Abstract
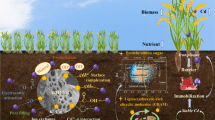
Biochars from two different feedstocks (peanut shell-PB; wheat straw-WB) were used in this study to understand the sorption mechanisms of atrazine (ATR), 17α-ethinyl estradiol (EE2), and phenanthrene (PHEN) to help minimize the bioavailability of the organic pollutants in the environment. Sorption isotherms of ATR, EE2, and PHEN by WB and PB biochars followed the Freundlich model where the sorption parameter (n) shows the trend: ATR > EE2 and PHEN, while the sorption capacity (log K oc ) increases from ATR < EE2 < PHEN and indicate that the most hydrophobic and planar organic pollutant (PHEN) is the most easily adsorbed organic compound on PB and WB. The higher H/C and (O + N)/C ratios of WB (0.099 and 0.525, respectively) suggest its stronger aliphaticity and polarity than PB (0.078 and 0.352, respectively) that induced stronger sorption affinity for ATR and PHEN. Higher specific surface area (m2 g−1) of PB (19.7) may be responsible for the higher sorption capacity for EE2 than WB (8.8) because it can accommodate the large molecule of EE2. Results from this study may be helpful to predict the bioavailability of organic pollutants when soils contaminated with pollutants are remediated with biochars produced from wheat straw and peanut shells.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad, M., Lee, S. S., Dou, X., Mohan, D., Sung, J., Yang J. E., OK, Y. S. (2012). Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soybean stover- and peanut shell-derived biochar properties and TCE adsorption in water. Bioresource Technology, 118, 536–544.
Ahmad, M., Rajapaksha, A. U., Lim, J. E., Zhang, M., Bolan, N., Mohan, D., Vithanage, M., Lee, S. S., & Ok, Y. S. (2014). Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere, 99, 19–33.
Bartholow, M. (2011). Top 200 Drugs of 2010. http://www.pharmacytimes.com/publications/issue/2011/may2011/top-200-drugs-of-2010.
Beesley, L., Moreno-Jiménez, E., Gomez-Eyles, J. L., Harris, E., Robinson, B., & Sizmur, T. (2011). A review of biochars’ potential role in the remediation, revegetation and restoration of contaminated soils. Envrionmental Polluttion, 159, 3269–3282.
Boehm, H. P. (1994). Some aspects of the surface chemistry of carbon blacks and other carbons. Carbon, 32(5), 759–769.
Bucheli, T. D., & Gustafsson, O. (2000). Quantification of the soot-water distribution coefficient of PAHs provides mechanistic basis for enhanced sorption observations. Environmental Science & Technology, 34, 5144–5151.
Cao, X., Ma, L., Gao, B., & Harris, W. (2009). Dairy-manure derived biochar effectively sorbs lead and atrazine. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 3285–3291.
Chen, B.-L., & Chen, Z.-M. (2009). Sorption of naphthalene and 1-naphthol by biochars of orange peels with different pyrolytic temperatures. Chemosphere, 76, 127–133.
Chen, B.-L., Zhou, D.-D., & Zhu, L.-Z. (2008). Transitional adsorption and partition of nonpolar and polar aromatic contaminants by biochars of pine needles with different pyrolytic temperatures. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 5137–5143.
Chen, Z.-M., Chen, B.-L., & Chiou, C.-T. (2012). Fast and slow rates of naphthalene sorption to biochars produced at different temperatures. Environmental Science & Technology, 46(20), 11104–11111.
Chen, C.-P., Zhou, W.-J., & Lin, D.-H. (2015). Sorption characteristics of N-nitrosodimethylamine onto biochar from aqueous solution. Bioresource Technology, 179, 359–366.
Chun, Y., Sheng, G.-Y., Chiou, C.-T., & Xing, B.-S. (2004). Compositions and sorptive properties of crop residue-derived chars. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 4649–4655.
