Abstract
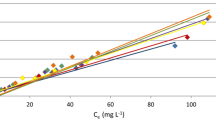
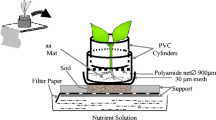
The goal of this work was to study quantitatively lead bioaccumulation from a lead-doped nutrient medium by using a living aquatic macrophytes Pistia stratiotes. Several sets of aquatic plants with approximately 30 g weight were grown in greenhouse conditions and in hydroponic solutions supplied with a non-toxic Pb2+ concentration. The synchrotron radiation total X-ray fluorescence spectrometry was used to determine the metal concentrations in dry plants and hydroponic media as a function of time. Four different non-structural bioaccumulation models were applied to describe the process dynamics and to estimate the accumulated lead maximum capacity and rate constants. According to the experimental data, both biosorption and bioaccumulation mechanisms can be considered. Due to the low desorption rate constant, the experimental data were well described by the irreversible kinetic model. The results concerning modeling of living macrophytes’ metal bioaccumulation kinetics can be used to predict the heavy metal removal dynamics from wastewaters in artificial wetlands.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiginger, H., & Wobrauschek, P. (1974). A method for quantitative X-ray fluorescence analysis in the nanogram region. Nuclear Instruments and Methods, 114, 157–158. doi:10.1016/0029–554X(74)90352-8.
Blázquez, G., Hernáinz, F., Calero, M., & Ruiz-Núñez, L. F. (2005). Removal of cadmium ions with olive stones: the effect of some parameters. Process Biochemistry, 40, 2649–2654. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.11.007.
Borgmann, U., Norwood, W. P., & Dixon, D. G. (2004). Re-evaluation of metal bioaccumulation and chronic toxicity in Hyalella azteca using saturation curves and the biotic ligand model. Environmental Pollution, 131, 469–484. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2004.02.010.
Clark, R. B. (1975). Characterization of phosphates in intact maize roots. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 23, 458–460. doi:10.1021/jf60199a002.
Cruz, C. C. V., Costa, A. C. A., Henriques, C. A., & Luna, A. S. (2004). Kinetic modeling and equilibrium studies during cadmium biosorption by dead Sargassum sp. biomass. Bioresource Technology, 91, 249–257. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(03)00194-9.
Espinoza-Quiñones, F. R., Zacarkim, C. E., Palácio, S. M., Obregón, C. L., Zenatti, D. C., Galante, R. M., Rossi, N., Rossi, F. L., Pereira, I. R. A., & Welter, R. A. (2005). Removal of heavy metal from polluted river water using aquatic macrophytes Salvinia sp. Brazilian Journal of Physics, 35, 744–746.
Georgieva, N. (2008). Growth of Trichosporon cutaneum R 57 in the presence of toxic concentration of cadmium and copper. International Journal of Agriculture & Biology, 10(3), 325–328.
Hadad, H. R., Maine, M. A., & Bonetto, C. A. (2006). Macrophyte growth in a pilot-scale constructed wetland for industrial wastewater treatment. Chemosphere, 63, 1744–1753. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.09.014.
Hashim, M. A., & Chu, K. H. (2004). Biosorption of cadmium by brown, green, and red seaweeds. Chemical Engineering Journal, 97, 249–295. doi:10.1016/S1385-8947(03)00216-X.
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R., & Shi, Y. (2001). Swarm intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann.
Kim, S. G., Jee, J. H., & Kang, J. C. (2004). Cadmium accumulation and elimination in tissues of juvenile olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus after sub-chronic cadmium exposure. Environmental Pollution, 127, 117–123. doi:10.1016/S0269-7491(03)00254-9.
Lodeiro, P., Cordeiro, B., Barriada, J. L., Herrero, R., & Sastre de Vicente, M. E. (2005). Biosorption of cadmium by biomass of brown marine macroalgae. Bioresource Technology, 96, 1796–1803. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2005.01.002.
Miretzky, P., Saralegui, A., & Cirelli, A. F. (2004). Aquatic macrophytes potential for the simultaneous removal of heavy metals (Buenos Aires, Argentina). Chemosphere, 57, 997–1005. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.07.024.
Pérez, C. A., Radtke, M., Sánchez, H. J., Tolentino, H., Neuenshwander, R. T., Barg, W., Rubio, M., Bueno, M. I. S., Raimundo, I. M., & Rohwedder, J. J. R. (1998). Synchrotron radiation X-ray fluorescence at the LNLS: beamline instrumentation and experiments. X-Ray Spectrometry, 28, 320–326. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4539(199909/10)28:5<320::AID-XRS359>3.0.CO;2-1.
Pettersson, R. P., & Olsson, M. (1998). A nitric acid–hydrogen peroxide digestion method for trace element analysis of milligram amounts of plankton and periphyton by total-reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 13, 609–613. doi:10.1039/a708575c.
Salvador, M. J., Moreira, S., Dias, D. A., & Zucchi, O. L. A. D. (2004). Determination of trace elements in Alternanthera brasiliana and Pfaffia glabrata by SRTXRF: application in environmental pollution control. Instrumentation Science & Technology, 32, 321–333. doi:10.1081/CI-120030545.
Schmitt, D., Müller, A., Csögör, Z., Frimmel, H. F., & Posten, C. (2001). The adsorption kinetics of metal ions onto different microalgae and siliceous earth. Water Research, 35, 779–785. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00317-1.
Sharma, S. S., & Gaur, J. P. (1995). Potential of Lemna polyrrhiza for removal of heavy metals. Ecological Engineering, 4, 37–43. doi:10.1016/0925-8574(94)00047-9.
Simabuco, S. M., & Matsumoto, E. (2000). Synchrotron radiation total reflection for rain water analysis. Spectrochimica Acta B, 55, 1173–1179. doi:10.1016/S0584-8547(00)00158-0.
Susarla, S., Medina, V. F., & McCutcheon, S. C. (2002). Phytoremediation: an ecological solution to organic chemical contamination. Ecological Engineering, 18, 647–658.
Terry, A. P., & Stone, W. (2002). Biosorption of cadmium and copper contaminated water by Scenedesmus abundans. Chemosphere, 47, 249–255. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(01)00303-4.
Van Espen, P., Janssens, K., & Swenters, I. (1986). AXIL X-ray analysis software. Zellik: Canberra Packard Benelux.
Veglio, F., & Beolchini, F. (1997). Removal of metals by biosorption: a review. Hydrometallurgy, 44, 301–316.
Yan, G., & Viraraghavan, T. (2003). Heavy-metal removal from aqueous solution by fungus Mucor rouxii. Water Research, 37, 4486–4496.
Yoneda, Y., & Horiuchi, T. (1971). Optical flats for use in X-ray spectrochemical micro-analysis. Review of Scientific Instruments, 42, 169–170.
Acknowledgment
We gratefully acknowledge The Brazilian Light Synchrotron Laboratory (LNLS) for partial financial support of this study through the 6718 project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R., Módenes, A.N., Costa, I.L. et al. Kinetics of Lead Bioaccumulation from a Hydroponic Medium by Aquatic Macrophytes Pistia stratiotes . Water Air Soil Pollut 203, 29–37 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9989-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-009-9989-8