Abstract
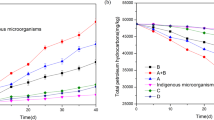
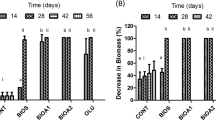
Three organic wastes (banana skin (BS), brewery spent grain (BSG), and spent mushroom compost (SMC)) were used for bioremediation of soil spiked with used engine oil to determine the potential of these organic wastes in enhancing biodegradation of used oil in soil. The rates of biodegradation of the oil were studied for a period of 84 days under laboratory conditions. Hydrocarbon-utilizing bacterial counts were high in all the organic waste-amended soil ranging between 10.2 × 106 and 80.5 × 106 CFU/g compared to unamended control soil throughout the 84 days of study. Oil-contaminated soil amended with BSG showed the highest reduction in total petroleum hydrocarbon with net loss of 26.76% in 84 days compared to other treatments. First-order kinetic model revealed that BSG was the best of the three organic wastes used with biodegradation rate constant of 0.3163 day−1 and half-life of 2.19 days. The results obtained demonstrated the potential of organic wastes for oil bioremediation in the order BSG > BS > SMC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adegoroye, G. (1997). Environmental considerations in property design, urban development and renewal. In O. Akinjide (Ed.), Dimensions of environmental problems in Nigeria (pp. 12–25). Washington: Friedrich Ebert Foundation.
Adelowo, O. O., Alagbe, S. O., & Ayandele, A. A. (2006). Time-dependent stability of used engine oil degradation by cultures of Pseudomonas fragi and Achromobacter aerogens. African Journal of Biotechnology, 5(24), 2476–2479.
Adesodun, J. K., & Mbagwu, J. S. C. (2008). Biodegradation of waste lubricating petroleum oil in a tropical alfisol as mediated by animal droppings. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5659–5665.
Ahn, Y. H., Sanseverino, J., & Sayler, G. S. (1999). Analyses of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria isolated from contaminated soils. Biodegradation, 10, 149–157.
Antai, S. P., & Mgbomo, E. (1989). Distribution of hydrocarbon utilizing bacteria in oil-spill areas. Microbiology Letters, 40, 137–143.
ATSDR. (1997). Public health statements: Used mineral based crankcase oil. Atlanta: ATSDR.
Bento, F. M., Camargo, F. O. A., Okeke, B. C., & Frankenberger, W. T. (2005). Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1049–1055.
Boonchan, S., Britz, M. L., & Stanley, G. A. (2000). Degradation and mineralization of high-molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by defined fungal–bacterial co-cultures. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 66(3), 1007–1019.
Brook, T. R., Stiver, W. H., & Zytner, R. G. (2001). Biodegradation of diesel fuel in soil under various nitrogen addition regimes. Soil Sediment Contamination, 10, 539–553.
Butler, C. S., & Mason, J. R. (1997). Structure–function analysis of the bacterial aromatic ring–hydroxylating dioxygenases. Advanced Microbial Physiology, 38, 47–84.
Das, K., & Mukherjee, A. K. (2007). Crude petroleum-oil biodegradation efficiency of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from petroleum oil contaminated soil from North–East India. Bioresource Technology, 98, 1339–1345.
Edewor, T. I., Adelowo, O. O., & Afolabi, T. J. (2004). Preliminary studies into the biological activities of a broad spectrum disinfectant formulated from used engine oil. Pollution Research, 23(4), 581–586.
Faboya, O. O. P. (1997). Industrial pollution and waste management. In O. Akinjide (Ed.), Dimensions of environmental problems in Nigeria (pp. 12–25). Washington: Friedrich Ebert Foundation.
Hagwell, I. S., Delfino, L. M., & Rao, J. J. (1992). Partitioning of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from oil into water. Environmental Science and Technology, 26, 2104–2110.
Hollender, J., Althoff, K., Mundt, M., & Dott, W. (2003). Assessing the microbial activity of soil samples, its nutrient limitation and toxic effects on contaminants using a simple respiration test. Chemosphere, 53, 269–275.
Husaini, A., Roslan, H. A., Hii, K. S. Y., & Ang, C. H. (2008). Biodegradation of aliphatic hydrocarbon by indigenous fungi isolated from used motor oil contaminated sites. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 24, 2789–2797.
Ijah, U. J. J. (1998). Studies on relative capabilities of bacterial and yeast isolates from tropical soil in degrading crude oil. Waste Management, 18, 293–299.
Ijah, U. J. J., & Antai, S. P. (2003a). The potential use of chicken-drop microorganisms for oil spill remediation. The Environmentalist, 23, 89–95.
Ijah, U. J., & Antai, S. P. (2003b). Removal of Nigerian light crude oil in soil over a 12 month period. International Biodeterioration and Biodegradation, 51, 93–99.