Cornelissen, G., & Gustafsson, O. (2004). Sorption of phenanthrene to environmental black carbon in sediment with and without organic matter and native sorbates. Environmental Science & Technology, 38(1), 148–155.
Cornelissen, G., Haftke, J., Parsons, J., & Gustafsson, O. (2005). Sorption to black carbon of organic compounds with varying polarity and planarity. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 3688–3694.
Fernandes, M. B., Skjemstad, J. O., Johnson, B. B., Wells, J. D., & Brooks, P. (2003). Characterization of carbonaceous combustion residues. I. Morphological, elemental and spectroscopic features. Chemosphere, 51, 785–795.
Frisch, M. J., Trucks, G. W., Schlegel, H. B., et al. (2009). Gaussian 09, Revision A.01. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford CT.
Goertzen, S. L., Theriault, K. D., Oickle, A. M., Tarasuk, A. C., & Andreas, H. A. (2010). Standardization of the Boehm titration. Part I. CO2 expulsion and endpoint determination. Carbon, 48, 1252–1261.
Guo, X., Tian, B., & Xin, L. (2013). Adsorption removal process and mechanism of diclofenac. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 7(10), 3779–3784.
Han, J., Qiu, W., Cao, Z., Hu, J.-Y., & Gao, W. (2013). Adsorption of ethinylestradiol (EE2) on polyamide 612: Molecular modeling and effects of water chemistry. Water Research, 47, 2273–2284.
Kasozi, G. N., Zimmerman, A. R., Nkedi-Kizza, P., & Gao, B. (2010). Catechol and humic acid sorption onto a range of laboratory-produced black carbons (biochars). Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 6189–6195.
Keiluweit, M., Nico, P. S., Johnson, M. G., & Kleber, M. (2010). Dynamic molecular structure of plant biomass-derived black carbon (biochar). Environmental Science & Technology, 44, 1247–1253.
Kulikova, N. A., & Perminova, I. V. (2002). Binding of atrazine to humic substances from soil, peat, and coal related to their structure. Environmental Science & Technology, 36, 3720–3724.
Kumari, K. G. I. D., Moldrup, P., Paradelo, M., & Jonge De, L. W. (2014). Phenanthrene sorption on biochar-amended soils: Application rate, aging, and physicochemical properties of soil. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution, 9(225), 2105.
Lehmann, J., Gaunt, J., & Rondon, M. (2006). Biochar sequestration in terrestrial ecosystems: A review. Mitig Adapt Strategy Global Change, 11, 403–427.
Li, J., Jiang, L., Xiang, X., Xu, S., Wen, R., & Liu, X. (2013). Competitive sorption between 17α-ethinyl estradiol and bisphenol A /4-n-nonylphenol by soils. Journal of Environmental Science, 25(6), 1154–1163.
Lian, F., Huang, F., Chen, W., Xing, B.-S., & Zhu, L.-Y. (2011). Sorption of apolar and polar organic contaminants by waste tire rubber and its chars in single- and bi-solute systems. Envrionmental Pollution, 159, 850–857.
Lian, F., Sun, B.-B., Song, Z.-G., Zhu, L.-Y., Qi, X.-H., & Xing, B.-S. (2014). Physicochemical properties of herb-residue biochar and its sorption to ionizable antibiotic sulfamethoxazole. Chemical Engineering Journal, 248, 128–134.
Lin, D.-H., Pan, B., Zhu, L.-Z., & Xing, B.-S. (2007). Characterization and phenanthrene sorption of tea leaf powders. Journal of Agricultural Food and Chemistry, 55, 5718–5724.
Ling, W. (2005). The influence of dissolved organic matter on atrazine sorption and desoption by soils and minerals. Zhejiang University Ph.D. Thesis.
Liu, Y.-X. (2011). Effect of biochar on the characteristic of nitrogen loss and green gas emission from soil. Zhejiang University Ph.D. thesis.
