, F. M. G. (2009). Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. The Science of the Total Environment, 407, 2919–2930.
Eriksson, N., & Destouni, G. (1997). Combined effects of dissolution kinetics, secondary mineral precipitation, and preferential flow on copper leaching from mining waste rock. Water Resources Research, 33, 471–483. doi:10.1029/96WR03466.
Förstner, U., Heise, S., Schwartz, R., Westrich, B., & Ahlf, W. (2004). Historical contaminated sediments and soils at the river basin scale. Examples from the Elbe river catchment area. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 4, 247–260. doi:10.1007/BF02991121.
Gee, A. K., & Bruland, K. W. (2002). Tracing Ni, Cu, and Zn kinetics and equilibrium partitioning between dissolved and particulate phases in South San Francisco Bay, California, using stable isotopes and high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66, 3063–3083. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00907-9.
Hinz, C., & Selim, H. M. (1999). Kinetics of Zn sorption–desorption using a thin disk flow method. Soil Science, 164, 92–100. doi:10.1097/00010694-199902000-00003.
IUSS/ISRIC/FAO (2006). World reference base for soil resources 2006. Rome: FAO.
Kalbe, U., Berger, W., Eckhardt, J., & Simon, F.-G. (2008). Evaluation of leaching and extraction procedures for soil and waste. Waste Management, 28, 1027–1038. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2007.03.008.
Kandpal, G., Srivastava, P. C., & Ram, B. (2005). Kinetics of desorption of heavy metals from polluted soils: Influence of soil type and metal source. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 161, 353–363. doi:10.1007/s11270-005-5548-0.
Kowalik, C., Kraft, J., & Einax, J. W. (2003). The situation of the German Elbe tributaries—Development of the loads in the last 10 years. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 334–345. doi:10.1002/aheh.200300507.
Krüger, F., & Gröngröft, A. (2003). The difficult assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils and plants in Elbe River floodplains. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 31, 436–443. doi:10.1002/aheh.200300495.
Lager, T., Delay, M., Karius, V., Hamer, K., Frimmel, F. H., & Schulz, H. D. (2006). Determination and quantification of the release of inorganic contaminants from municipal waste incineration ash. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 34, 73–85. doi:10.1002/aheh.200500610.
Miretzky, P., Munoz, C., & Carrillo-Chavez, A. (2006). Experimental Zn(II) retention in a sandy loam soil by very small columns. Chemosphere, 65, 2082–2089. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.06.047.
Overesch, M., Rinklebe, J., Broll, G., & Neue, H.-U. (2007). Metals and arsenic in soils and corresponding vegetation at Central Elbe River floodplains (Germany). Environmental Pollution, 145, 800–812. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2006.05.016.
Pang, L., Close, M., Schneider, D., & Stanton, G. (2002). Effect of pore-water velocity on chemical nonequilibrium transport of Cd, Zn, and Pb in alluvial gravel columns. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 57, 247–258. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(01)00223-6.
Prechtel, A., Knabner, P., Schneid, E., & Totsche, K. U. (2002). Simulation of carrier facilitated transport of phenanthrene in a layered soil profile. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 56, 209–225. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(01)00211-X.
Rinklebe, J. (2004). Differenzierung von Auenböden der Mittleren Elbe und Quantifizierung des Einflusses von deren Bodenkennwerten auf die mikrobielle Biomasse und die Bodenenzymaktivitäten von ß-Glucosidase, Protease und alkalischer Phosphatase. PhD thesis, Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, Germany.
Rinklebe, J., Franke, C., & Neue, H.-U. (2007). Aggregation of floodplain soils as an instrument for predicting concentrations of nutrients and pollutants. Geoderma, 141, 210–223. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.06.001.
Scheithauer, M. (2003). Aktuelle Ergebnisse des F&E-Vorhabens “Emissionsabschätzung/Prüfwerte”. In R. Röder & C. Schertler (Eds.), Münchener Beiträge zur Sickerwasserprognose—Forschung und Praxis, vol. 56, (pp. 111–128). München: Bayerisches Landesamt für Wasserwirtschaft.