Joo, H. S., Phae, C. G., & Ryu, J. Y. (2001). Comparison and analysis on characteristics for recycling of multifarious food waste. J KOWREC, 9, 117–124.
Joo, H. S., Shoda, M., & Phae, C. G. (2007). Degradation of diesel oil in soil using a food waste composting process. Biodegradation, 18, 597–605.
Jørgensen, K. S., Puustinen, J., & Suortti, A. M. (2000). Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by composting in biopiles. Environmental Pollution, 107, 245–254.
Keith, L. H., & Telliard, W. A. (1979). Priority pollutants 1—A perspective view. Environmental Science and Technology, 13, 416–423.
Kyung-Hwa, B., Byung-Dae, Y., Hee-Mock, O., Hee-Sik, K., & In-Sook, L. (2006). Biodegradation of aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons by Nocardia sp. H17-1. Geomicrobiology Journal, 23(5), 253–259.
Lloyd, C. A., & Cackette, T. A. (2001). Diesel engines: Environmental impact and control. Air and Waste Management Association, 51, 805–847.
Majid, Z., Mnouchehr, V., & Sussan, K. A. (2008). Naphthalene metabolism in Nocardia otitidiscaviarum strain TSH 1, a moderately thermophilic microorganism. Chemosphere, 72, 905–909.
Mandri, T., & Lin, J. (2007). Isolation and characterization of engine oil degrading indigenous microorganisms in Kwazulu-Natal, South Africa. African Journal of Biotechnology, 6(1), 23–27.
Margesin, R., & Schinner, F. (2001). Bioremediation (natural attenuation and biostimulation) of diesel-oil-contaminated soil in an Alpine glacier skiing area. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 67, 3127–3133.
Margesin, R., Zimmerbauer, A., & Schinner, F. (2000). Monitoring of bioremediation by soil biological activities. Chemosphere, 40, 339–346.
Margesin, R., Hammerle, M., & Tscherko, D. (2007). Microbial activity and community composition during bioremediation of diesel-oil-contaminated soil: Effects of hydrocarbon concentration, fertilizers, and incubation time. Microbiol Ecol, 53, 259–269.
Mishra, S. J., Jyot, R. C., & Kuhad, B. L. (2001). Evaluation of inoculum addition to stimulate in situ Bioremediation of oily–sludge-contaminated soil. Applied Environmental Microbiology, 67(4), 1675–1681.
Nakasaki, K., Yaguchi, H., Sasaki, Y., & Kubota, H. (1992). Effect of C/N ratio on thermophilic composting of garbage. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering, 73, 43–45.
Propst, T. L., Lochmiller, R. L., Qualis, C. W., & McBee, K., Jr. (1999). In situ (mesocosm) assessment of immune-toxicity risks to small mammals inhabiting petrochemical waste sites. Chemosphere, 38, 1049–1067.
Riffaldi, R., Levi-Minzi, R., Cardelli, R., Palumbo, S., & Saviozzi, A. (2006). Soil biological activities in monitoring the bioremediation of diesel oil-contaminated soil. Water, Air & Soil Pollution, 170, 3–15.
Semple, K. T., Dew, N. M., Doick, K. J., & Rhodes, A. H. (2006). Can mineralization be used to estimate microbial availability of organic contaminants in soil? Environmental Pollution, 140, 164–172.
Tauscher, W. (1988). The option for re-cycling and re-utilizing used petroleum oils. Natural Resources Development, 28, 100–107.
USEPA. (1996). Recycling used oil: What can you do? Cooperation Extension Services ENRI, 317, 1–2.
Van Hamme, J. D., Singh, A., & Ward, O. P. (2003). Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Review, 67(4), 503–549.
Walworth, J., Pond, A., Snape, I., Rayner, J., Ferguson, S., & Harvey, P. (2007). Nitrogen requirements for maximizing petroleum bioremediation in a sub-Antarctic soil. Cold Regions Science and Technology, 48, 84–91.
Yeung, P. Y., Johnson, R. L., & Xu, J. G. (1997). Biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in soil as affected by heating and forced aeration. Journal of Environmental Quality, 26, 1511–1576.
Zajic, E., & Supplission, B. (1972). Emulsification and degradation of “Banker C” fuel oil by microorganisms. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 14, 331–343.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of the University of Malaya IPPP Grant PS 244/2008C. Also, we would like to thank the managements of Carlsberg Brewery for providing brewery spent grain and Gano farm for the provision of spent mushroom compost.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abioye, P.O., Abdul Aziz, A. & Agamuthu, P. Enhanced Biodegradation of Used Engine Oil in Soil Amended with Organic Wastes. Water Air Soil Pollut 209, 173–179 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0189-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-0189-3