Lou, L.-P., Wu, B.-B., Wang, L.-N., Luo, L., Xu, X.-H., Xun, B., & Chen, Y. X. (2011). Sorption and ecotoxicity of pentachlorophenol polluted sediment amended with rice-straw derived biochar. Bioresource Technology, 102, 4036–4041.
Mankasingh, U., Choi, P. C., & Ragnarsdottir, V. (2011). Biochar application in a tropical, agricultural region: A plot scale study in Tamil Nadu, India. Applied Geochemistry, 26, S218–S221.
Mukome, F, N. D., Zhang, X., Silva, L. C. R., Six, J., & Parikh, S. J. (2013) Use of chemical and physical characteristics to investigate trends in biochar feedstock. Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61, 2196–2204.
Oh, S. Y., & Seo, Y. D. (2015). Sorption of halogenated phenols and pharmaceuticals to biochar: affecting factors and mechanisms. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 18. doi:10.1007/s11356-015-4201-8.
Park, J., Huang, I., Gan, Z., Rojas, O. J., Lim, K.-H., & Park, S. (2013). Activated carbon from biochar: Influence of its physicochemical properties on the sorption characteristics of phenanthrene. Bioresource Technology, 149, 383–389.
Qiu, Y. P., Xiao, X. Y., Cheng, H. Y., Zhou, Z. L., & Sheng, G. D. (2009). Influence of environmental factors on pesticide adsorption by black carbon: pH and model dissolved organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 43, 4973–4978.
Ran, Y., Sun, K., Yang, Y., Xing, B.-S., & Zeng, E. (2007). Strong sorption of phenanthrene by condensed organic matter in soils and sediments. Environmental Science & Technology, 41, 3952–3958.
Senesi, N. (1992). Binding mechanisms of pesticides to soil humic substances. The Science of the Total Environment, 123(124), 63–76.
Shechter, M., & Chefetz, B. (2008). Insights into the sorption properties of cutin and cutan biopolymers. Environmental Science & Technology, 42, 1165–1171.
Spokas, K. A., Koskenen, W. C., Baker, J. M., & Reicosky, D. C. (2009). Impacts of woodchip biochar additions on greenhouse gas production and sorption/degradation of two herbicides in a Minnesota soil. Chemosphere, 77, 574–581.
Sun, X.-S., Peng, P.-A., Song, J.-Z., Zhang, G., & Hu, J.-F. (2008). Sedimentary record of black carbon in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent northern South China Sea. Applied Geochemistry, 23, 3464–3472.
Sun, K., Gao, B., Zhang, Z.-Y., Zhang, G.-X., Zhao, Y., & Xing, B.-S. (2010). Sorption of atrazine and phenanthrene by organic matter fractions in soil and sediment. Environmental Pollution, 158(12), 3520–3526.
Sun, K., Ro, K., Guo, M., Novak, J., Mashayekhi, H., & Xing, B.-S. (2011a). Sorption of bisphenol A, 17α-ethinyl estradiol and phenanthrene on thermally and hydrothermally produced biochars. Bioresource Technology, 102, 5757–5763.
Sun, K., Keiluweit, M., Kleber, M., Pan, Z.-Z., & Xing, B.-S. (2011b). Sorption of fluorinated herbicides to plant biomass-derived biochars as a function of molecular structure. Bioresource Technology, 102, 9897–9903.
Sun, K., Jin, J., Gao, B., Zhang, Z.-Y., Wang, Z., Pan, Z.-Z., Xu, D., & Zhao, Y. (2012a). Sorption of 17α-ethinyl estradiol, bisphenol A and phenanthrene to different size fractions of soil and sediment. Chemosphere, 88, 577–583.
Sun, K., Jin, J., Keiluweit, M., Kleber, M., Wang, Z.-Z., Pan, Z.-Z., & Xing, B.-S. (2012b). Polar and aliphatic domains regulate sorption of phthalic acid esters (PAEs). Bioresource Technology, 118, 120–127.