Schlichting, E., Blume, H.-P., & Stahr, K. (1995). Bodenkundliches Praktikum. Berlin: Blackwell Wissenschaftsverlag.
Schneid, E., Prechtel, A., & Knabner, P. (2000). A comprehensive tool for the simulation of complex reactive transport and flow in soils. Land Contamination & Reclamation, 8, 357–365.
Schuwirth, N., & Hofmann, T. (2006). Comparability of leaching tests and soil water sampling as an alternative for the assessment of inorganic soil contaminations. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 6, 102–112. doi:10.1065/jss2005.10.149.
Shi, Z., Di Toro, D. M., Allen, H. E., & Sparks, D. L. (2008). A WHAM-based kinetics model for Zn adsorption and desorption to soils. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 5630–5636. doi:10.1021/es800454y.
Sommerfeld, F., & Schwedt, G. (1996). Vergleich ausgewählter Elutionsverfahren zur Beurteilung der Mobilität von Metallen. Acta Hydrochimica et Hydrobiologica, 24, 255–259. doi:10.1002/aheh.19960240602.
Strobel, B. W., Hansen, H. C. B., Borggaard, O. K., Andersen, M. K., & Raulund-Rasmussen, K. (2001). Cadmium and copper release kinetics in relation to afforestation of cultivated soil. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65, 1233–1242. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00602-5.
Sukreeyapongse, O., Holm, P. E., Strobel, B. W., Panichsakpatana, S., Magid, J., & Hansen, H. C. B. (2002). pH-Dependent release of cadmium, copper, and lead from natural and sludge-amended soils. Journal of Environmental Quality, 31, 1901–1909.
Toride, N., Leji, F. J., & van Genuchten, M. T. (1995). The CXTFIT code for estimating transport parameters from laboratory or field tracer experiments. Riverside: US Salinity Laboratory.
van der Sloot, H. A., Comans, R. N. J., & Hjelmar, O. (1996). Similarities in the leaching behavior of trace contaminants from waste, stabilized waste, construction materials and soils. Science of the Total Environment, 178, 111–126. doi:10.1016/0048-9697(95)04803-0.
Voegelin, A., & Kretzschmar, R. (2005). Formation and dissolution of single and mixed Zn and Ni precipitates in soil: Evidence from column experiments and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 5311–5318. doi:10.1021/es0500097.
Wehrer, M., & Totsche, K. U. (2003). Detection of non-equilibrium contaminant release in soil columns: Delineation of experimental conditions by numerical simulations. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 166, 475–483. doi:10.1002/jpln.200321095.
Wehrer, M., & Totsche, K. U. (2008). Effective rates of heavy metal release from alkaline wastes—Quantified by column outflow experiments and inverse simulations. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 97, 53–66. doi:10.1016/j.jconhyd.2008.07.005.
Wijnhoven, S., van der Velde, G., Leuven, R. S. E. W., Eijsackers, H. J. P., & Smits, A. J. M. (2006). The effect of turbation on zinc relocation in a vertical floodplain soil profile. Environmental Pollution, 140, 444–452. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2005.08.011.
Zeien, H., & Brümmer, G. W. (1989). Chemische Extraktion zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallbindungsformen in Böden. Mitteilungen der Deutschen Bodenkundlichen Gesellschaft, 59, 505–510.
Acknowledgements
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG, Re 2251/1). We would like to thank K. Greef, K. Kinze, S. Meißner, Dr. H.-J. Staerk, J. Steffen, Dr. M. Thönnessen and Dr. R. Wennrich for various analyses as well as Dr. M. Wehrer for valuable suggestions concerning the modelling.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0110-0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rennert, T., Rinklebe, J. Release of Ni and Zn from Contaminated Floodplain Soils Under Saturated Flow Conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut 205, 93–105 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0058-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0058-0