Sun, K., Kang, M.-J., Zhang, Z.-Z., Jin, J., Wang, Z.-Y., Pan, Z.-Z., Xu, D., Wu, F., & Xing, B.-S. (2013). Impact of deashing treatment on biochar structural properties and potential sorption mechanisms of phenanthrene. Environmental Science & Technology, 47, 11473–11481.
Trigo, C., Spokas, K. A., Cox, L., & Koskinen, W. C. (2014). Influence of soil biochar aging on sorption of the herbicides MCPA, nicosulfuron, terbuthylazine, indaziflam, and fluoroethyldiaminotriazine. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 62, 10855–10860.
Tsui, L., & Roy, W. R. (2008). The potential applications of using compost chars for removing the hydrophobic herbicide atrazine from solution. Bioresource Technology, 99, 5673–5678.
Uchimiya, M., Wartelle, L. H., Lima, I. M., & Klasson, K. T. (2010). Sorption of deisopropylatrazine on broiler litter biochars. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 58, 12350–12356.
Van Krevelen, D. W. (1950). Graphical-statistical method for the study of structure and reaction processes of coal. Fuel, 29, 269–284.
Wang, P., & Keller, A. A. (2009). Sorption and desorption of atrazine and diuron onto water dispersible soil primary size fractions. Water Resources, 43, 1448–1456.
Wang, X. L., Guo, X. Y., Yang, Y., Tao, S., & Xing, B. S. (2011). Sorption mechanisms of phenanthrene, lindane, and atrazine with various humic acid fractions from a single soil sample. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(6), 2124–2130.
Wu, Z., Rodgers, R. P., & Marshall, A. G. (2004). Two- and three-dimensional van Krevelen diagrams: A graphical analysis complementary to the Kendrick mass plot for sorting elemental compositions of complex organic mixtures based on ultrahigh-resolution broadband Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass measurements. Analytical Chemistry, 76(9), 2511–2516.
Xu, T., Lou, L.-P., Luo, L., Cao, R.-K., Duan, D.-C., & Chen, Y.-X. (2012). Effect of bamboo biochar on pentachlorophenol leachability and bioavailability in agricultural soil. The Science of the Total Environment, 414, 727–731.
Yadav, A. B. (2007). Approaches to mitigate the impact of dissolved organic matter on the adsorption of synthetic organic contaminants by activated carbon. A Thesis Presented to the Graduate School of Clemson University.
Yu, Z.-Q., Xiao, B.-H., Huang, W.-L., & Peng, P.-A. (2004). Sorption of steroid estrogens to soils and sediments. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 23, 531–539.
Yu, Z.-Q., Sharma, S., & Huang, W.-L. (2006). Differential roles of humic acid and particulate organic matter in the equilibrium sorption of atrazine by soils. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 25(8), 1975–1983.
Zheng, W., Guo, M.-X., Chow, T., Bennett, D. N., & Rajagopalan, N. (2010). Sorption properties of greenwaste biochar for two triazine pesticides. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 121–126.
Zhou, D.-D. (2008). Sorption characteristics and mechanisms of biochars with organic contaminants in water. Zhejiang University Master degree thesis.
Zhu, D., Hyun, D., Pignaello, J. J., & Lee, L.-S. (2004). Evidence for π-πelectron donor acceptor interactions between π-donor aromatic compounds and π-acceptor sites in soil organic matter through pH effects on sorption. Environmental Science & Technology, 38, 4361–4368.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation (ZJNSF, Project No.LY14D030001). The authors thank Qiang Huang and all other laboratory and support personnel who helped with this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Chen, H., Huang, W. et al. Sorption of Atrazine, 17α-Estradiol, and Phenanthrene on Wheat Straw and Peanut Shell Biochars. Water Air Soil Pollut 227, 7 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2699-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-015-2699-5